Abstract
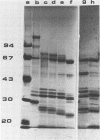
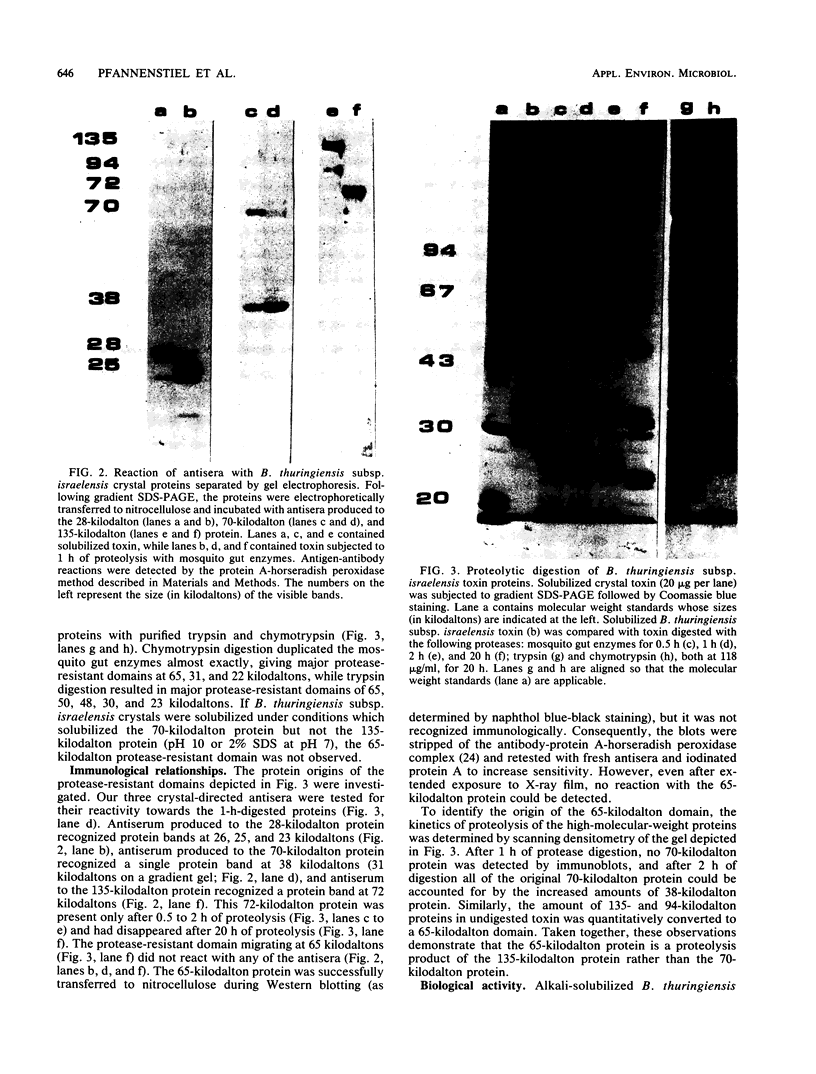
The immunological relationships among the proteins of the mosquito larvicidal toxin produced by Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis have been investigated by using polyclonal antisera specific for the 28-, 70-, and 135-kilodalton proteins. Each of these proteins was immunologically distinct. There was no cross-reaction among the three proteins and the two non-homologous antisera. Treatment of toxin proteins with larval gut enzymes for 20 h identified protease-resistant domains at approximately 65, 38, and 22 kilodaltons. Similar domains were generated by treatment with trypsin and chymotrypsin. Our immunological and kinetic data indicate that the 28-kilodalton protein is degraded successively to protein bands at 26, 25, 23, and 22 kilodaltons, the 70-kilodalton protein is degraded to a protein at 38 kilodaltons, and the 135-kilodalton protein is degraded successively to protein bands at 94, 72, and, probably, 65 kilodaltons. Solubilized toxin possesses two biological activities, larvicidal and general cytolytic (hemolytic). We used nondenaturing gel electrophoresis to show that the hemolytic activity resides in the 28-kilodalton protein. However, higher-molecular-weight proteins are required to achieve the level of toxicity observed in intact toxin.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews R. E., Jr, Bibilos M. M., Bulla L. A., Jr Protease activation of the entomocidal protoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Oct;50(4):737–742. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.4.737-742.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. L., Rohrmann G. F., Beaudreau G. S. Delta endotoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):39–46. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.39-46.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belfort M. Anomalous behavior of bacteriophage lambda polypeptides in polyacrylamide gels: resolution, identification, and control of the lambda rex gene product. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):270–278. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.270-278.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin D. C., Berzofsky J. A., East I. J., Gurd F. R., Hannum C., Leach S. J., Margoliash E., Michael J. G., Miller A., Prager E. M. The antigenic structure of proteins: a reappraisal. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:67–101. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Grushoff P. Cereolysin: production, purification and partial characterization. J Gen Microbiol. 1967 Jan;46(1):143–150. doi: 10.1099/00221287-46-1-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulla L. A., Jr, Davidson L. I., Kramer K. J., Jones B. L. Purification of the insecticidal toxin from the parasporal crystal of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. kurstaki. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Dec 14;91(3):1123–1130. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91997-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulla L. A., Jr, Kramer K. J., Cox D. J., Jones B. L., Davidson L. I., Lookhart G. L. Purification and characterization of the entomocidal protoxin of Bacillus thuringiensis. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 25;256(6):3000–3004. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulla L. A., Jr, Kramer K. J., Davidson L. I. Characterization of the entomocidal parasporal crystal of Bacillus thuringiensis. J Bacteriol. 1977 Apr;130(1):375–383. doi: 10.1128/jb.130.1.375-383.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese D. M., Nickerson K. W., Lane L. C. A comparison of protein crystal subunit sizes in Bacillus thuringiensis. Can J Microbiol. 1980 Aug;26(8):1006–1010. doi: 10.1139/m80-170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dadd R. H. Alkalinity within the midgut of mosquito larvae with alkaline-active digestive enzymes. J Insect Physiol. 1975 Nov;21(11):1847–1853. doi: 10.1016/0022-1910(75)90252-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson R. S., Peterson J. A., Yousten A. A. Unique biochemical events in bacterial sporulation. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1970;24:53–90. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.24.100170.000413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. M., Lee S. G., Andrews R. E., Jr, Klowden M. J., Bulla L. A., Jr Separation of the cytolytic and mosquitocidal proteins of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 31;126(2):961–965. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90279-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ibarra J. E., Federici B. A. Isolation of a relatively nontoxic 65-kilodalton protein inclusion from the parasporal body of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):527–533. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.527-533.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insell J. P., Fitz-James P. C. Composition and Toxicity of the Inclusion of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jul;50(1):56–62. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.1.56-62.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. G., Eckblad W., Bulla L. A., Jr Diversity of protein inclusion bodies and identification of mosquitocidal protein in Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 31;126(2):953–960. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90278-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legocki R. P., Verma D. P. Multiple immunoreplica Technique: screening for specific proteins with a series of different antibodies using one polyacrylamide gel. Anal Biochem. 1981 Mar 1;111(2):385–392. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90577-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilley M., Ruffell R. N., Somerville H. J. Purification of the insecticidal toxin in crystals of Bacillus thuringiensis. J Gen Microbiol. 1980 May;118(1):1–11. doi: 10.1099/00221287-118-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfannenstiel M. A., Couche G. A., Muthukumar G., Nickerson K. W. Stability of the larvicidal activity of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis: amino acid modification and denaturants. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Nov;50(5):1196–1199. doi: 10.1128/aem.50.5.1196-1199.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schesser J. H., Kramer K. J., Bulla L. A., Jr Bioassay for homogeneous parasporal crystal of Bacillus thuringiensis using the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Apr;33(4):878–880. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.4.878-880.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnell D. J., Pfannenstiel M. A., Nickerson K. W. Bioassay of solubilized Bacillus thuringiensis var. israelensis crystals by attachment to latex beads. Science. 1984 Mar 16;223(4641):1191–1193. doi: 10.1126/science.6701520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W. E., Ellar D. J. Bacillus thuringiensis var israelensis crystal delta-endotoxin: effects on insect and mammalian cells in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Sci. 1983 Mar;60:181–197. doi: 10.1242/jcs.60.1.181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W. E., Ellar D. J. Mechanism of action of Bacillus thuringiensis var israelensis insecticidal delta-endotoxin. FEBS Lett. 1983 Apr 18;154(2):362–368. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80183-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung J. S., Knight C. A. Relative importance of some factors affecting the electrophoretic migration of proteins in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1972 Jul;48(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(72)90179-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrell D. J., Bulla L. A., Jr, Andrews R. E., Jr, Kramer K. J., Davidson L. I., Nordin P. Comparative biochemistry of entomocidal parasporal crystals of selected Bacillus thuringiensis strains. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1052–1062. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1052-1062.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrell D. J., Davidson L. I., Bulla L. A., Jr, Ramoska W. A. Toxicity of parasporal crystals of Bacillus thuringiensis subsp. israelensis to mosquitoes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Oct;38(4):656–658. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.4.656-658.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Y. J., Davies D. M. Digestive enzymes in the excreta of Aedes aegypti larvae. J Insect Physiol. 1971 Nov;17(11):2119–2123. doi: 10.1016/0022-1910(71)90172-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]