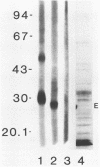
Abstract
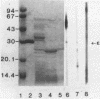
The cross-reactivity of monoclonal antibodies produced against staphylococcal enterotoxin A with purified and crude enterotoxins B, C1, D, and E and the specificity of such reactions were evaluated by the indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunoblotting of Western blots (from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis) followed by autoradiography. Purified and crude enterotoxins B were also tested with polyclonal antibodies. Specificity of reactivity was demonstrated by immunoblotting of crude enterotoxin A, crude enterotoxin A treated with trypsin, crude enterotoxin E, and also with crude A, B, C1, and D that were pretreated with Sepharose-4B-linked normal rabbit immunoglobulin G to remove protein A. A band corresponding to each staphylococcal enterotoxin was seen with monoclonal antibodies under all conditions tested and also with crude and purified enterotoxin B with two different (rabbit and goat) polyclonal antisera.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casman E. P., Bennett R. W., Dorsey A. E., Stone J. E. The micro-slide gel double diffusion test for the detection and assay of staphylococcal enterotoxins. Health Lab Sci. 1969 Oct;6(4):185–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesbro W., Carpenter D., Silverman G. J. Heterogeneity of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin B as a function of growth stage: implications for surveillance of foods. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Apr;31(4):581–589. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.4.581-589.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. W., Angel J. M., Bowen J. M. A quantitative immunobinding radioimmunoassay for antigens attached to nitrocellulose paper. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Mar 16;67(2):271–278. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90467-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwin C., Tatini S. R., Strobel R. S., Maheswaran S. K. Production of monoclonal antibodies to staphylococcal enterotoxin A. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Dec;48(6):1171–1175. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.6.1171-1175.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M., Bukovic J. A., Kauffman P. E. Antigenic cross-reactivity of staphylococcal enterotoxins. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):645–647. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.645-647.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson H. M., Bukovic J. A., Kauffman P. E., Peeler J. T. Staphylococcal enterotoxin B: solid-phase radioimmunoassay. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Nov;22(5):837–841. doi: 10.1128/am.22.5.837-841.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee A. C., Robbins R. N., Reiser R. F., Bergdoll M. S. Isolation of specific and common antibodies to staphylococcal enterotoxins B, C1, and C2. Infect Immun. 1980 Feb;27(2):431–434. doi: 10.1128/iai.27.2.431-434.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March S. C., Parikh I., Cuatrecasas P. A simplified method for cyanogen bromide activation of agarose for affinity chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jul;60(1):149–152. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90139-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer R. F., Miller L., Bennett R. W., MacMillan J. D. Development of a monoclonal antibody capable of interacting with five serotypes of Staphylococcus aureus enterotoxin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Feb;47(2):283–287. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.2.283-287.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noskova V. P., Ezepchuk YuV, Noskov A. N. Topology of the functions in molecule of staphylococcal enterotoxin Type A. Int J Biochem. 1984;16(2):201–206. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(84)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. E., Ketterhagen M. J., Bergdoll M. S. Monoclonal antibodies to staphylococcal enterotoxins B and C: cross-reactivity and localization of epitopes on tryptic fragments. Infect Immun. 1984 Jul;45(1):281–285. doi: 10.1128/iai.45.1.281-285.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tweten R. K., Iandolo J. J. Transport and processing of staphylococcal enterotoxin B. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):297–303. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.297-303.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weirether F. J., Lewis E. E., Rosenwald A. J., Lincoln R. E. Rapid quantitative serological assay of staphylococcal enterotoxin B. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Mar;14(2):284–291. doi: 10.1128/am.14.2.284-291.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]