Abstract
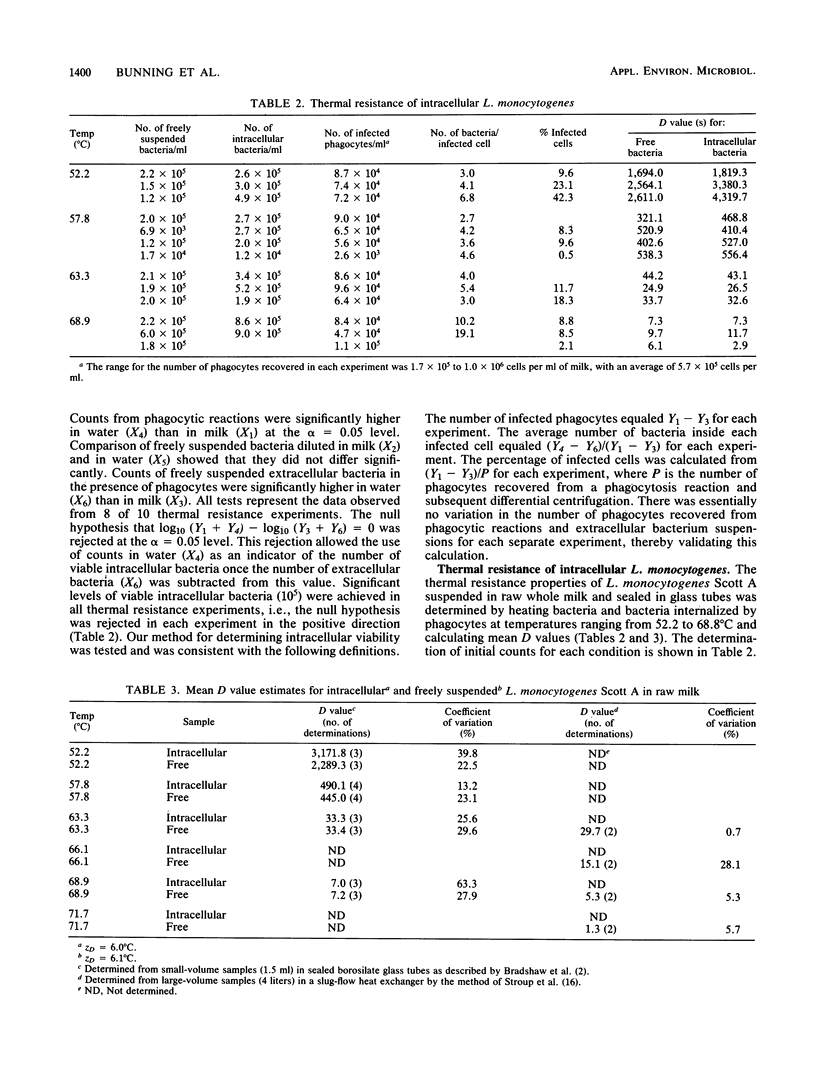
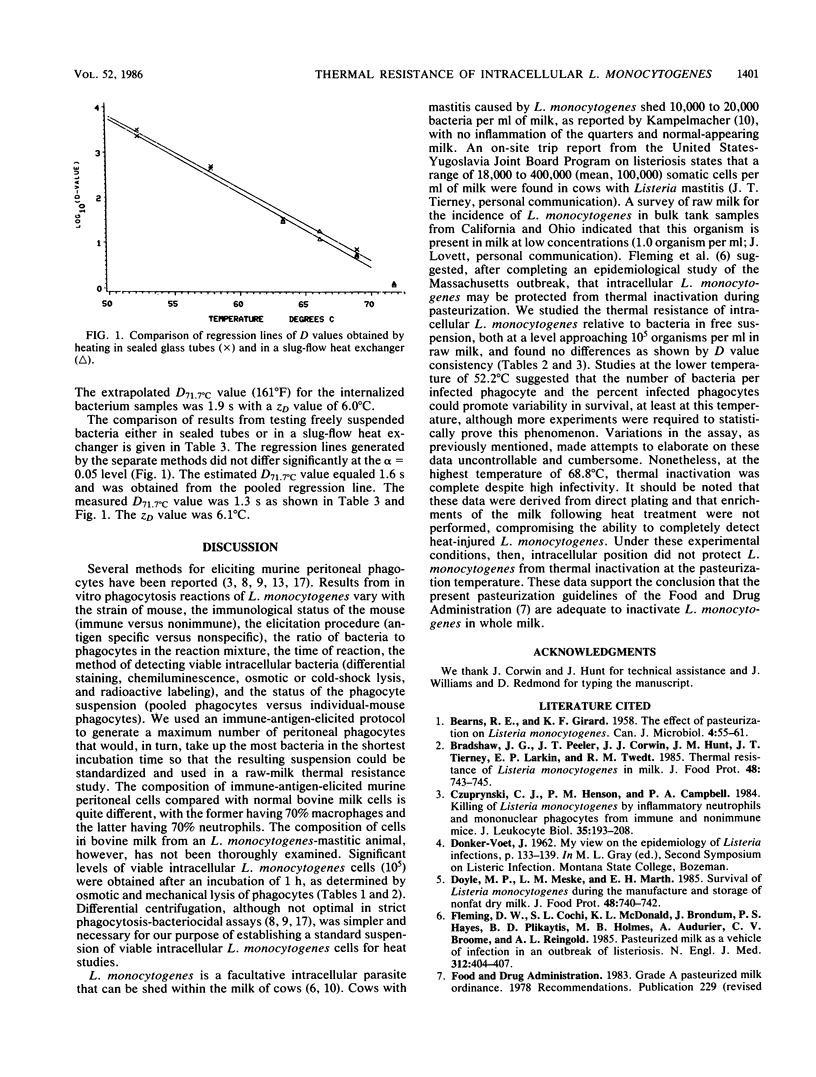
The thermal resistance of Listeria monocytogenes associated with a milk-borne outbreak of listeriosis was determined in parallel experiments by using freely suspended bacteria and bacteria internalized by phagocytes. The latter inoculum was generated by an in vitro phagocytosis reaction with immune-antigen-elicited murine peritoneal phagocytes. The heat suspension medium was raw whole bovine milk. Both suspensions were heated at temperatures ranging from 52.2 to 71.7 degrees C for various periods of time. Mean D values for each temperature and condition of heated suspension revealed no significant differences. The extrapolated D71.7 degrees C (161 degrees F) value for bacteria internalized by phagocytes was 1.9 s. Combined tube and slug-flow heat exchanger results yielded an estimated D71.7 degrees C value of 1.6 s for freely suspended bacteria. The intracellular position did not protect L. monocytogenes from thermal inactivation.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BEARNS R. E., GIRARD K. F. The effect of pasteurization on Listeria monocytogenes. Can J Microbiol. 1958 Feb;4(1):55–61. doi: 10.1139/m58-007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czuprynski C. J., Henson P. M., Campbell P. A. Killing of Listeria monocytogenes by inflammatory neutrophils and mononuclear phagocytes from immune and nonimmune mice. J Leukoc Biol. 1984 Feb;35(2):193–208. doi: 10.1002/jlb.35.2.193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming D. W., Cochi S. L., MacDonald K. L., Brondum J., Hayes P. S., Plikaytis B. D., Holmes M. B., Audurier A., Broome C. V., Reingold A. L. Pasteurized milk as a vehicle of infection in an outbreak of listeriosis. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 14;312(7):404–407. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502143120704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington-Fowler L., Henson P. M., Wilder M. S. Fate of Listeria monocytogenes in resident and activated macrophages. Infect Immun. 1981 Jul;33(1):11–16. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.1.11-16.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. H., Spencer L. K., McDonald P. J., Finlay-Jones J. J. Evaluation of intracellular killing of bacteria by enriched populations of mouse peritoneal exudate neutrophils. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1985 Aug;63(Pt 4):361–370. doi: 10.1038/icb.1985.42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottendorfer D., Bitter-Suermann D., Hadding U. An in vitro system to study listericidal capacity of macrophages from separate mice: resident macrophages exhibit different activation patterns. Infect Immun. 1985 Sep;49(3):685–691. doi: 10.1128/iai.49.3.685-691.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POTEL J. Die Morphologie, Kultur und Tierpathogenität des Corynebacterium infantisepticum. Zentralbl Bakteriol Orig. 1951 Jun 16;156(7):490–493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroup W. H., Dickerson R. W., Jr, Read R. B., Jr Two-phase slug flow heat exchanger for microbial thermal inactivation research. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):889–892. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.889-892.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilder M. S., Edberg J. C. Interaction of virulent and avirulent Listeria monocytogenes with cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages. Infect Immun. 1973 Mar;7(3):409–415. doi: 10.1128/iai.7.3.409-415.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



