Abstract
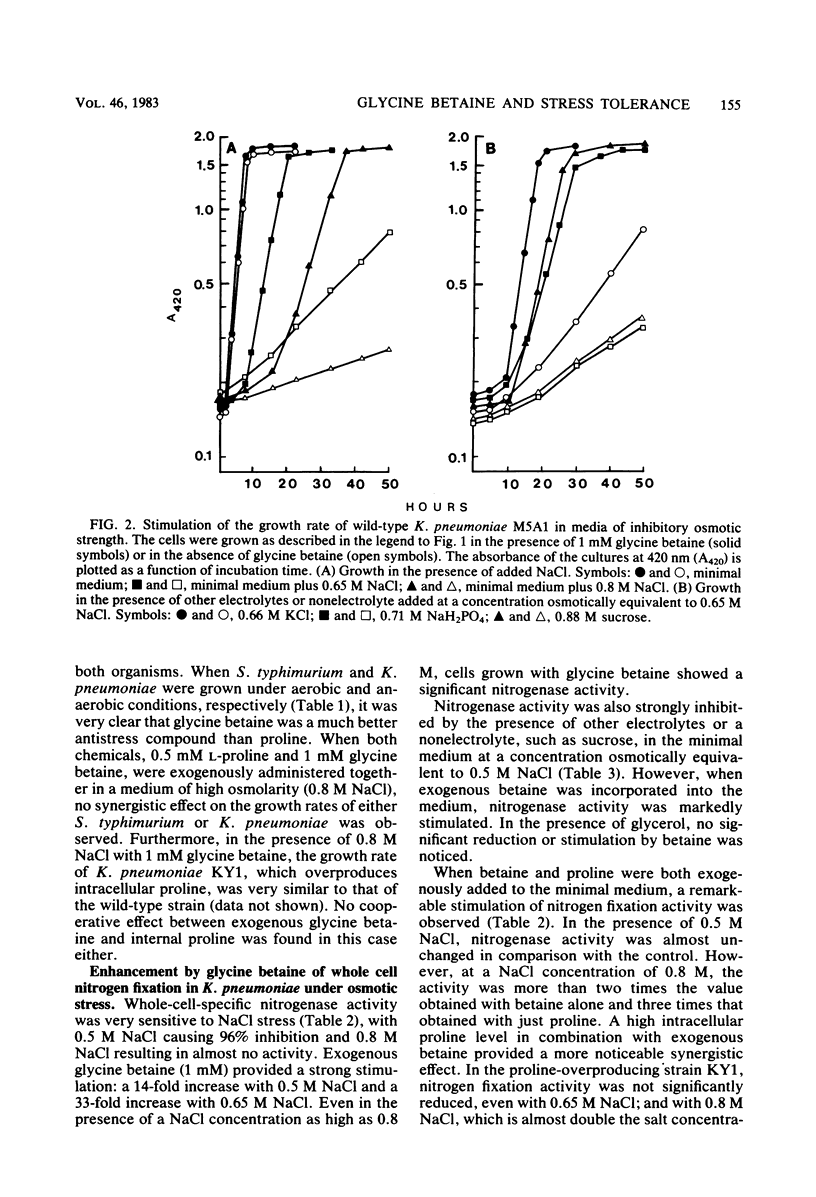
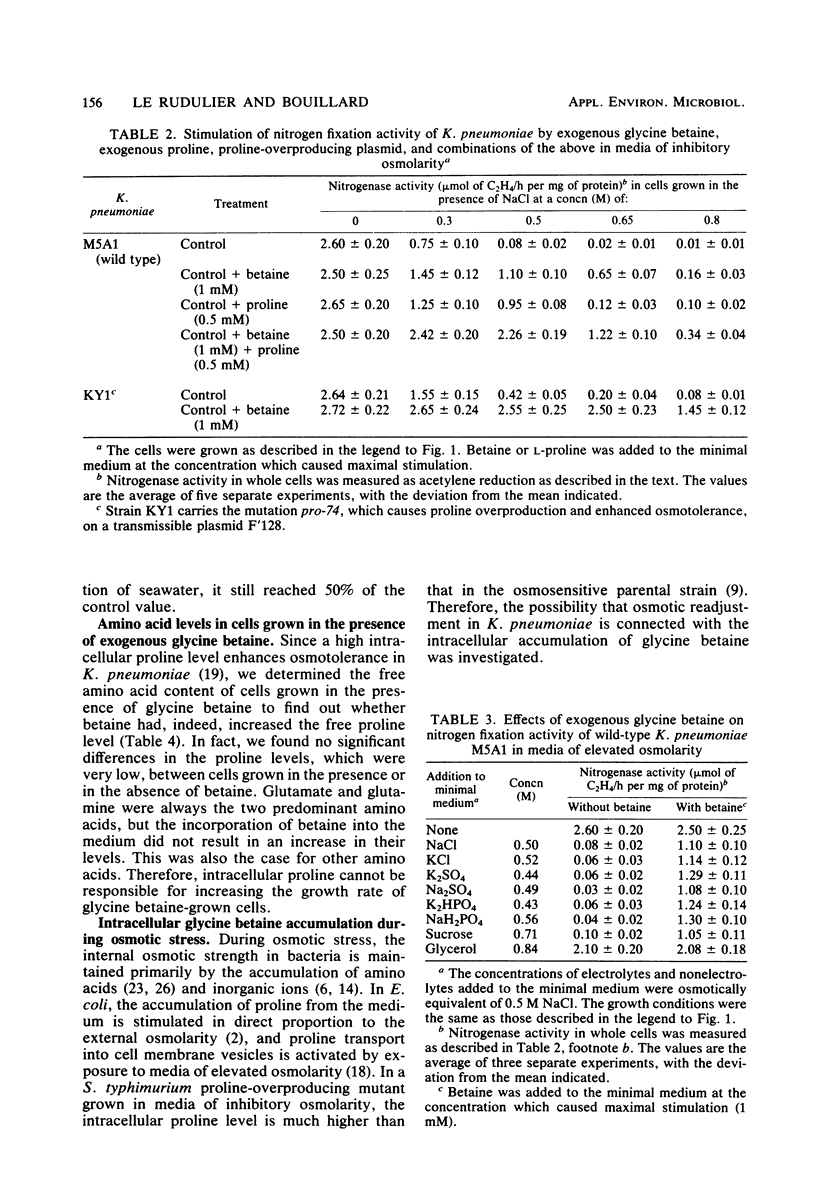
Osmoregulation was examined in members of the Enterobacteriaceae. Exogenous glycine betaine at a concentration as low as 1 mM was found to stimulate the growth rate of Escherichia coli, Salmonella typhimurium, and Klebsiella pneumoniae in media of inhibitory osmotic strength. The stimulation was shown to be independent of any specific solutes, electrolytes, or nonelectrolytes. Therefore, the stimulatory effect of glycine betaine was a consequence of high osmotic potential. This effect was found to be far greater than the proline effect previously observed in S. typhimurium. Whereas nitrogen fixation by K. pneumoniae is completely inhibited under conditions of osmotic stress, nitrogenase activity could be partially restored by the addition of exogenous glycine betaine to the culture medium. Furthermore, glycine betaine in combination with proline, especially proline produced internally at a high level because of regulatory mutations affecting proline biosynthesis, strongly stimulated nitrogen fixation activity during osmotic stress. Glycine betaine was accumulated by the cells, and the amount taken up was correlated with the osmolarity of the medium. These findings are discussed in relation to the possible mechanisms by which glycine betaine might cause enhanced osmotolerance.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BRITTEN R. J., McCLURE F. T. The amino acid pool in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1962 Sep;26:292–335. doi: 10.1128/br.26.3.292-335.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byerrum R. U., Sato C. S., Ball C. D. Utilization of Betaine as a Methyl Group Donor in Tobacco. Plant Physiol. 1956 Sep;31(5):374–377. doi: 10.1104/pp.31.5.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHRISTIAN J. H., WALTHO J. A. The sodium and potassium content of non-halophilic bacteria in relation to salt tolerance. J Gen Microbiol. 1961 May;25:97–102. doi: 10.1099/00221287-25-1-97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN G. N., RICKENBERG H. V. Concentration spécifique réversible des amino acides chez Escherichia coli. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1956 Nov;91(5):693–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka L. N. A third L-proline permease in Salmonella typhimurium which functions in media of elevated osmotic strength. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1433–1443. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1433-1443.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka L. N. Proline over-production results in enhanced osmotolerance in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(1):82–86. doi: 10.1007/BF00422771. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka L. N. The role of proline in osmoregulation in Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. Basic Life Sci. 1981;18:533–542. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3980-9_32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DURELL J., ANDERSON D. G., CANTONI G. L. The synthesis of methionine by enzymic transmethylation. I. Purification and properties of thetin homocysteine methylpherase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1957 Nov;26(2):270–281. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(57)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson A. D., Nelsen C. E. Betaine Accumulation and [C]Formate Metabolism in Water-stressed Barley Leaves. Plant Physiol. 1978 Aug;62(2):305–312. doi: 10.1104/pp.62.2.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R., Deuel F. Proline uptake by disrupted membrane preparations from Escherichia coli. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Jun;132(1):118–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90343-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Rudulier D., Yang S. S., Csonka L. N. Nitrogen fixation in Klebsiella pneumoniae during osmotic stress. Effect of exogenous proline or a proline overproducing plasmid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Nov 24;719(2):273–283. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90099-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Measures J. C. Role of amino acids in osmoregulation of non-halophilic bacteria. Nature. 1975 Oct 2;257(5525):398–400. doi: 10.1038/257398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafaeli-Eshkol D., Avi-Dor Y. Studies on halotolerance in a moderately halophilic bacterium. Effect of betaine on salt resistance of the respiratory system. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(4):687–691. doi: 10.1042/bj1090687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafaeli-Eshkol D. Studies on halotolerance in a moderately halophilic bacterium. Effect of growth conditions on salt resistance of the respiratory system. Biochem J. 1968 Oct;109(4):679–685. doi: 10.1042/bj1090679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh H. S. Enzymatic oxidation of 14C-labelled betaine by the marine microbe Achromobacter cholinophagum. Can J Biochem. 1968 Jan;46(1):21–23. doi: 10.1139/o68-004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shkedy-Vinkler C., Avi-Dor Y. Betaine-induced stimulation of respiration at high osmolarities in a halotolerant bacterium. Biochem J. 1975 Aug;150(2):219–226. doi: 10.1042/bj1500219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streicher S., Gurney E., Valentine R. C. Transduction of the nitrogen-fixation genes in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1174–1177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempest D. W., Meers J. L., Brown C. M. Influence of environment on the content and composition of microbial free amino acid pools. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(2):171–185. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Wilson T. H. The role of energy coupling in the transport of beta-galactosides by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1966 May 25;241(10):2200–2211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoch D. C., Pengra R. M. Effect of amino acids on the nitrogenase system of Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1966 Sep;92(3):618–622. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.3.618-622.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



