Abstract
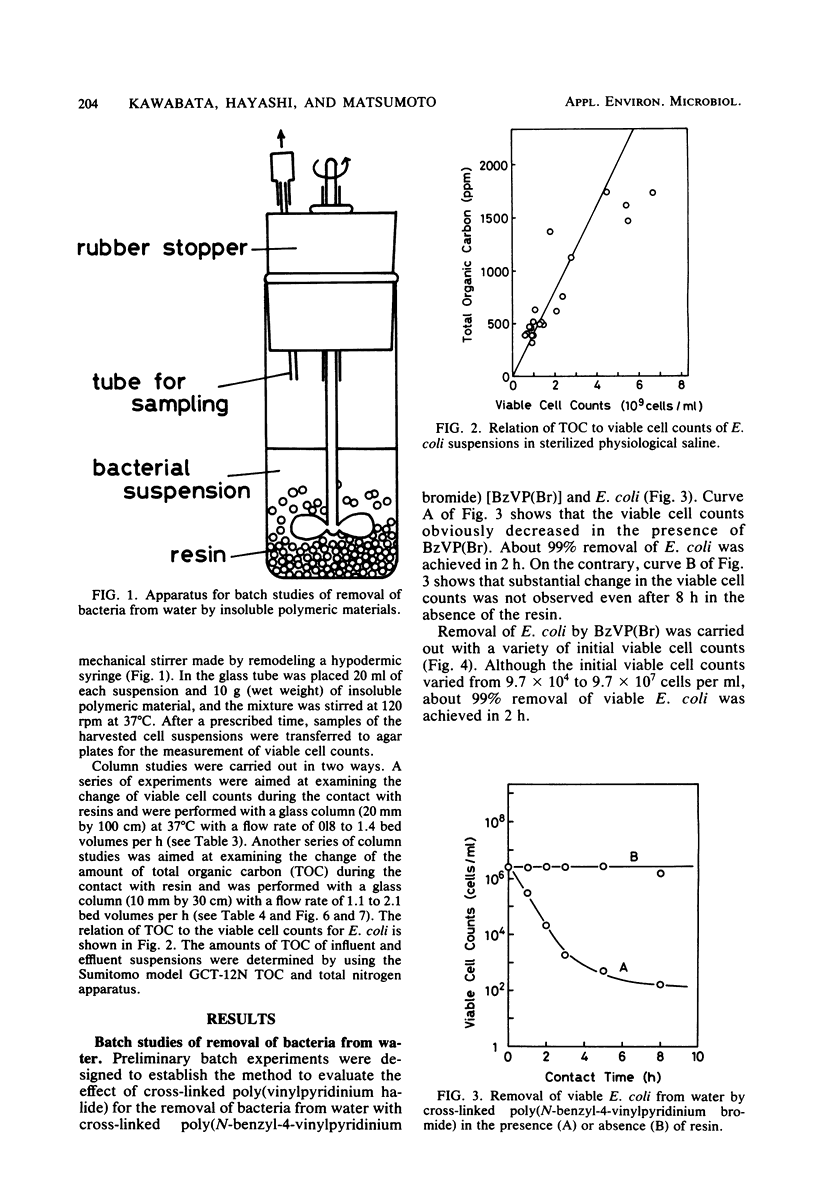
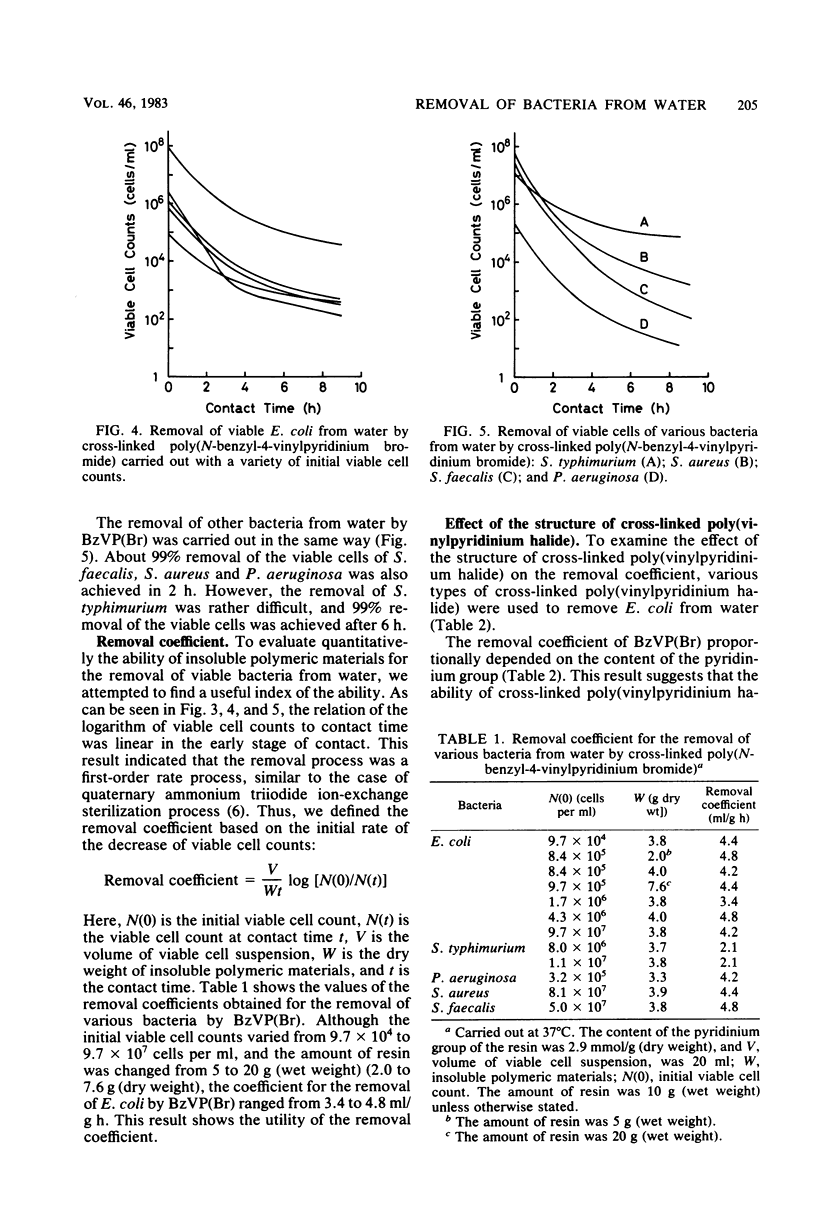
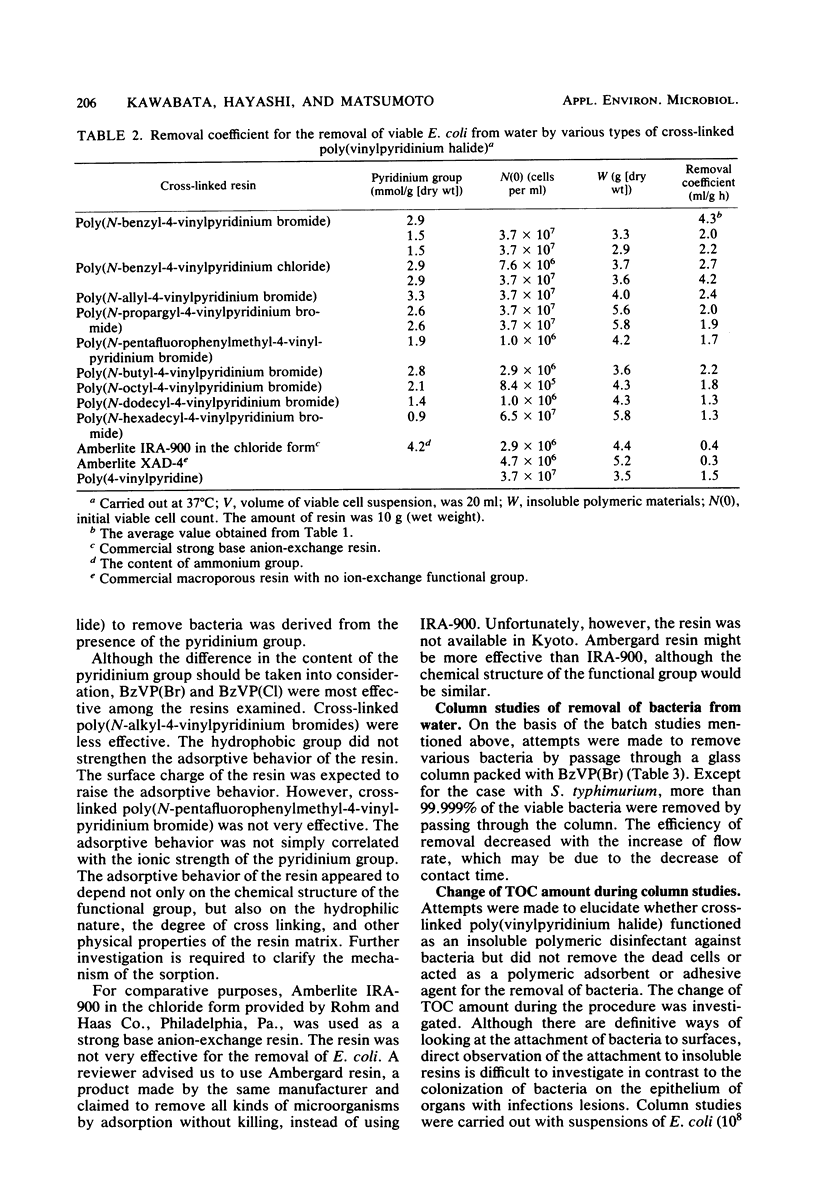
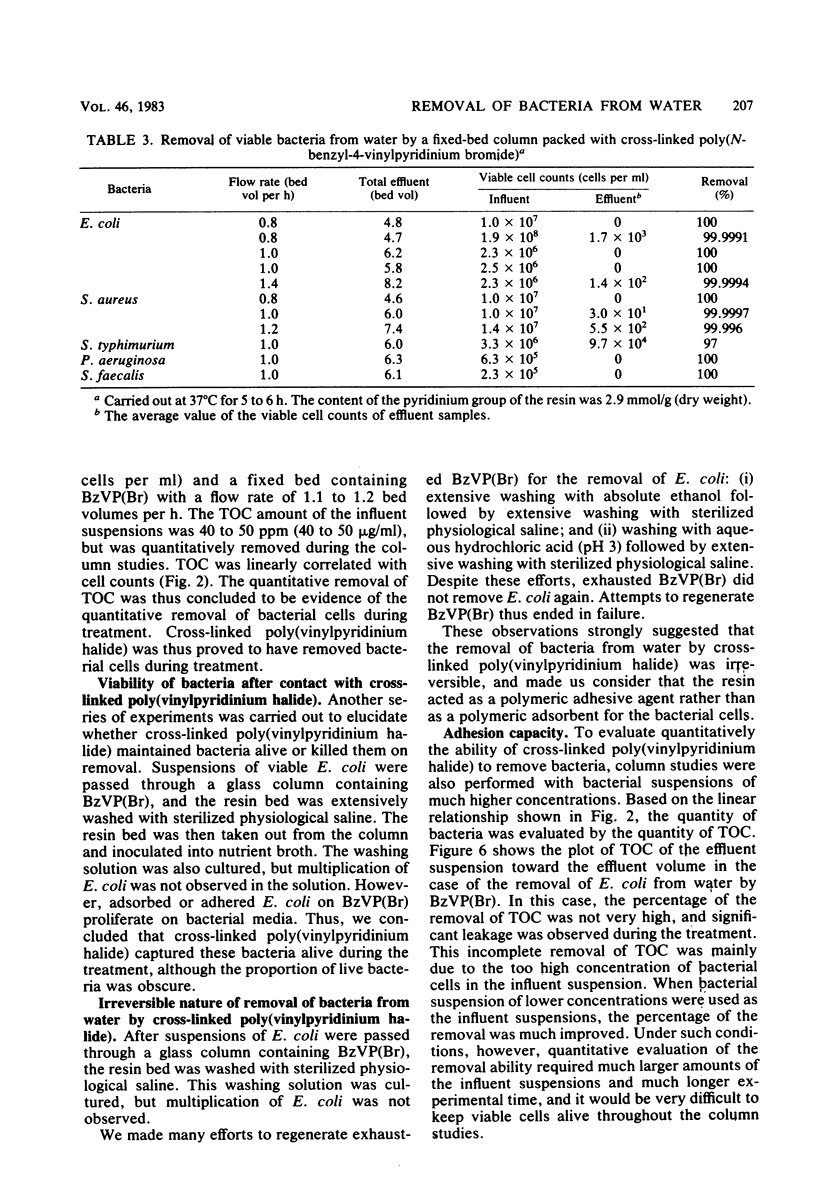
Cross-linked poly(vinylpyridinium halide) was found to have a novel and remarkable ability to remove bacteria from water. For example, when 10 g (wet weight) of cross-linked poly(N-benzyl-4-vinylpyridinium bromide) was contacted with 20 ml of suspensions of Escherichia coli (9.7 X 10(4) to 9.7 X 10(7)/ml), Salmonella typhimurium (8.0 X 10(6) to 1.1 X 10(7)/ml), Streptococcus faecalis (5.0 X 10(7)/ml), Staphylococcus aureus (8.1 X 10(7)/ml), and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (3.2 X 10(5)/ml) under stirring in sterilized physiological saline at 37 degrees C, 99% of the viable cells of these bacteria were removed in 2 to 6 h. When suspensions of these bacteria (10(5) to 10(8) cells per ml) were passed through a column (20 mm by 100 cm) of cross-linked poly(N-benzyl-4-vinylpyridinium bromide) at 37 degrees C with a flow rate of 0.8 to 1.4 bed volumes per h, 97 to 100% of the viable cells were eliminated from the suspensions during the treatment. Mechanistic studies demonstrated that cross-linked poly(vinylpyridinium halide) irreversibly captured these bacteria alive during the treatment. That is, total organic carbon was removed during the treatment, and the bacteria which adhered to the resin proliferated on the bacterial medium. The adhesion capacity was estimated to be 10(10) cells per g (dry weight). Total organic carbon was also removed even when the bacteria were killed by heat treatment before the column studies.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- FOLSOME C. E., LESLIE S. A., THOMS R. K. Control of chronic lower genital tract infections; the use of an ion-exchange resin. Obstet Gynecol. 1955 Nov;6(5):532–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isquith A. J., Abbott E. A., Walters P. A. Surface-bonded antimicrobial activity of an organosilicon quaternary ammonium chloride. Appl Microbiol. 1972 Dec;24(6):859–863. doi: 10.1128/am.24.6.859-863.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTMAN B. Uses of ion exchange resins in microbiology. Bacteriol Rev. 1960 Jun;24(2):251–260. doi: 10.1128/br.24.2.251-260.1960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



