Abstract
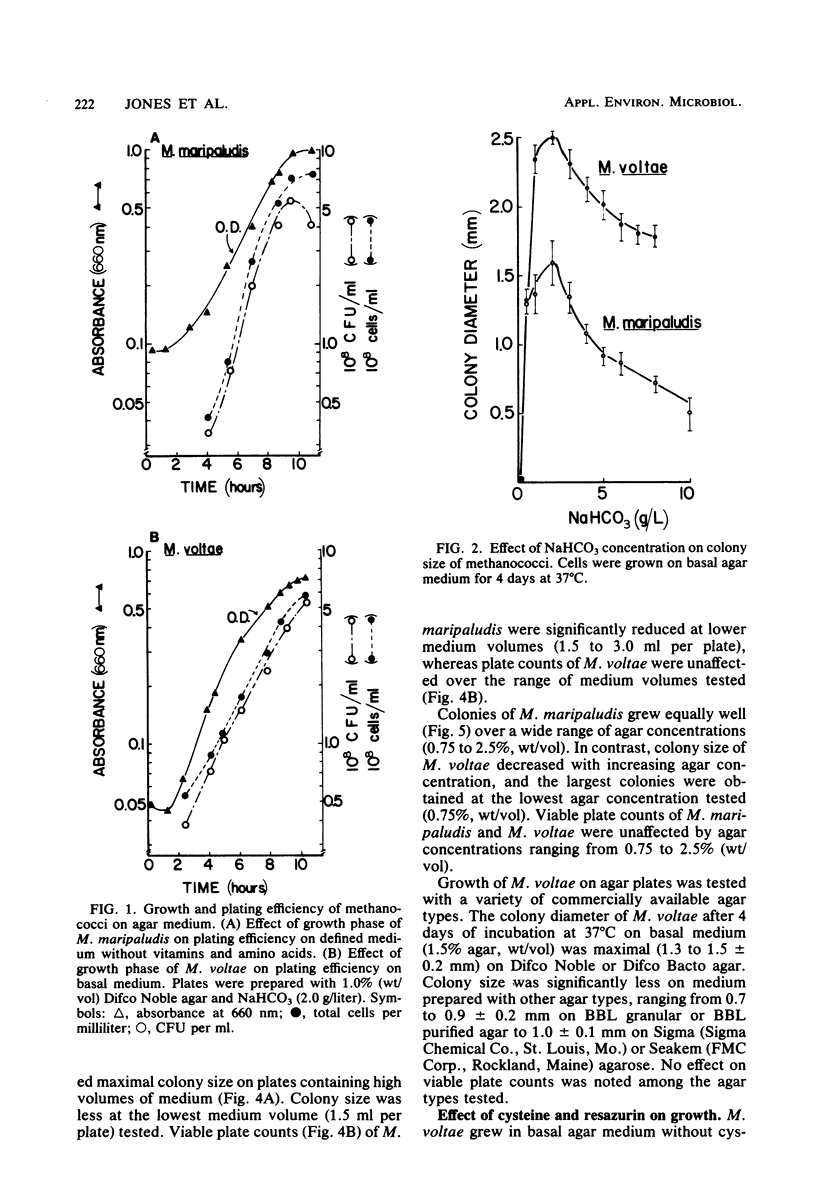
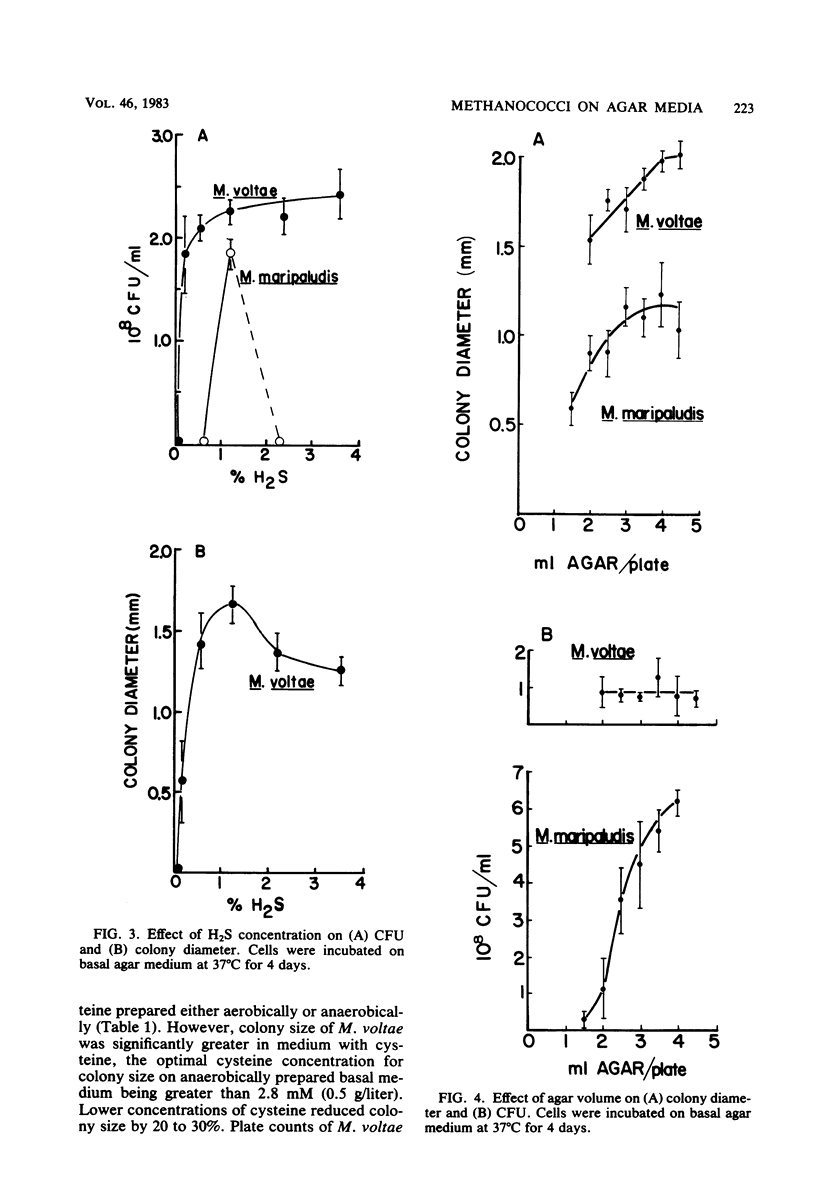
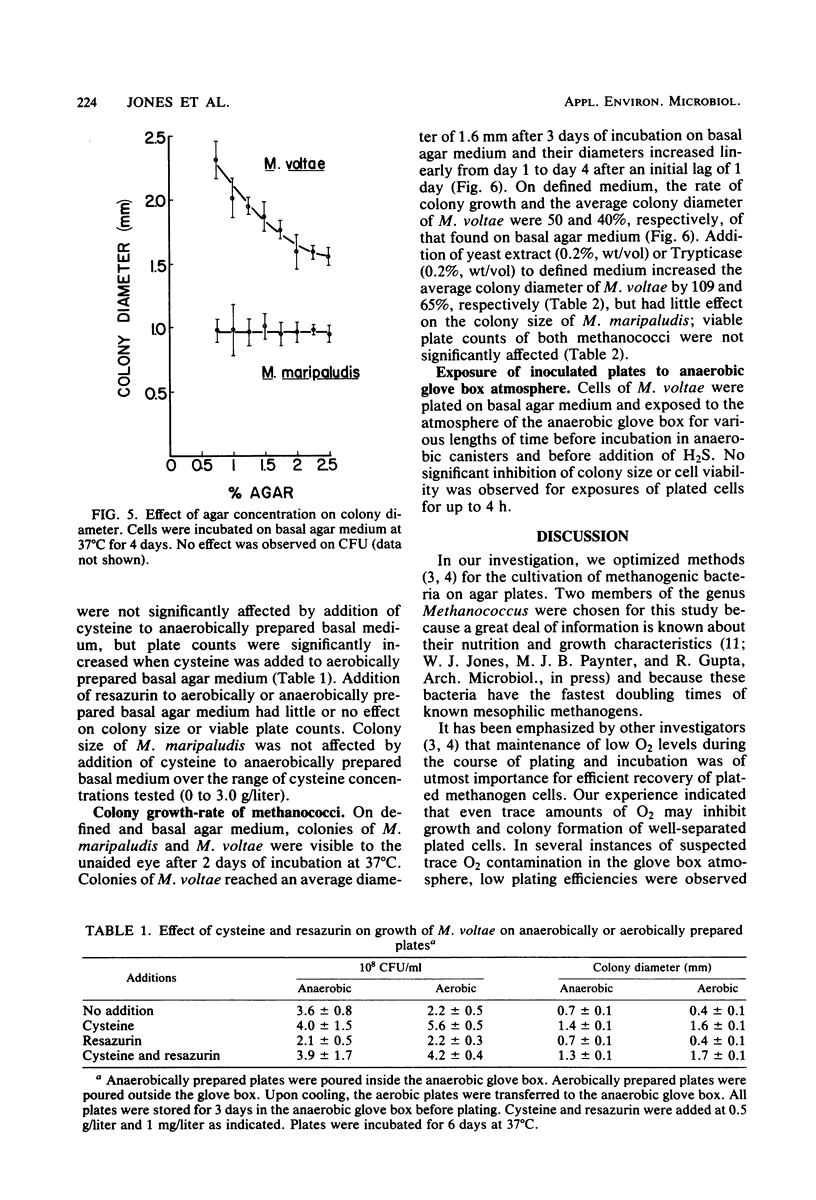
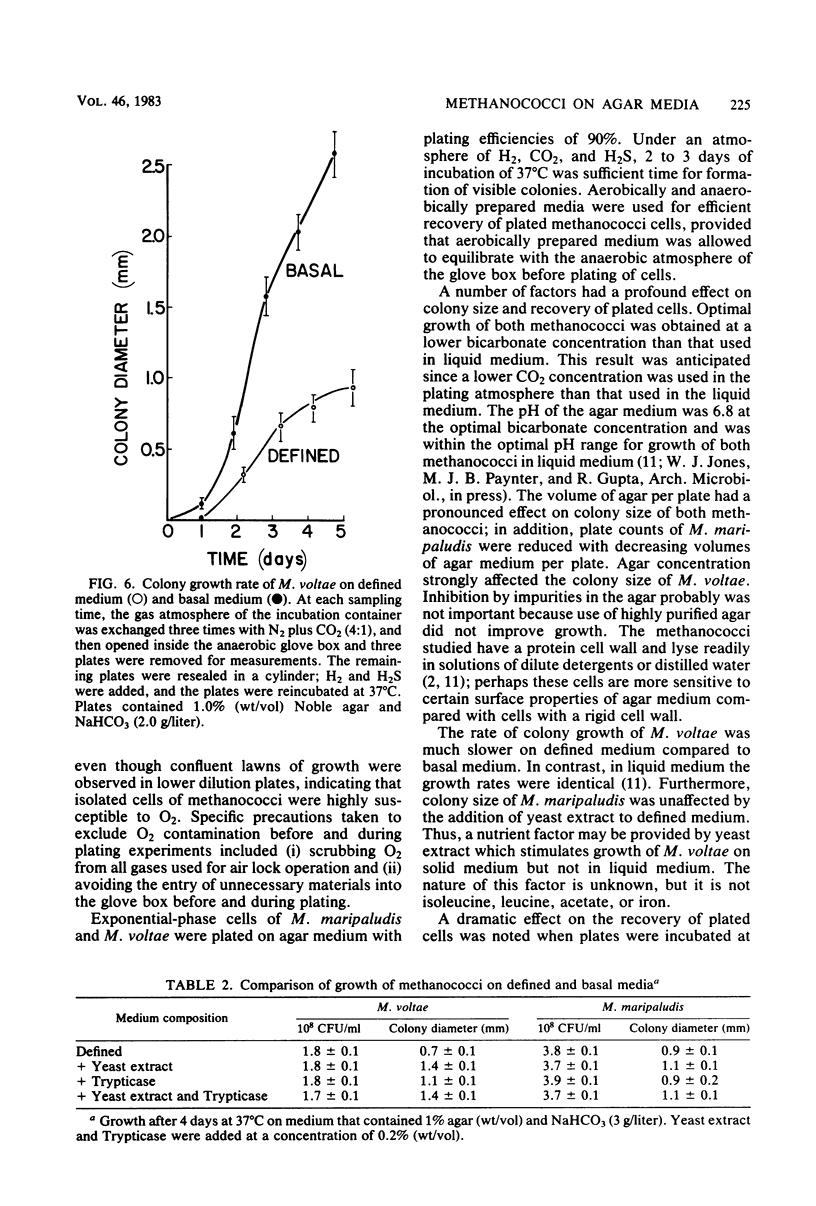
Plating techniques for cultivation of methanogenic bacteria have been optimized for two members of the genus Methanococcus. Methanococcus maripaludis and Methanococcus voltae were cultivated on aerobically and anaerobically prepared agar media. Maintenance of O2 levels below 5 μl/liter within an anaerobic glove box was necessary during plating and incubation for 90% recovery of plated cells. Under an atmosphere of H2, CO2, and H2S (79:20:1), 2 to 3 days of incubation at 37°C were sufficient for the formation of visible colonies. The viability of plated cells was significantly affected by the growth phase of the culture, H2S concentration, and the volume of medium per plate. In addition, colony size of methanococci was affected by agar type, as well as by the concentrations of agar, H2S, and bicarbonate.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aranki A., Freter R. Use of anaerobic glove boxes for the cultivation of strictly anaerobic bacteria. Am J Clin Nutr. 1972 Dec;25(12):1329–1334. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/25.12.1329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Fox G. E., Magrum L. J., Woese C. R., Wolfe R. S. Methanogens: reevaluation of a unique biological group. Microbiol Rev. 1979 Jun;43(2):260–296. doi: 10.1128/mr.43.2.260-296.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Wolfe R. S. New approach to the cultivation of methanogenic bacteria: 2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid (HS-CoM)-dependent growth of Methanobacterium ruminantium in a pressureized atmosphere. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Dec;32(6):781–791. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.6.781-791.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards T., McBride B. C. New method for the isolation and identification of methanogenic bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Apr;29(4):540–545. doi: 10.1128/am.29.4.540-545.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNGATE R. E. The anaerobic mesophilic cellulolytic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1950 Mar;14(1):1–49. doi: 10.1128/br.14.1.1-49.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountfort D. O., Asher R. A. Effect of inorganic sulfide on the growth and metabolism of Methanosarcina barkeri strain DM. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Apr;37(4):670–675. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.4.670-675.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudo S. Z., Hersch P. A. Monitoring the atmosphere in an anaerobic chamber. Appl Microbiol. 1974 Oct;28(4):582–585. doi: 10.1128/am.28.4.582-585.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman W. B., Ankwanda E., Wolfe R. S. Nutrition and carbon metabolism of Methanococcus voltae. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):852–863. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.852-863.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeikus J. G. The biology of methanogenic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Jun;41(2):514–541. doi: 10.1128/br.41.2.514-541.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



