Abstract
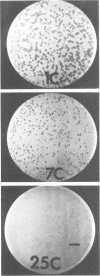
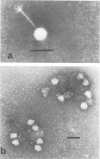
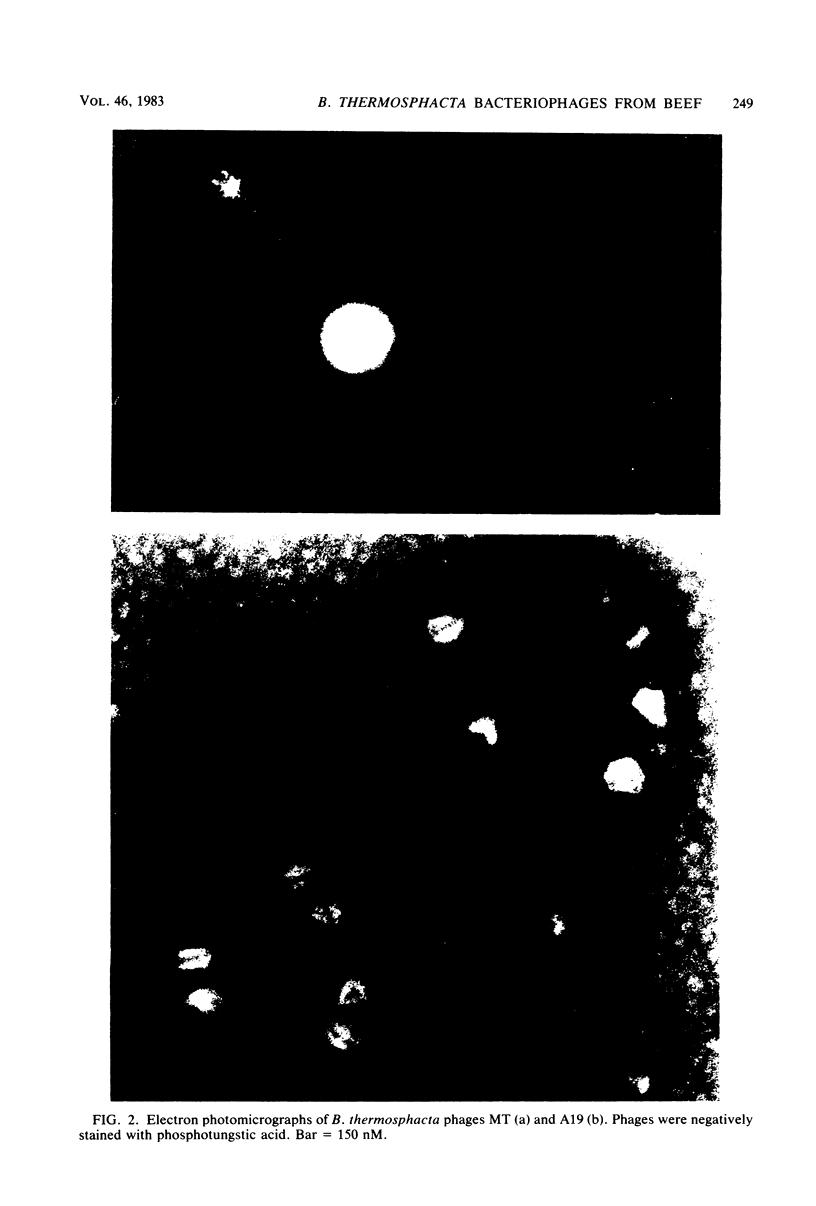
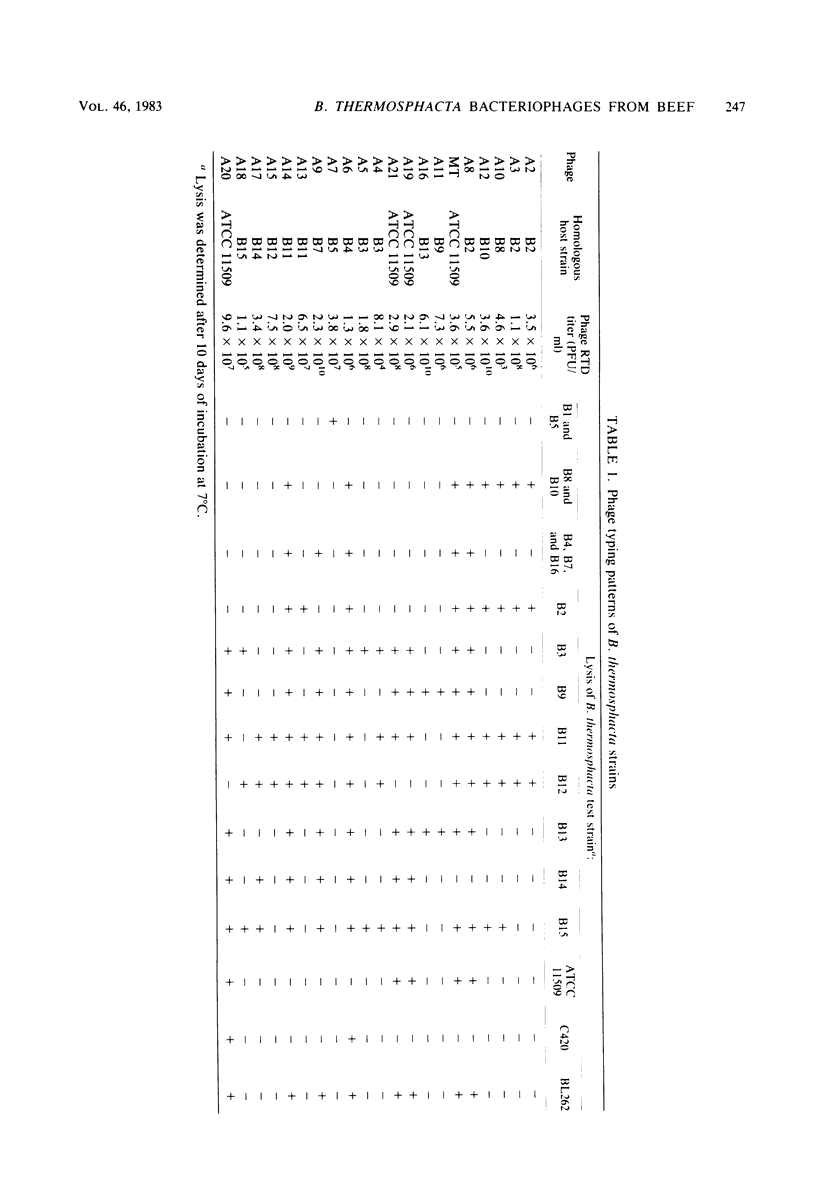
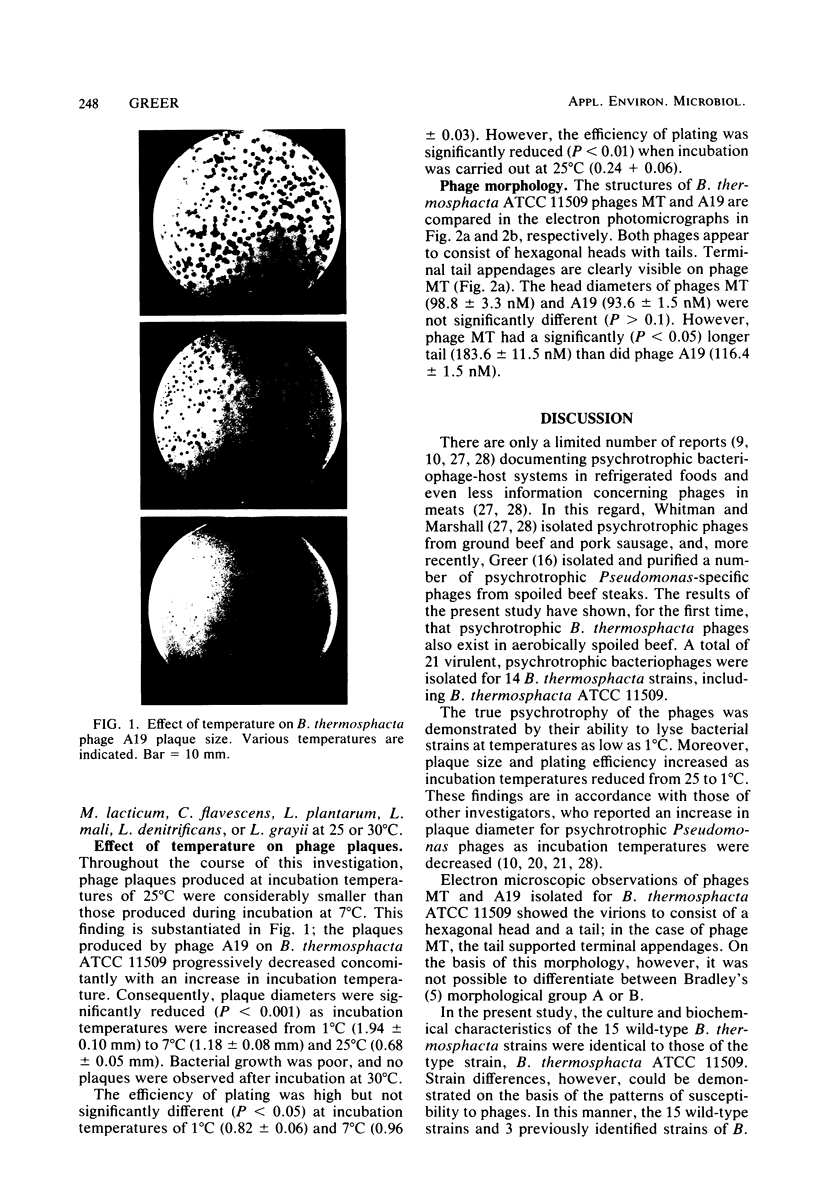
A total of 15 wild-type Brocothrix thermosphacta strains isolated from beef and the type strain, B. thermosphacta ATCC 11509, were used as hosts for the isolation of bacteriophages under psychrotrophic conditions (7 degrees C). A total of 21 virulent, psychrotrophic phages were successfully isolated and purified from aqueous extracts of spoiled rib steaks. Phage plaque size and plating efficiency significantly increased as incubation temperature was reduced from 25 to 1 degree C. Electron microscopy of two homologous B. thermosphacta phages showed the virions to consist of hexagonal heads and tails, with terminal appendages clearly visible on one of the phages. On the basis of culture and biochemical data, the wild-type B. thermosphacta strains had characteristics identical to those of strain ATCC 11509. However, specific differences in the pattern of susceptibilities to the phages revealed the presence of 14 distinct phage lysotypes. Phage typing may provide a rapid and sensitive means of differentiating B. thermosphacta strains.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bradley D. E. Ultrastructure of bacteriophage and bacteriocins. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):230–314. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.230-314.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell R. J., Egan A. F., Grau F. H., Shay B. J. The growtn of Microbacterium thermosphactum on beef. J Appl Bacteriol. 1979 Dec;47(3):505–509. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1979.tb01211.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dainty R. H., Hibbard C. M. Aerobic metabolism of Brochothrix thermosphacta growing on meat surfaces and in laboratory media. J Appl Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;48(3):387–396. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1980.tb01027.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delisle A. L., Levin R. E. Bacteriophages of psychrophilic pseudomonads. I. Host range of phage pools active against fish spoilage and fish-pathogenic pseudomonads. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1969;35(3):307–317. doi: 10.1007/BF02219151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delisle A. L., Levin R. E. Bacteriophages of psychrophilic pseudomonads. II. Host range of phage active against Pseudomonas putrefaciens. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1969;35(3):318–324. doi: 10.1007/BF02219152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner G. A. A selective medium for the enumeration of Microbacterium thermosphactum in meat and meat products. J Appl Bacteriol. 1966 Dec;29(3):455–460. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1966.tb03497.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCLEAN R. A., SULZBACHER W. L. Microbacterium thermosphactum, spec: nov.; a nonheat resistant bacterium from fresh pork sausage. J Bacteriol. 1953 Apr;65(4):428–433. doi: 10.1128/jb.65.4.428-433.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. H. Isolation and growth of psychrophilic bacteriophage. Appl Microbiol. 1967 Jan;15(1):198–198. doi: 10.1128/am.15.1.198-.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. H., Metcalf E. S., Todd J. K. Characteristics of bacteriophages attacking psychrophilic and mesophilic pseudomonads. J Virol. 1968 Apr;2(4):357–364. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.4.357-364.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley G., Shaw K. J., Egan A. F. Volatile Compounds Associated with Spoilage of Vacuum-Packaged Sliced Luncheon Meat by Brochothrix thermosphacta. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Mar;41(3):816–818. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.3.816-818.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman P. A., Marshall R. T. Characterization of two psychrophilic Pseudomonas bacteriophages isolated from ground beef. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Sep;22(3):463–468. doi: 10.1128/am.22.3.463-468.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman P. A., Marshall R. T. Isolation of psychrophilic bacteriophage-host systems from refrigerated food products. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Aug;22(2):220–223. doi: 10.1128/am.22.2.220-223.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson B. J., Jones D. A numerical taxonomic survey of Listeria and related bacteria. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Feb;98(2):399–421. doi: 10.1099/00221287-98-2-399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]