Abstract
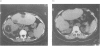
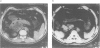
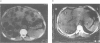
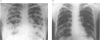
As the effectiveness of mebendazole and albendazole in patients with echinococcosis has been found to vary, we investigated some of the factors likely to be responsible. A total of 79 patients who were treated with mebendazole (44 patients) or albendazole (35 patients) were included in the study. Evaluation of the treatment results was based on the changes in cyst morphology, as evidenced by the results of X-ray radiography, sonography, and computed tomography, and on analysis of the findings in relation to parasitic and drug factors. The response of cysts according to their site did not vary much, with the exception of the poor response of bone cysts. A more important factor seems to be cyst size, since the treatment was more efficacious against smaller and younger cysts. The presence of daughter cysts should be regarded as an unfavourable factor for treatment response. Cyst multiplicity did not present insurmountable difficulties, provided the cysts were small and a prolonged course of therapy was undergone. The choice of drug used for the therapy was important, with the results supporting the advantage of albendazole. In planning the chemotherapy of hydatid disease, factors such as cyst condition and drug used should therefore be taken into consideration.
Full text
PDF
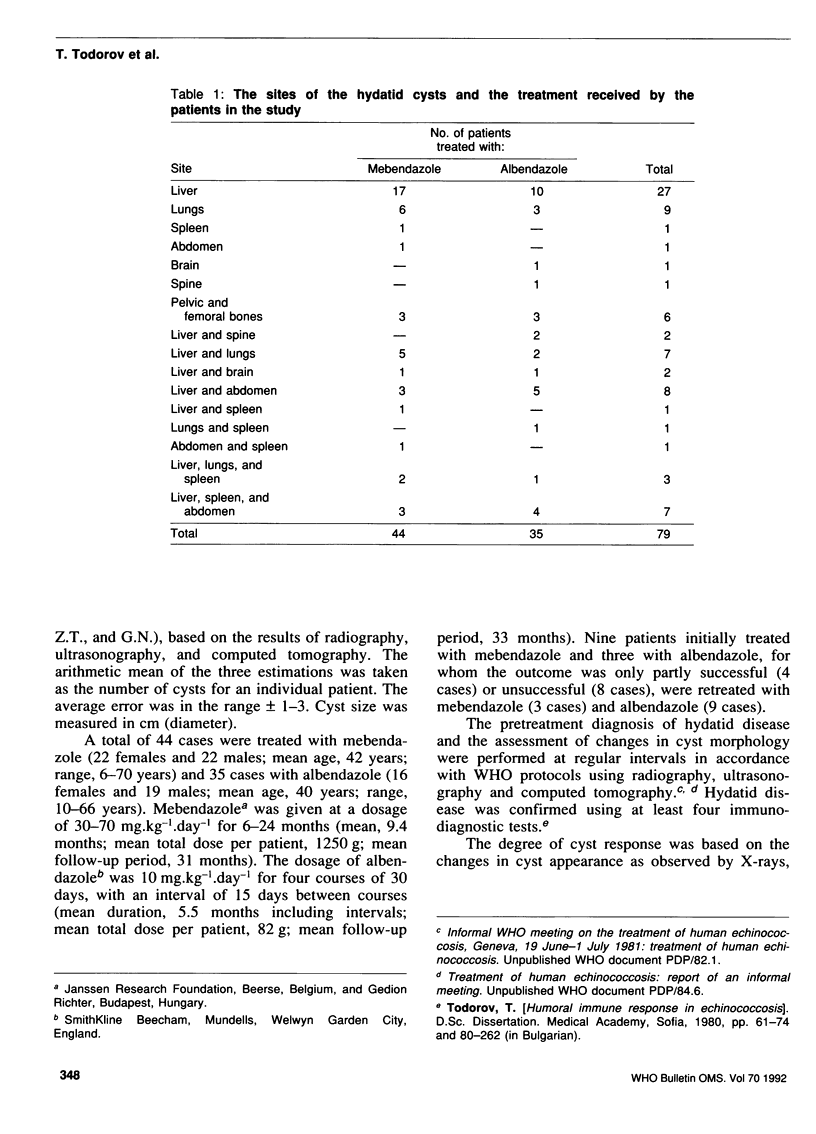

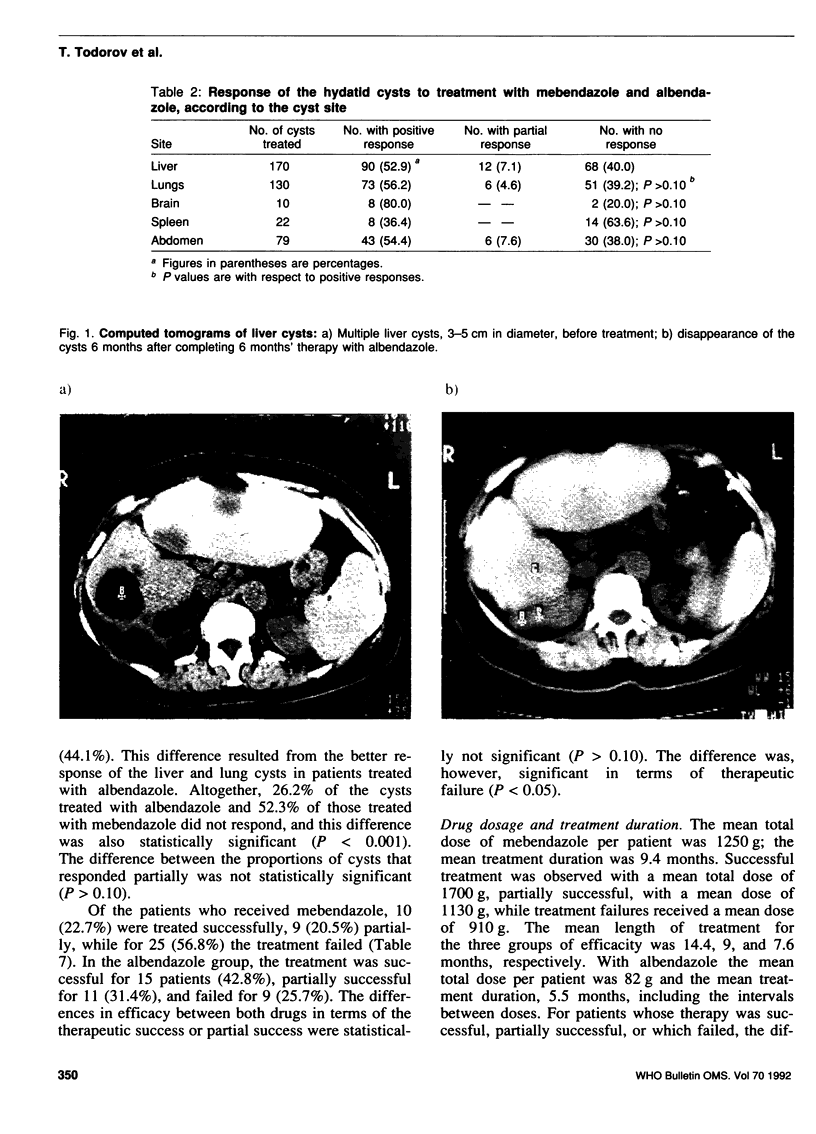
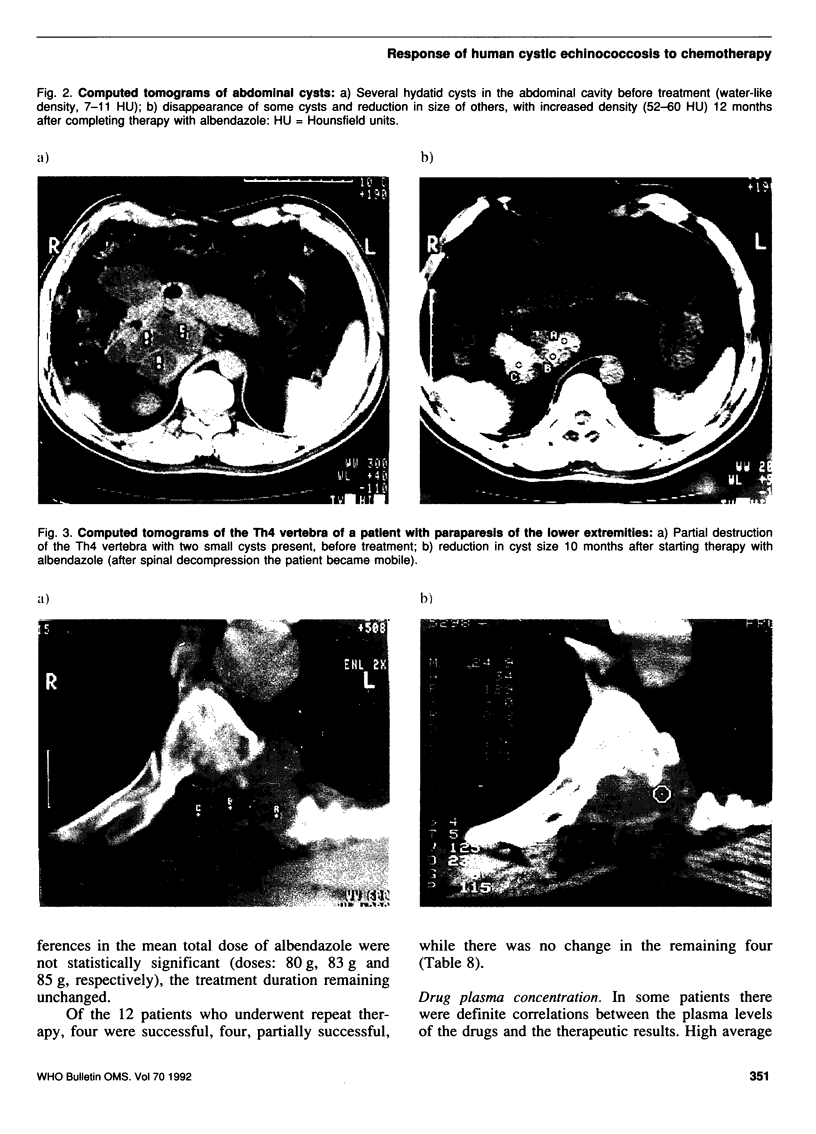
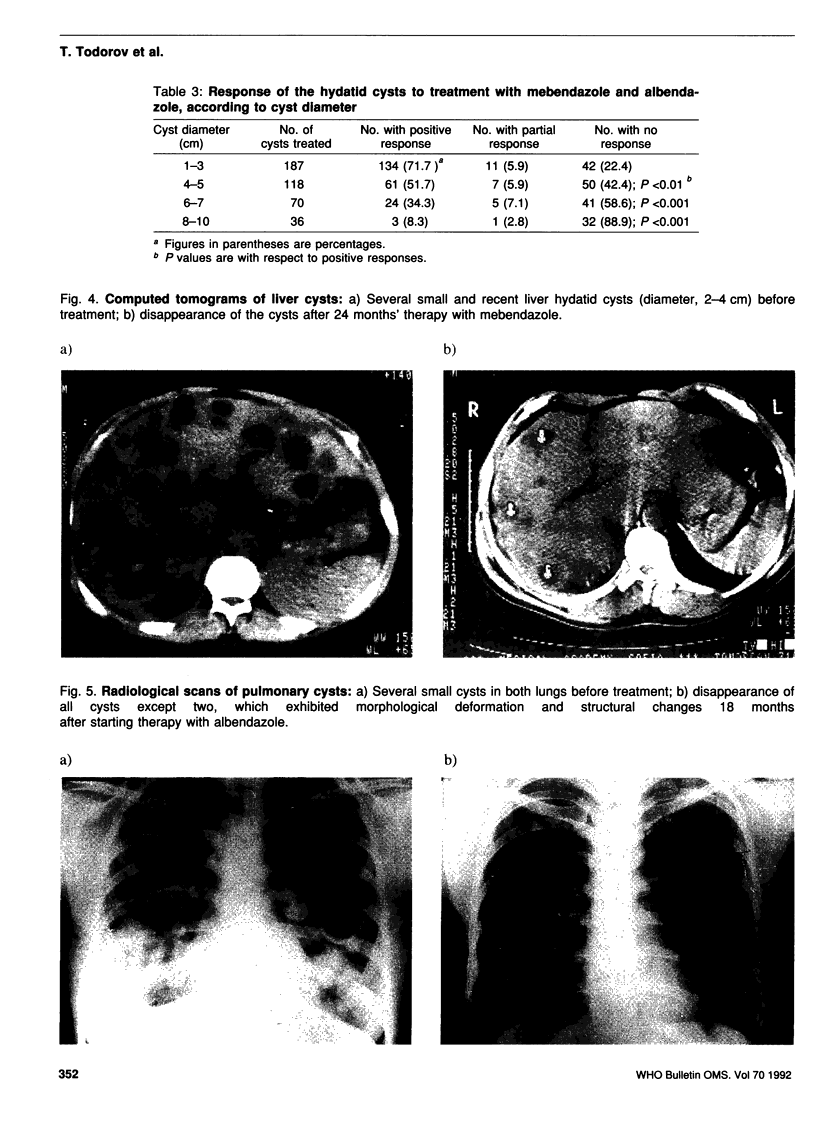
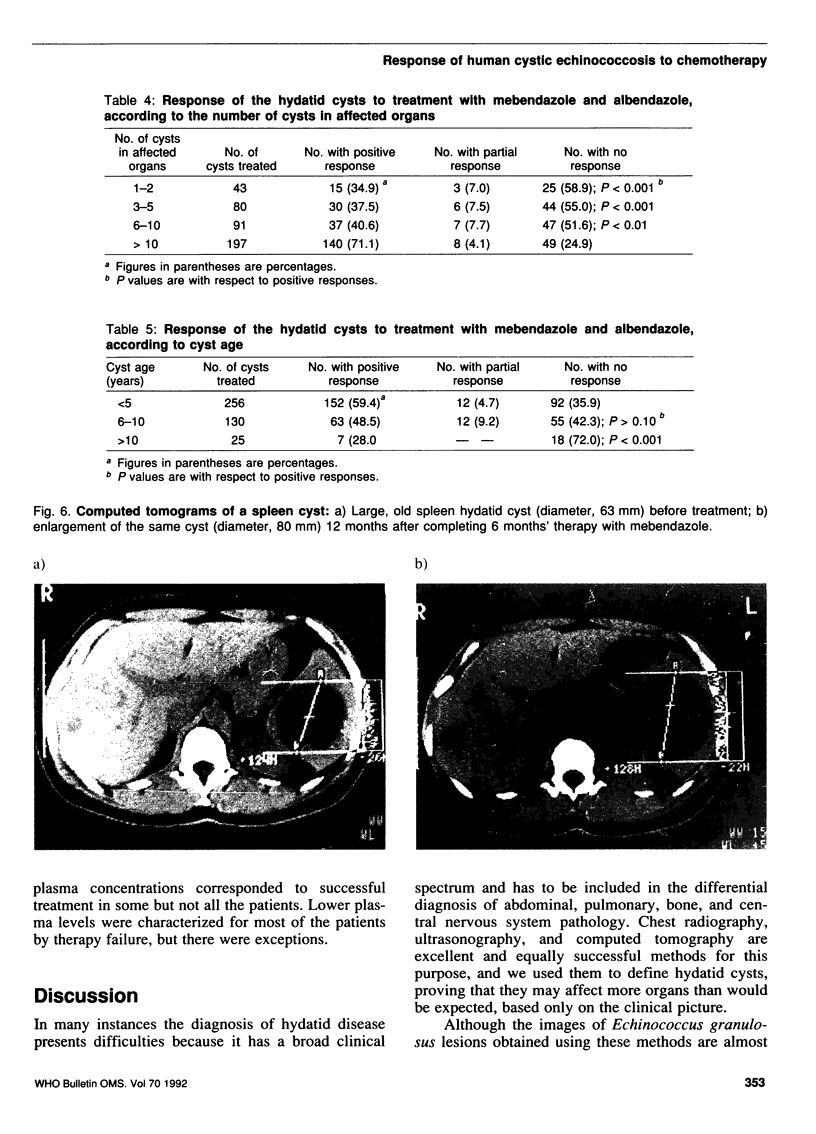
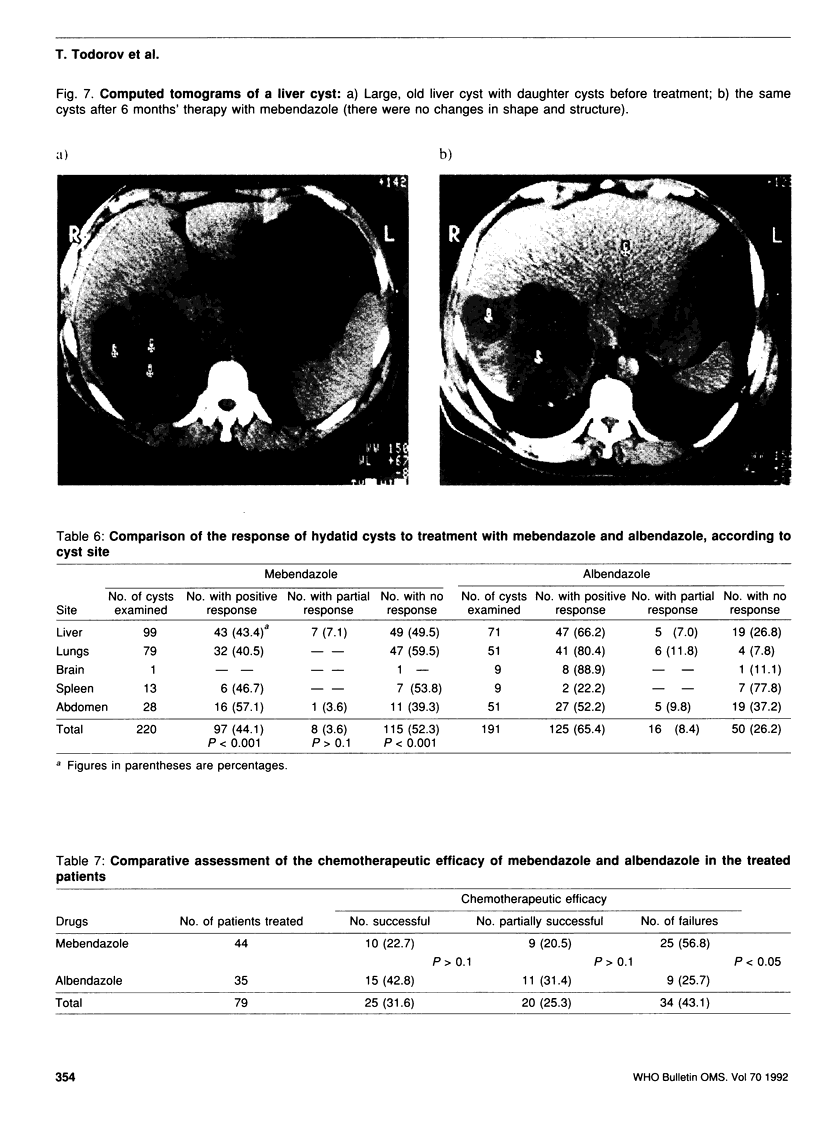




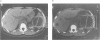
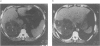
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- De Rosa F., Teggi A. First experience in the treatment of human hydatid disease with mebendazole. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 1985;11(12):875–878. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kammerer W. S., Schantz P. M. Long term follow-up of human hydatid disease (Echinococcus granulosus) treated with a high-dose mebendazole regimen. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 Jan;33(1):132–137. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1984.33.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudwan M. A., Mousa A. M., Muhtaseb S. A. Abdominal hydatid disease: follow-up of mebendazole therapy by CT and ultrasonography. Int Surg. 1986 Jan-Mar;71(1):22–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teggi A., Capozzi A., De Rosa F. Treatment of Echinococcus granulosus hydatid disease with mebendazole. J Chemother. 1989 Oct;1(5):310–317. doi: 10.1080/1120009x.1989.11738914. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todorov T., Vutova K., Petkov D., Mechkov G., Kolev K. Albendazole treatment of human cystic echinococcosis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1988;82(3):453–459. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(88)90161-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]