Abstract
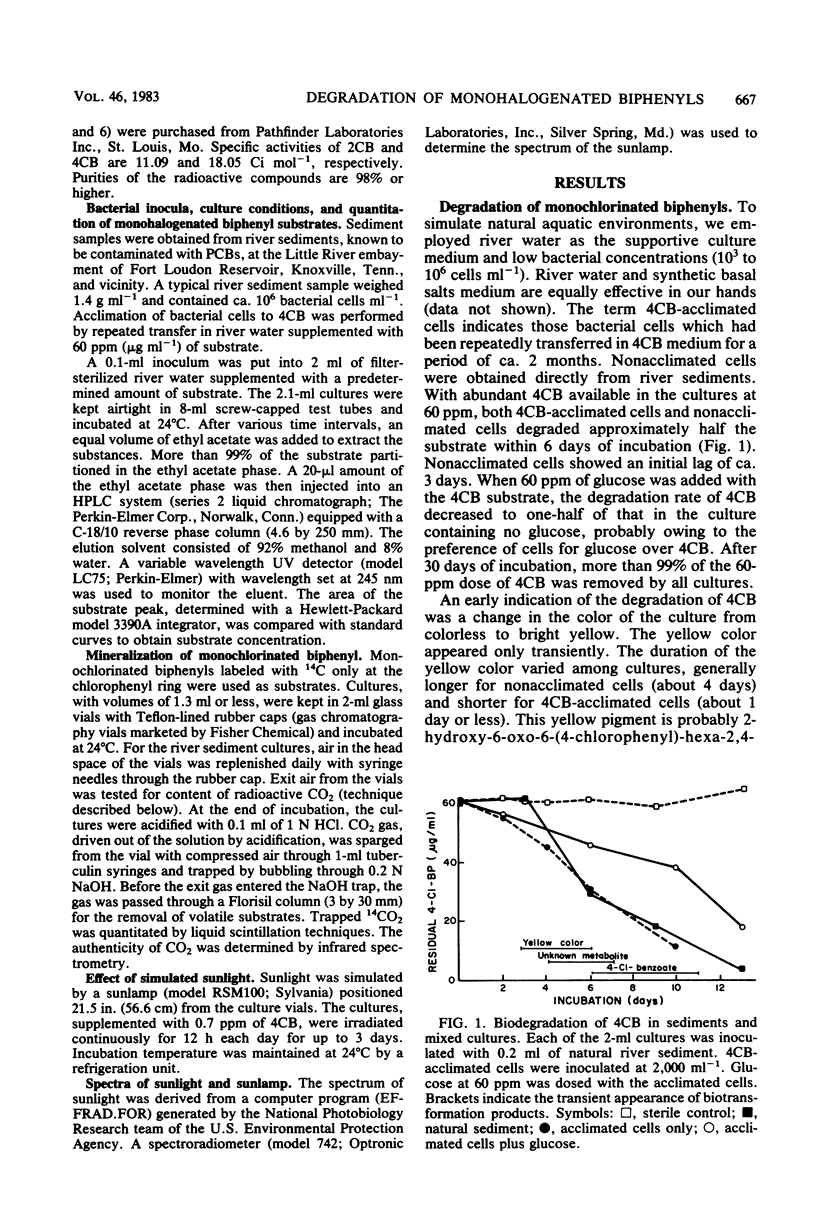
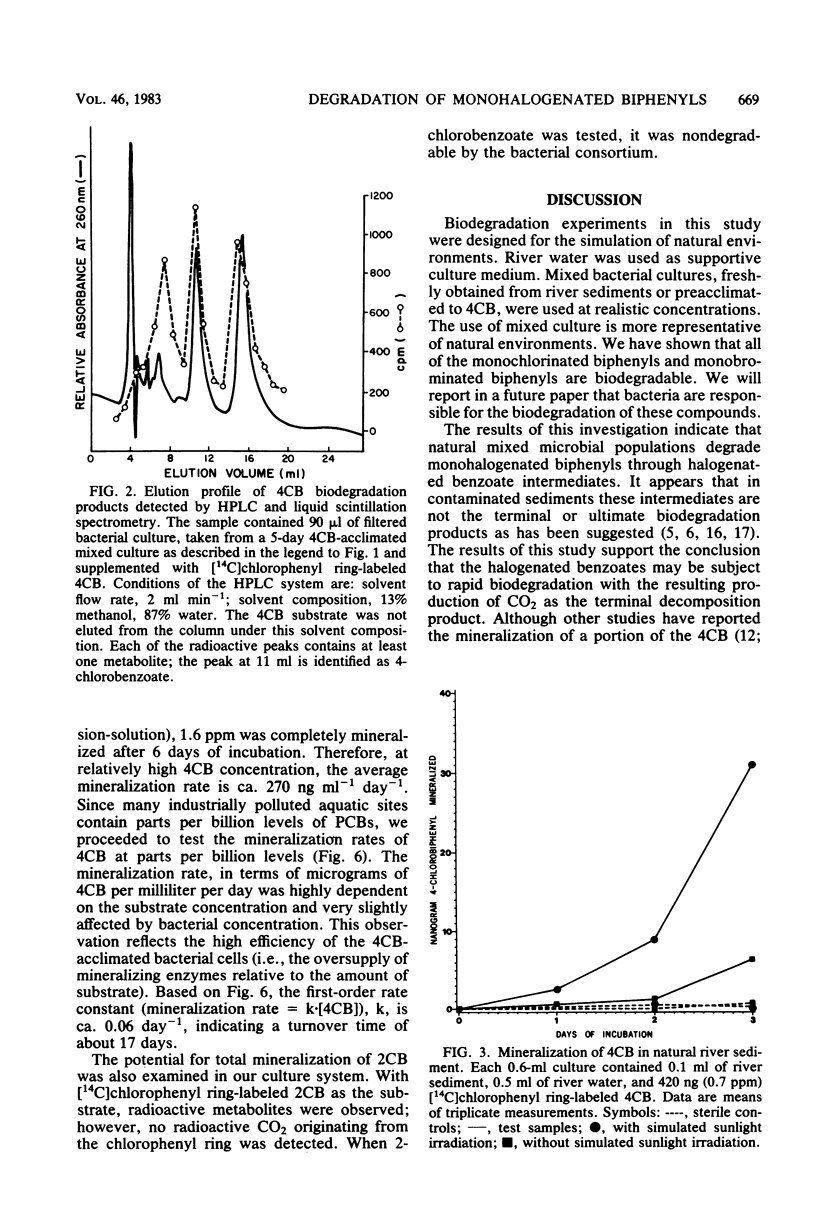
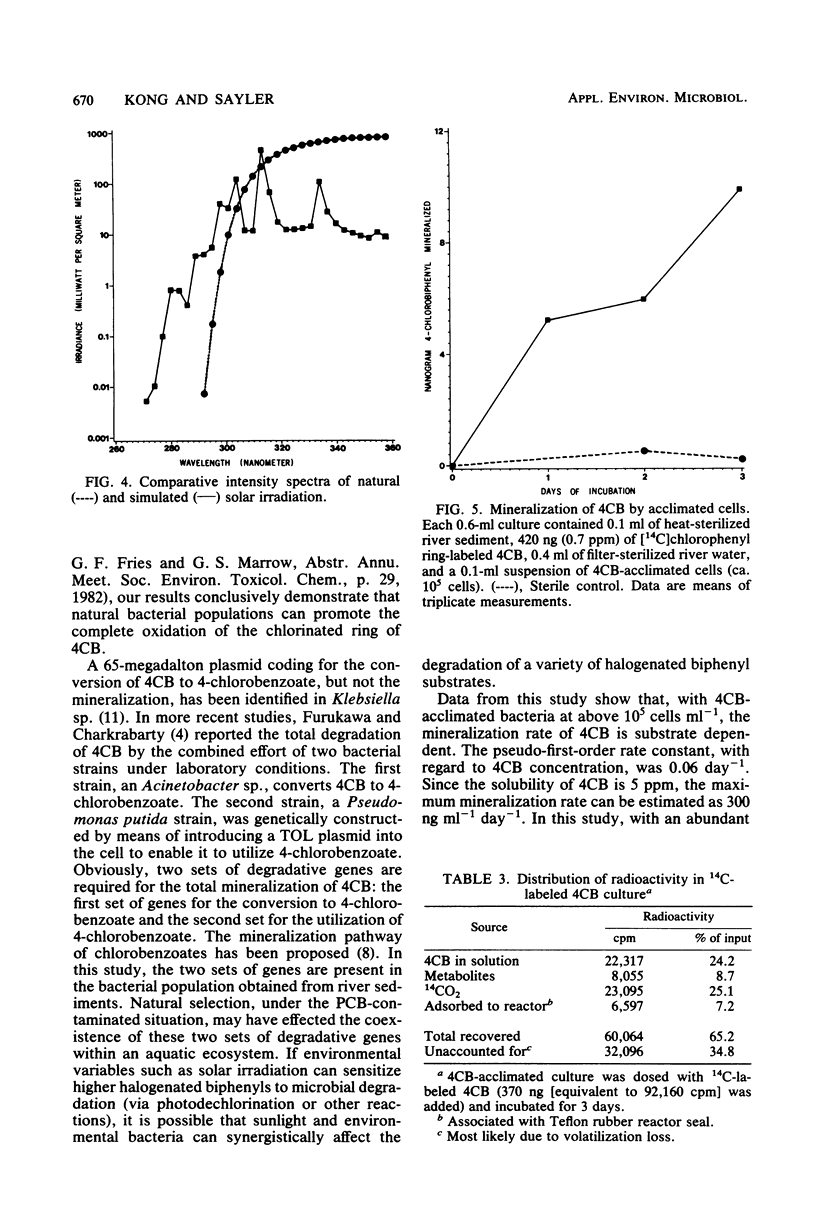
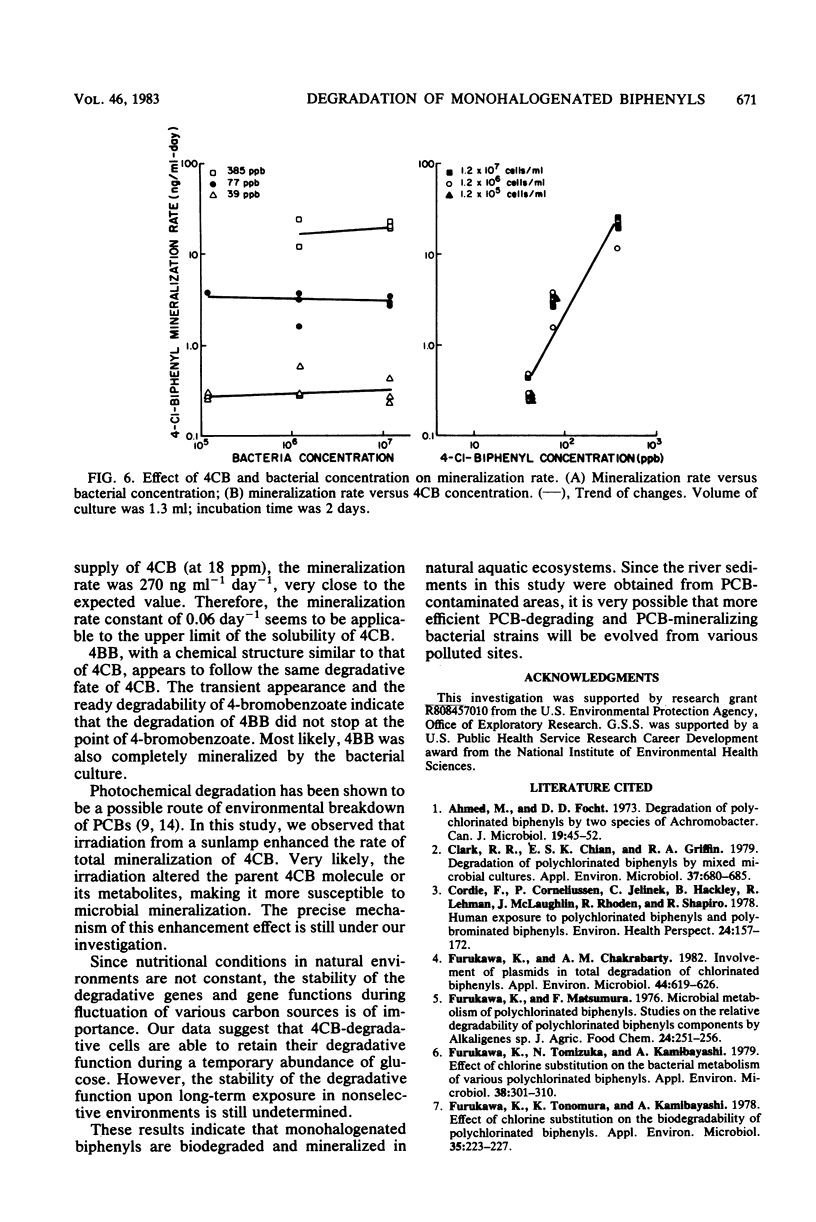
Mixed bacterial cultures obtained from polychlorinated biphenyl-contaminated river sediments are capable of degrading monohalogenated biphenyls under simulated natural conditions. Culture conditions include river water as supportive medium and mixed bacterial cultures obtained from river sediments. Degradation occurs when the substrates are supplied as the sole carbon source or when added together with glucose. The degradation rates of 2-, 3-, and 4-chlorobiphenyl, at 30 micrograms ml-1, were 1.1, 1.6, and 2.0 micrograms ml-1 day-1, respectively. Monobrominated biphenyls, including 2-, 3-, and 4-bromobiphenyl, were degraded at rates of 2.3, 4.2, and 1.4 micrograms ml-1 day-1, respectively. Metabolites, including halogenated benzoates, were detected by high-performance liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. By using chlorophenyl ring-labeled monochlorobiphenyls as substrates, total mineralization (defined as CO2 production from the chlorophenyl ring) was observed for 4-chlorobiphenyl but not for 2-chlorobiphenyl. Rates of total mineralization of 4-chlorobiphenyl (at 39 to 385 micrograms ml-1 levels) were dependent on substrate concentration, whereas variation of cell number in the range of 10(5) to 10(7) cells ml-1 had no significant effects. Simulated sunlight enhanced the rate of mineralization by ca. 400%.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed M., Focht D. D. Degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls by two species of Achromobacter. Can J Microbiol. 1973 Jan;19(1):47–52. doi: 10.1139/m73-007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark R. R., Chian E. S., Griffin R. A. Degradation of polychlorinated biphenyls by mixed microbial cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Apr;37(4):680–685. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.4.680-685.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordle F., Corneliussen P., Jelinek C., Hackley B., Lehman R., McLaughlin J., Rhoden R., Shapiro R. Human exposure to polychorinated biphenyls and polybrominated biphenyls. Environ Health Perspect. 1978 Jun;24:157–172. doi: 10.1289/ehp.7824157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Chakrabarty A. M. Involvement of plasmids in total degradation of chlorinated biphenyls. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Sep;44(3):619–626. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.3.619-626.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Matsumura F. Microbial metabolism of polychlorinated biphenyls. Studies on the relative degradability of polychlorinated biphenyl components by Alkaligenes sp. J Agric Food Chem. 1976 Mar-Apr;24(2):251–256. doi: 10.1021/jf60204a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Tomizuka N., Kamibayashi A. Effect of chlorine substitution on the bacterial metabolism of various polychlorinated biphenyls. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):301–310. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.2.301-310.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa K., Tonomura K., Kamibayashi A. Effect of chlorine substitution on the biodegradability of polychlorinated biphenyls. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Feb;35(2):223–227. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.2.223-227.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann J., Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Metabolism of 3-chloro-, 4-chloro-, and 3,5-dichlorobenzoate by a pseudomonad. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):421–428. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.421-428.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herring J. L., Hannan E. J., Bills D. D. UV irradiation of Aroclor 1254. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1972 Sep;8(3):153–157. doi: 10.1007/BF01684470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risebrough R. W., Rieche P., Peakall D. B., Herman S. G., Kirven M. N. Polychlorinated biphenyls in the global ecosystem. Nature. 1968 Dec 14;220(5172):1098–1102. doi: 10.1038/2201098a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safe S., Hutzinger O. Polychlorinated biphenyls: photolysis of 2,4,6,2',4',6'-hexachlorobiphenyl. Nature. 1971 Aug 27;232(5313):641–642. doi: 10.1038/232641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


