Abstract
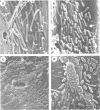
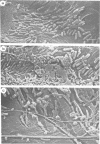
Test blocks of beech (Fagus sylvatica) and Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris) were buried in fresh, brackish, and seawater anaerobic muds for periods ranging between 1 and 18 months. At appropriate time intervals the test blocks were recovered and examined for changes in weight and for bacterial attack of lignified wood cell walls. Only small weight losses occurred. Scanning electron microscopy studies revealed that there was extensive superficial bacterial erosion of beech wood cell walls. The decay patterns are illustrated by micrographs and discussed in relation to other types of bacterial attack.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akin D. E. Evaluation by electron microscopy and anaerobic culture of types of rumen bacteria associated with digestion of forage cell walls. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jan;39(1):242–252. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.1.242-252.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akin D. E. Ultrastructure of rigid and lignified forage tissue degradation by a filamentous rumen microorganism. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):1156–1162. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.1156-1162.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antai S. P., Crawford D. L. Degradation of softwood, hardwood, and grass lignocelluloses by two streptomyces strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Aug;42(2):378–380. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.2.378-380.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Akin D. E., Costerton J. W. Rumen bacteria: interaction with particulate dietary components and response to dietary variation. Fed Proc. 1977 Feb;36(2):193–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford D. L. Lignocellulose decomposition by selected streptomyces strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jun;35(6):1041–1045. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.6.1041-1045.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinsdale D., Morris E. J., Bacon J. S. Electron microscopy of the microbial populations present and their modes of attack on various cellulosic substrates undergoing digestion in the sheep rumen. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jul;36(1):160–168. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.1.160-168.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vines H. M., Oberbacher M. F. Response of oxidation and phosphorylation in citrus mitochondria to arsenate. Nature. 1965 Apr 17;206(981):319–320. doi: 10.1038/206319b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]