Abstract
The binding of metal ions by the outer membrane of Escherichia coli K-12 strain AB264 was investigated by using outer membrane obtained after Triton X-100 extraction of purified cell envelopes. Binding studies, conducted under saturating conditions, indicated a selective trapping of certain metallic ions. Low-dose electron microscopy of metal-loaded samples revealed an aggregative deposition of lead on one surface of the membrane which suggests that at least one distinctive binding site is asymmetrically arranged in these outer membrane vesicles.
Full text
PDF
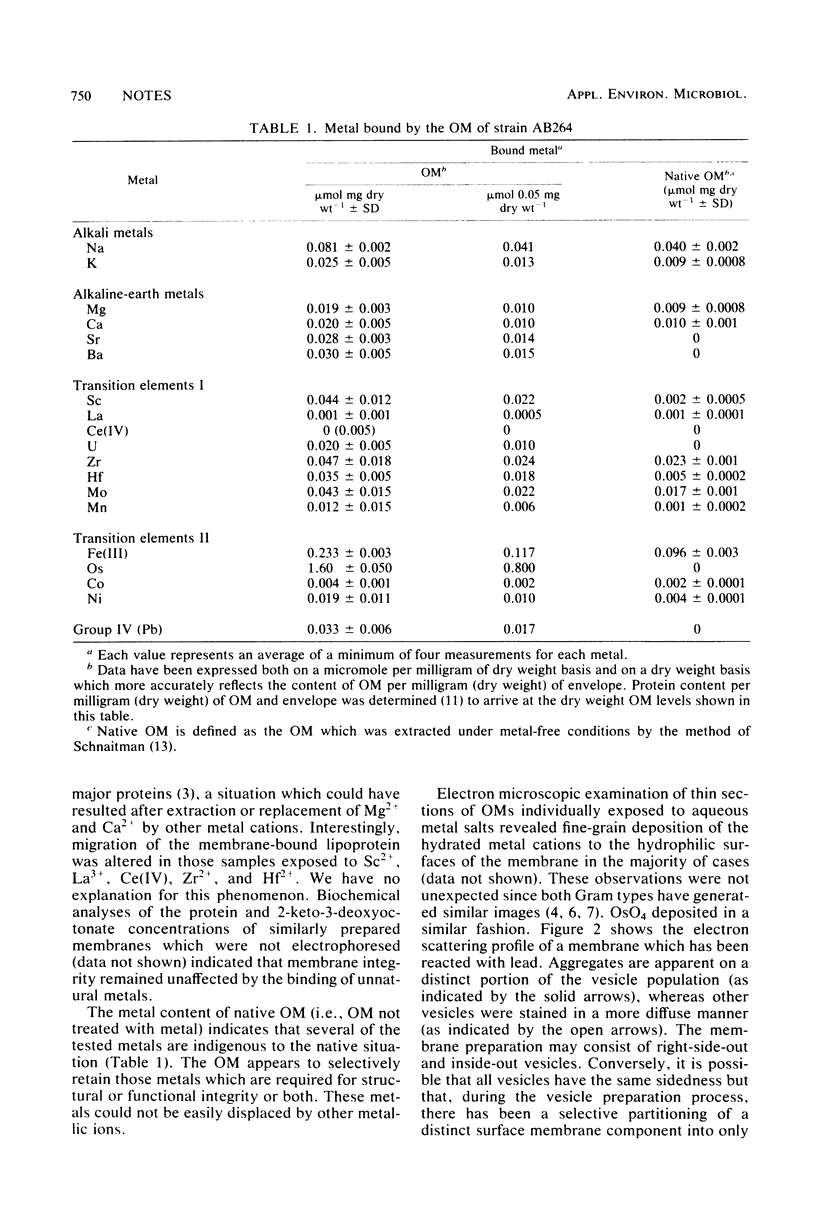
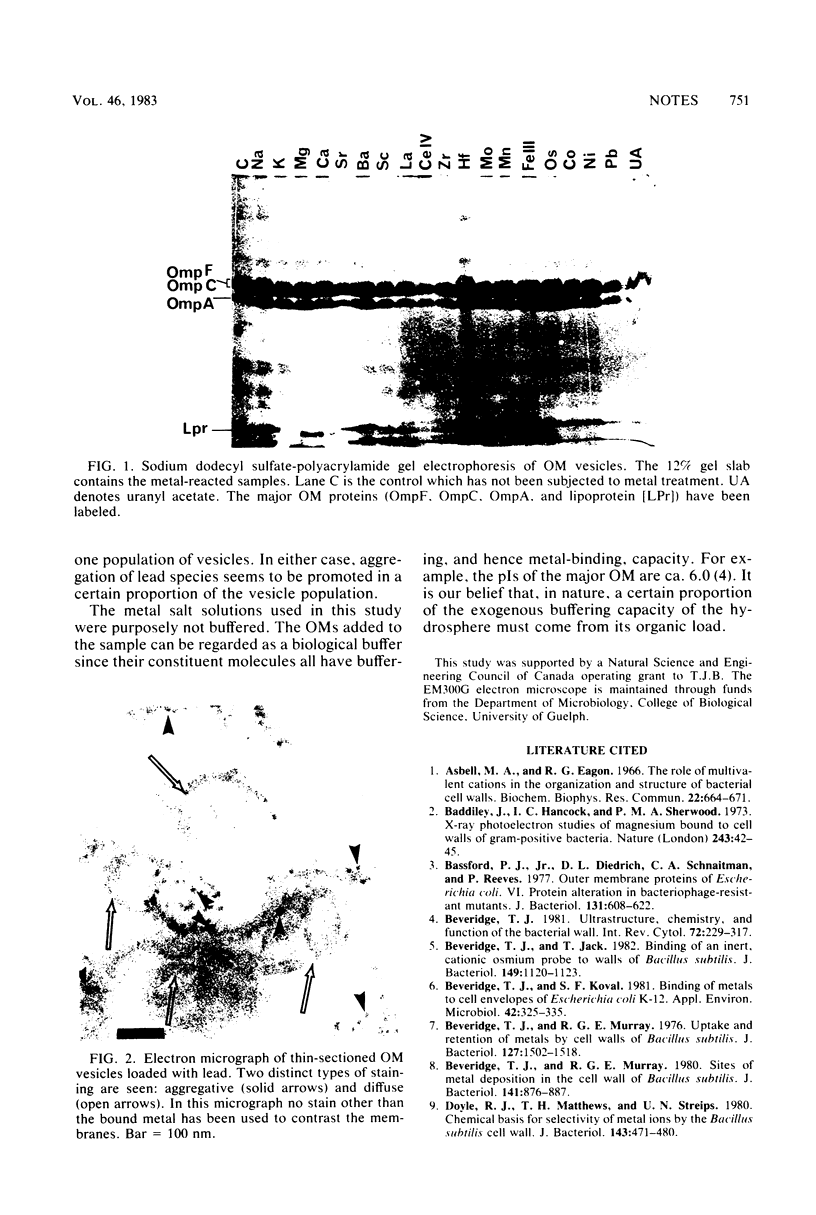

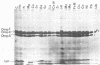
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asbell M. A., Eagon R. G. The role of multivalent cations in the organization and structure of bacterial cell walls. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Mar 22;22(6):664–671. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90198-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baddiley J., Hancock I. C., Sherwood P. M. X-ray photoelectron studies of magnesium ions bound to the cell walls of gram-positive bacteria. Nature. 1973 May 4;243(5401):43–45. doi: 10.1038/243043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bassford P. J., Jr, Diedrich D. L., Schnaitman C. L., Reeves P. Outer membrane proteins of Escherichia coli. VI. Protein alteration in bacteriophage-resistant mutants. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):608–622. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.608-622.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Jack T. Binding of an inert, cationic osmium probe to walls of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):1120–1123. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.1120-1123.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Koval S. F. Binding of metals to cell envelopes of Escherichia coli K-12. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Aug;42(2):325–335. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.2.325-335.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Murray R. G. Sites of metal deposition in the cell wall of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1980 Feb;141(2):876–887. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.2.876-887.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J., Murray R. G. Uptake and retention of metals by cell walls of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1502–1518. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1502-1518.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J. Ultrastructure, chemistry, and function of the bacterial wall. Int Rev Cytol. 1981;72:229–317. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle R. J., Matthews T. H., Streips U. N. Chemical basis for selectivity of metal ions by the Bacillus subtilis cell wall. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):471–480. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.471-480.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. A., Hancock I. C., Baddiley J. The interaction of magnesium ions with teichoic acid. Biochem J. 1975 Sep;149(3):519–524. doi: 10.1042/bj1490519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M. J., Gander J. E., Parisi E., Carson J. Mechanism of assembly of the outer membrane of Salmonella typhimurium. Isolation and characterization of cytoplasmic and outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jun 25;247(12):3962–3972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Solubilization of the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli by Triton X-100. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):545–552. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.545-552.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]