Abstract
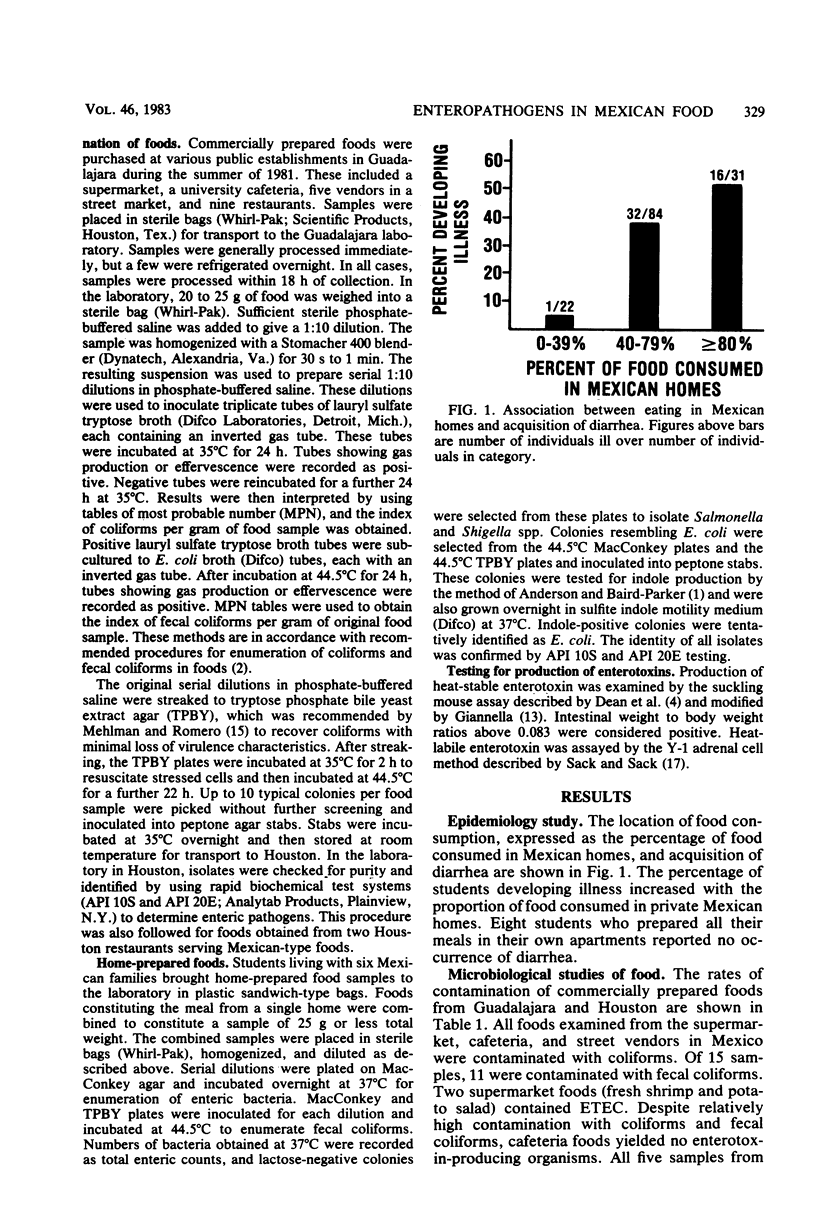
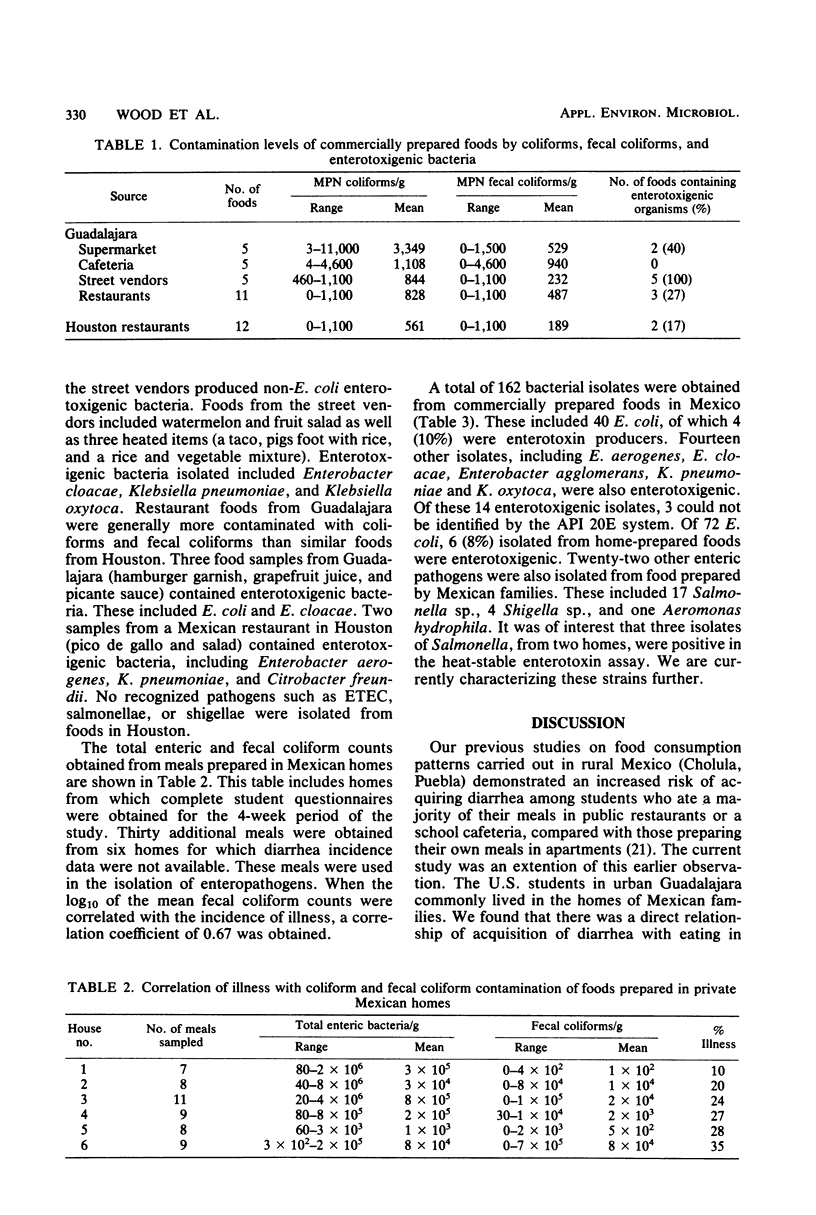
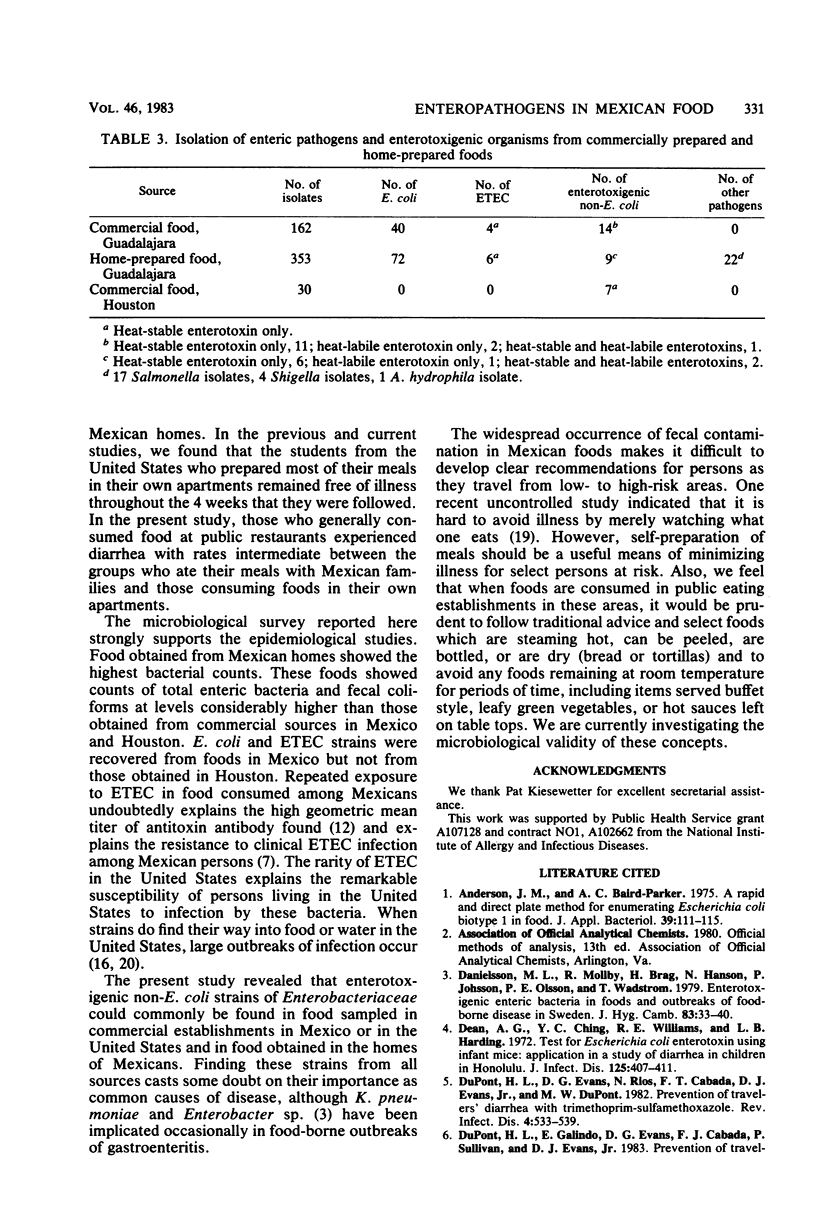
We examined food consumption patterns of U.S. students temporarily living in Guadalajara, Mexico. Consumption of foods prepared in Mexican homes was associated with an increased risk of acquisition of diarrhea. Foods from commercial sources and private Mexican homes in Guadalajara were subsequently examined for contamination with coliforms, fecal coliforms, and bacterial enteropathogens. For comparison, selected restaurant foods were obtained in Houston, Tex. Food obtained from Mexican homes showed generally higher counts of coliforms and fecal coliforms than those obtained from commercial sources in Mexico and Houston. The foods in Mexico, both from homes and commercial sources, commonly contained Escherichia coli and occasionally enterotoxigenic E. coli. Foods in Houston were not contaminated with E. coli or enterotoxigenic E. coli. Salmonella (17 isolates), Shigella (4 isolates), and Aeromonas hydrophila (1 isolate) were found only in the foods obtained from Mexican homes. Enterotoxigenic non-E. coli Enterobacteriaceae was recovered with approximately equal frequency from all food sources.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. M., Baird-Parker A. C. A rapid and direct plate method for enumerating Escherichia coli biotype I in food. J Appl Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;39(2):111–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1975.tb00551.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsson M. L., Möllby R., Brag H., Hansson N., Jonsson P., Olsson E., Wadström T. Enterotoxigenic enteric bacteria in foods and outbreaks of food-borne diseases in Sweden. J Hyg (Lond) 1979 Aug;83(1):33–40. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400025808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean A. G., Ching Y. C., Williams R. G., Harden L. B. Test for Escherichia coli enterotoxin using infant mice: application in a study of diarrhea in children in Honolulu. J Infect Dis. 1972 Apr;125(4):407–411. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.4.407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Evans D. G., Rios N., Cabada F. J., Evans D. J., Jr, DuPont M. W. Prevention of travelers' diarrhea with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Rev Infect Dis. 1982 Mar-Apr;4(2):533–539. doi: 10.1093/clinids/4.2.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Olarte J., Evans D. G., Pickering L. K., Galindo E., Evans D. J. Comparative susceptibility of latin american and united states students to enteric pathogens. N Engl J Med. 1976 Dec 30;295(27):1520–1521. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197612302952707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Reves R. R., Galindo E., Sullivan P. S., Wood L. V., Mendiola J. G. Treatment of travelers' diarrhea with trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole and with trimethoprim alone. N Engl J Med. 1982 Sep 30;307(14):841–844. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198209303071401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DuPont H. L., Sullivan P., Evans D. G., Pickering L. K., Evans D. J., Jr, Vollet J. J., Ericsson C. D., Ackerman P. B., Tjoa W. S. Prevention of traveler's diarrhea (emporiatric enteritis). Prophylactic administration of subsalicylate bismuth). JAMA. 1980 Jan 18;243(3):237–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Verhaert L., Basaca-Sevilla V., Banson T., Cross J., Orskov F., Orskov I. Search for heat-labile enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli in humans, livestock, food, and water in a community in the Philippines. J Infect Dis. 1978 Jul;138(1):87–90. doi: 10.1093/infdis/138.1.87. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ericsson C. D., Pickering L. K., Sullivan P., DuPont H. L. The role of location of food consumption in the prevention of travelers' diarrhea in Mexico. Gastroenterology. 1980 Nov;79(5 Pt 1):812–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. J., Jr, Ruiz-Palacios G., Evans D. E., DuPont H. L., Pickering L. K., Olarte J. Humoral immune response to the heat-labile enterotoxin of Escherichia coli in naturally acquired diarrhea and antitoxin determination by passive immune hemolysis. Infect Immun. 1977 Jun;16(3):781–788. doi: 10.1128/iai.16.3.781-788.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giannella R. A. Suckling mouse model for detection of heat-stable Escherichia coli enterotoxin: characteristics of the model. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):95–99. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.95-99.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiwa S. F., Krovacek K., Wadström T. Enterotoxigenic bacteria in food and water from an Ethiopian community. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Apr;41(4):1010–1019. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.4.1010-1019.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M. L., Koplan J. P., Wachsmuth I. K., Wells J. G., Gangarosa E. J., Guerrant R. L., Sack D. A. Epidemic diarrhea at Crater Lake from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. A large waterborne outbreak. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Jun;86(6):714–718. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-6-714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack D. A., Sack R. B. Test for enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli using Y-1 adrenal cells in miniculture. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):334–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.334-336.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack R. B., Sack D. A., Mehlman I. J., Orskov F., Orskov I. Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated from food. J Infect Dis. 1977 Feb;135(2):313–317. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.2.313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen R., van der Linde F., Gyr K., Schär M. Epidemiology of diarrhea in travelers. JAMA. 1983 Mar 4;249(9):1176–1180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. R., Schell W. L., Wells J. G., Choi K., Kinnunen D. E., Heiser P. T., Helstad A. G. A foodborne outbreak of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli diarrhea. N Engl J Med. 1982 May 6;306(18):1093–1095. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198205063061807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjoa W. S., DuPont H. L., Sullivan P., Pickering L. K., Holguin A. H., Olarte J., Evans D. G., Evans D. J., Jr Location of food consumption and travelers' diarrhea. Am J Epidemiol. 1977 Jul;106(1):61–66. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



