Abstract
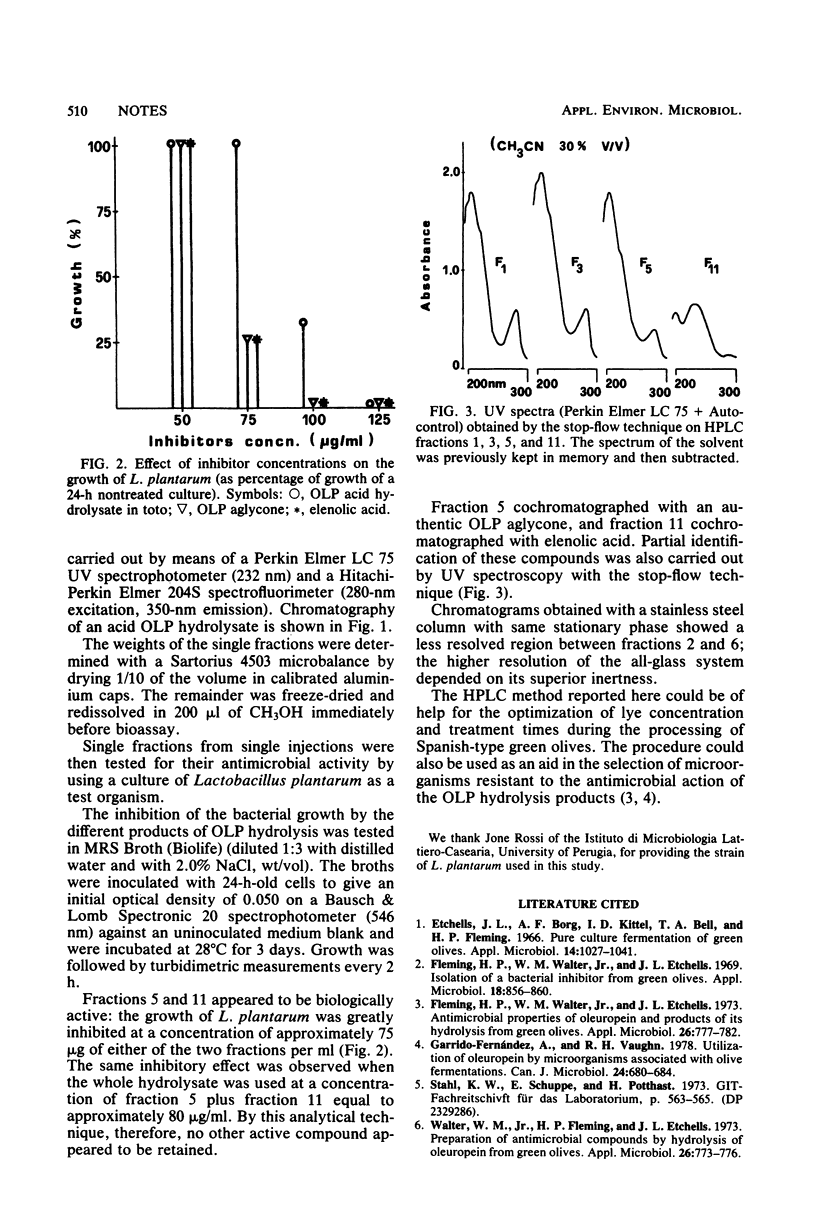
A new high-pressure liquid chromatography multidetection quantitative method for the isolation of the products of oleuropein hydrolysis is described. A single analysis yields sufficient amounts of the compounds to test their inhibitory effect on bacterial growth.
Full text
PDF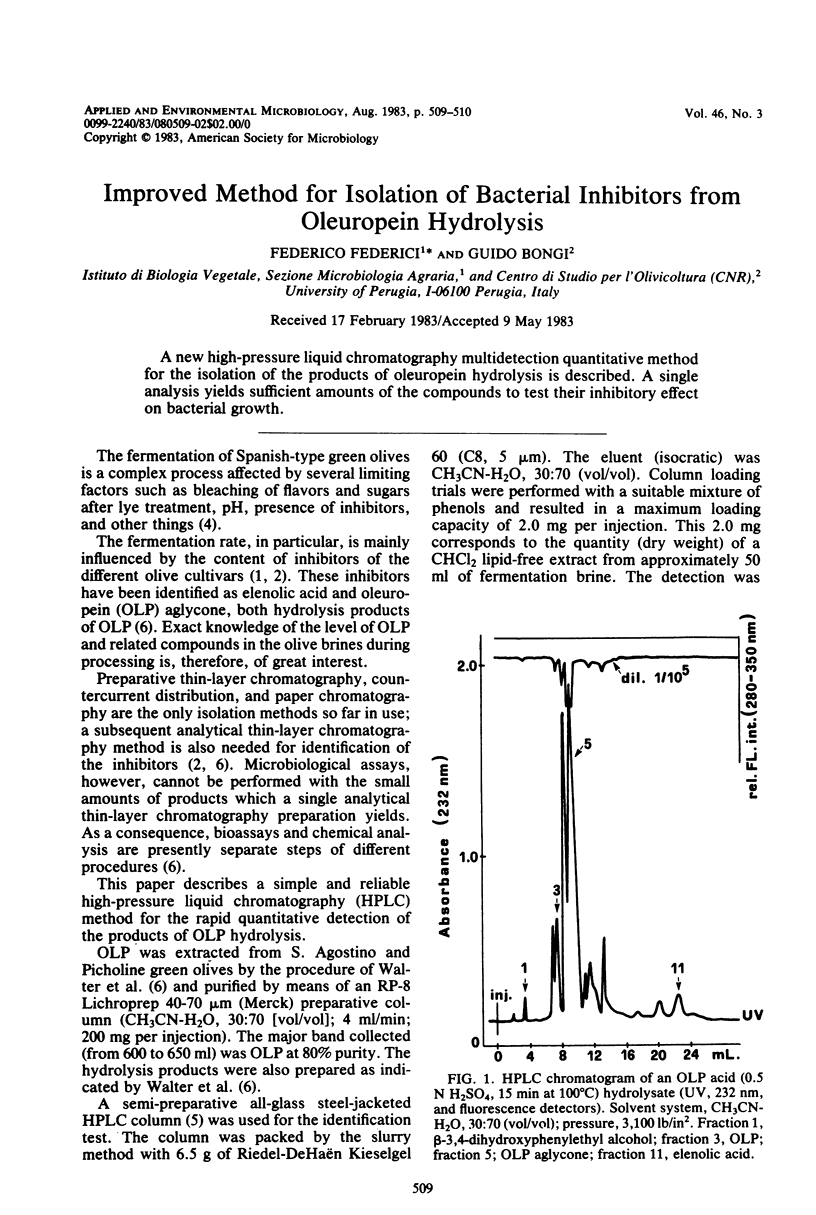
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Etchells J. L., Borg A. F., Kittel I. D., Bell T. A., Fleming H. P. Pure culture fermentation of green olives. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Nov;14(6):1027–1041. doi: 10.1128/am.14.6.1027-1041.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming H. P., Walter W. M., Etchells J. L. Isolation of a bacterial inhibitor from green olives. Appl Microbiol. 1969 Nov;18(5):856–860. doi: 10.1128/am.18.5.856-860.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleming H. P., Walter W. M., Jr, Etchells J. L. Antimicrobial properties of oleuropein and products of its hydrolysis from green olives. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Nov;26(5):777–782. doi: 10.1128/am.26.5.777-782.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrido-Fernandez A., Vaughn R. H. Utilization of oleuropein by microorganisms associated with olive fermentations. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Jun;24(6):680–684. doi: 10.1139/m78-114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter W. M., Jr, Fleming H. P., Etchells J. L. Preparation of antimicrobial compounds by hydrolysis of oleuropein from green olives. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Nov;26(5):773–776. doi: 10.1128/am.26.5.773-776.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


