Abstract
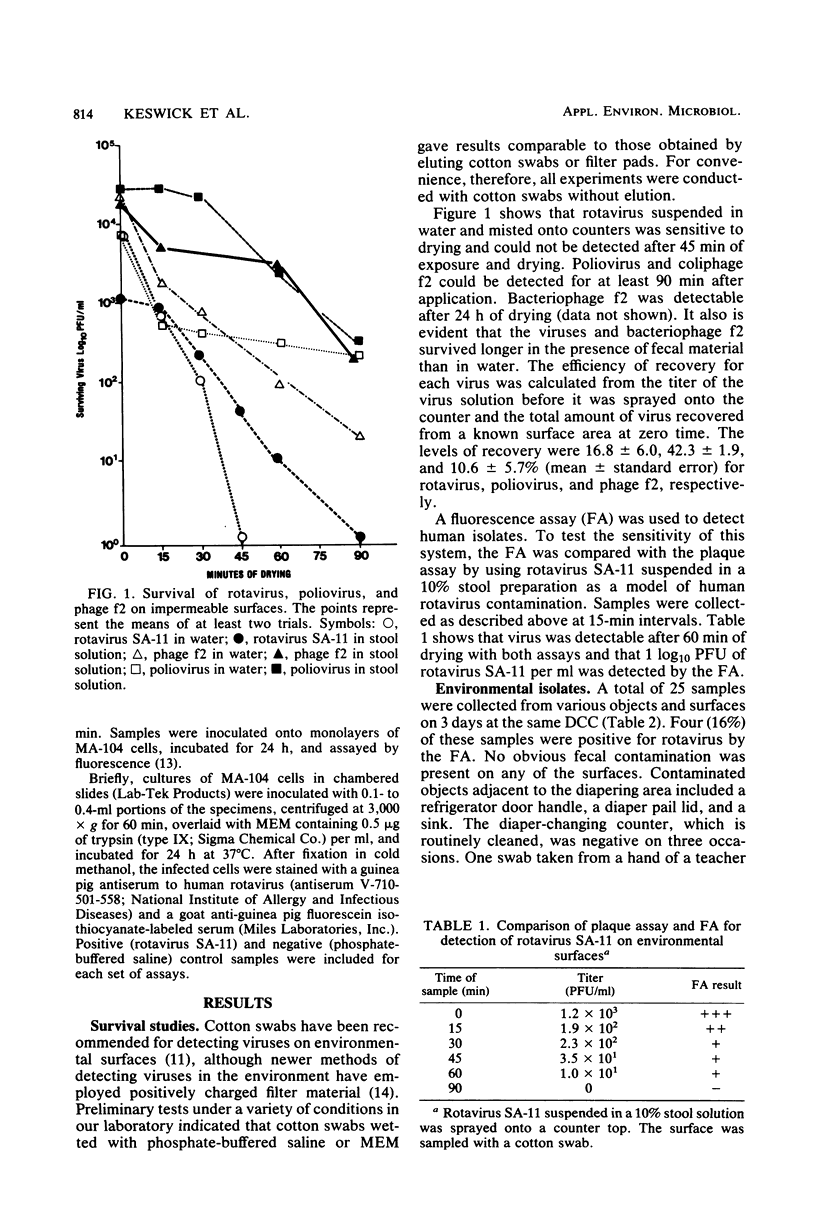
Previously, we demonstrated that children in day care centers commonly experience diarrhea due to rotavirus, giardia, and bacterial pathogens. Multiple agents frequently coexist, and the environment is heavily contaminated with enteric bacteria during outbreaks. A study of environmental surface contamination with rotavirus was performed during three non-outbreak periods. Of 25 samples collected from environmental surfaces and teachers hands at a day care center, 4 (16%) were positive for rotavirus antigen when a fluorescence assay was used. We also examined the survival of two animal viruses, rotavirus SA-11 and poliovirus type 1, and bacteriophage 12 on similar environmental surfaces in a laboratory. Poliovirus type 1 and bacteriophage f2 were more resistant to drying than rotavirus SA-11 and could be recovered after a 90-min exposure on a dry surface. Rotavirus SA-11 could be detected for 30 min. All three viruses survived longer when they were suspended in fecal material than when they were suspended in distilled water. These data suggest that several agents, including rotavirus, can remain viable on contaminated surfaces long enough to be transmitted to susceptible children. This finding helps explain why rotavirus shows a mode of spread like that of parasitic and bacterial agents within day care center settings.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Black R. E., Dykes A. C., Anderson K. E., Wells J. G., Sinclair S. P., Gary G. W., Jr, Hatch M. H., Gangarosa E. J. Handwashing to prevent diarrhea in day-care centers. Am J Epidemiol. 1981 Apr;113(4):445–451. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goyal S. M., Gerba C. P. Comparative adsorption of human enteroviruses, simian rotavirus, and selected bacteriophages to soils. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):241–247. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.2.241-247.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwaltney J. M., Jr, Hendley J. O. Transmission of experimental rhinovirus infection by contaminated surfaces. Am J Epidemiol. 1982 Nov;116(5):828–833. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a113473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hejkal T. W., Wellings F. M., LaRock P. A., Lewis A. L. Survival of poliovirus within organic solids during chlorination. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jul;38(1):114–118. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.1.114-118.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes I. H. Viral gastroenteritis. Prog Med Virol. 1979;25:1–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lecce J. G., King M. W., Dorsey W. E. Rearing regimen producing piglet diarrhea (rotavirus) and its relevance to acute infantile diarrhea. Science. 1978 Feb 17;199(4330):776–778. doi: 10.1126/science.203032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melnick J. L., Rennick V. Infectivity titers of enterovirus as found in human stools. J Med Virol. 1980;5(3):205–220. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890050305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minor T. E., Allen C. I., Tsiatis A. A., Nelson D. B., D'Alessio D. J. Human infective dose determinations for oral poliovirus type 1 vaccine in infants. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Feb;13(2):388–389. doi: 10.1128/jcm.13.2.388-389.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moe K., Shirley J. A. The effects of relative humidity and temperature on the survival of human rotavirus in faeces. Arch Virol. 1982;72(3):179–186. doi: 10.1007/BF01348963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PHILLIPS C. A., GRIM C. A. COMPARISON OF THE ELUTION AND ADSORPTION OF PICORNAVIRUSES BY COTTON AND CALCIUM ALGINATE WOOL SWABS. Appl Microbiol. 1965 May;13:457–459. doi: 10.1128/am.13.3.457-459.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickering L. K., Woodward W. E. Diarrhea in day care centers. Pediatr Infect Dis. 1982 Jan-Feb;1(1):47–52. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198201000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith E. M., Gerba C. P. Development of a method for detection of human rotavirus in water and sewage. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1440–1450. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1440-1450.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobsey M. D., Glass J. S. Poliovirus concentration from tap water with electropositive adsorbent filters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Aug;40(2):201–210. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.2.201-210.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zavate O., Cotor F., Ivan A., Tiron S., Avram G. Investigations on the circulation of enteroviruses in a children community. Virologie. 1980 Oct-Dec;31(4):289–293. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



