Abstract
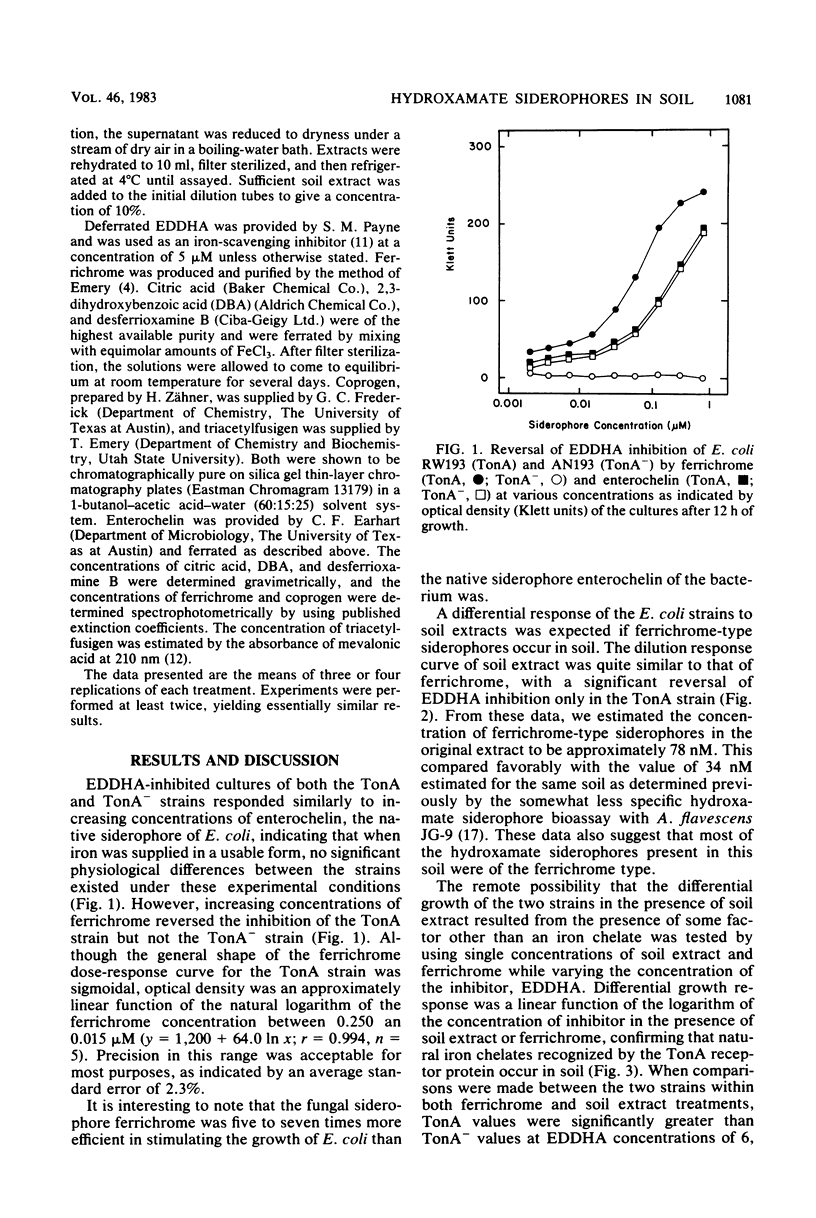
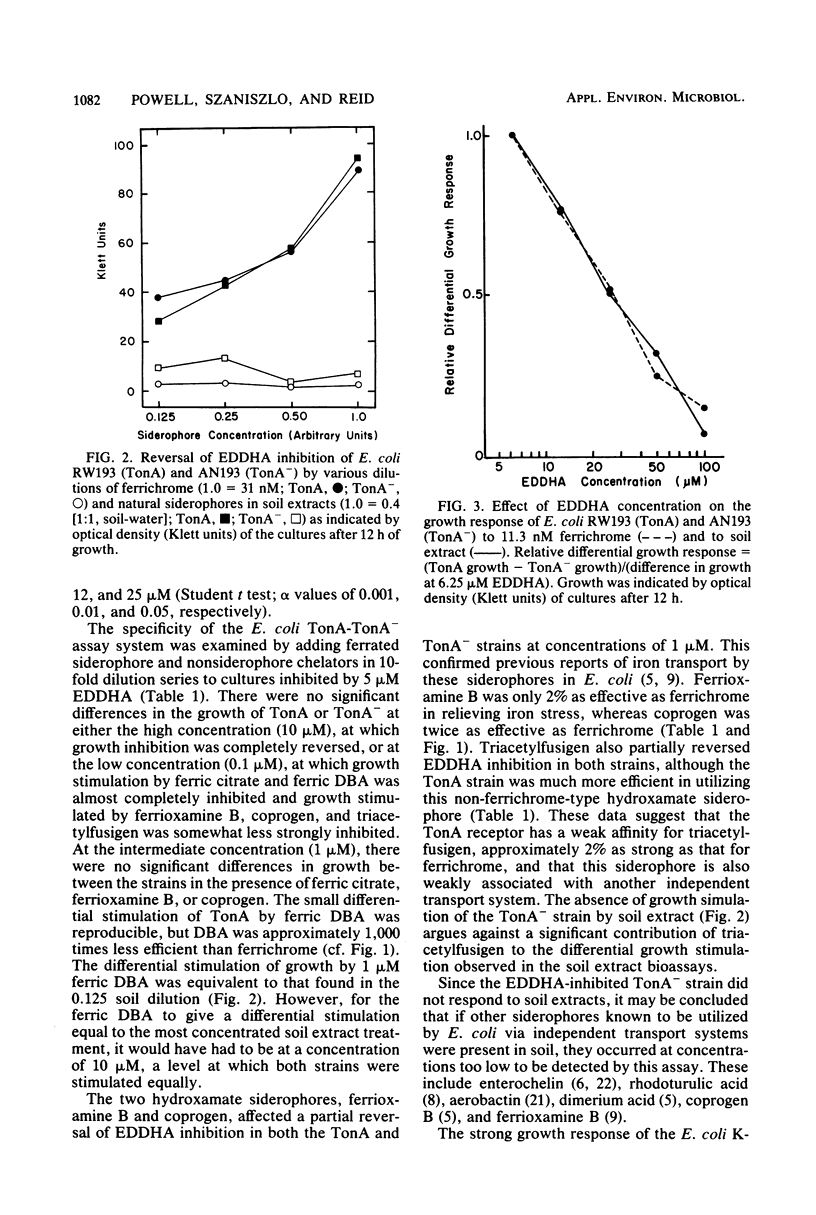
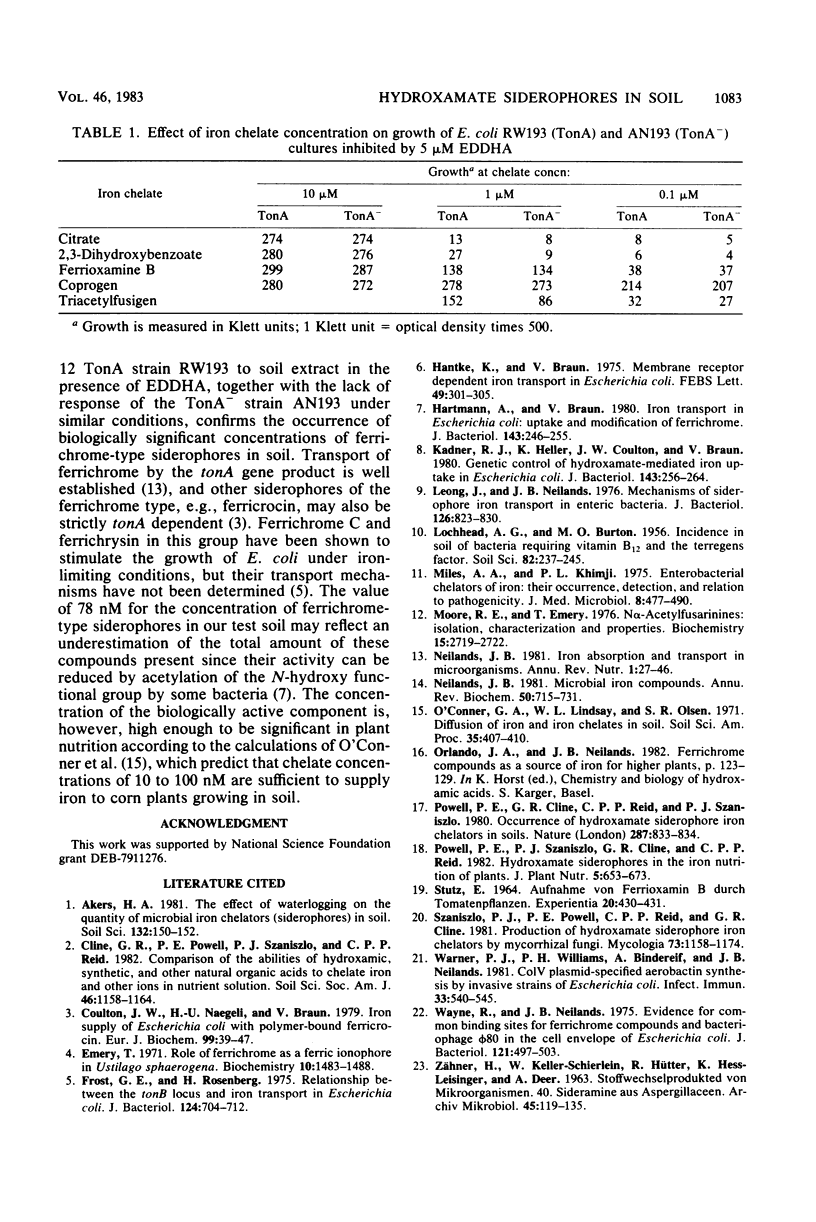
The occurrence of ferrichrome-type hydroxamate siderophores in soil was confirmed. In the presence of the iron-scavenging chelator ethylenediamine[di(o-hydroxyphenylacetic)acid], soil extract stimulated the growth of an Escherichia coli strain possessing the ferrichrome transport protein (TonA) but did not stimulate growth of a strain lacking this protein (TonA−). The siderophore concentration in a 1:1 (soil-water) extract was estimated to be approximately 78 nM. Specificity of the assay was supported by the absence of significant differential strain responses to ferric citrate, ferric 2,3-dihydroxybenzoate, enterochelin, ferrioxamine B, coprogen, and triacetylfusigen.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Coulton J. W., Naegeli H. U., Braun V. Iron supply of Escherichia coli with polymer-bound ferricrocin. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Aug 15;99(1):39–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13228.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emery T. Role of ferrichrome as a ferric ionophore in Ustilago sphaerogena. Biochemistry. 1971 Apr 13;10(8):1483–1488. doi: 10.1021/bi00784a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost G. E., Rosenberg H. Relationship between the tonB locus and iron transport in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):704–712. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.704-712.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hantke K., Braun V. Membrane receptor dependent iron transport in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jan 1;49(3):301–305. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80771-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann A., Braun V. Iron transport in Escherichia coli: uptake and modification of ferrichrome. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):246–255. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.246-255.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadner R. J., Heller K., Coulton J. W., Braun V. Genetic control of hydroxamate-mediated iron uptake in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):256–264. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.256-264.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong J., Neilands J. B. Mechanisms of siderophore iron transport in enteric bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):823–830. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.823-830.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles A. A., Khimji P. L. Enterobacterial chelators of iron: their occurrence, detection, and relation to pathogenicity. J Med Microbiol. 1975 Nov;8(4):477–490. doi: 10.1099/00222615-8-4-477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore R. E., Emery T. Nalpha-acetylfusarinines: isolation, characterization, and properties. Biochemistry. 1976 Jun 29;15(13):2719–2723. doi: 10.1021/bi00658a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Iron absorption and transport in microorganisms. Annu Rev Nutr. 1981;1:27–46. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nu.01.070181.000331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neilands J. B. Microbial iron compounds. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:715–731. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stutz E. Aufnahme von Ferrioxamin B durch Tomatenpflanzen. Experientia. 1964 Aug 15;20(8):430–431. doi: 10.1007/BF02152129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner P. J., Williams P. H., Bindereif A., Neilands J. B. ColV plasmid-specific aerobactin synthesis by invasive strains of Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1981 Aug;33(2):540–545. doi: 10.1128/iai.33.2.540-545.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayne R., Neilands J. B. Evidence for common binding sites for ferrichrome compounds and bacteriophage phi 80 in the cell envelope of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):497–503. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.497-503.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


