Abstract
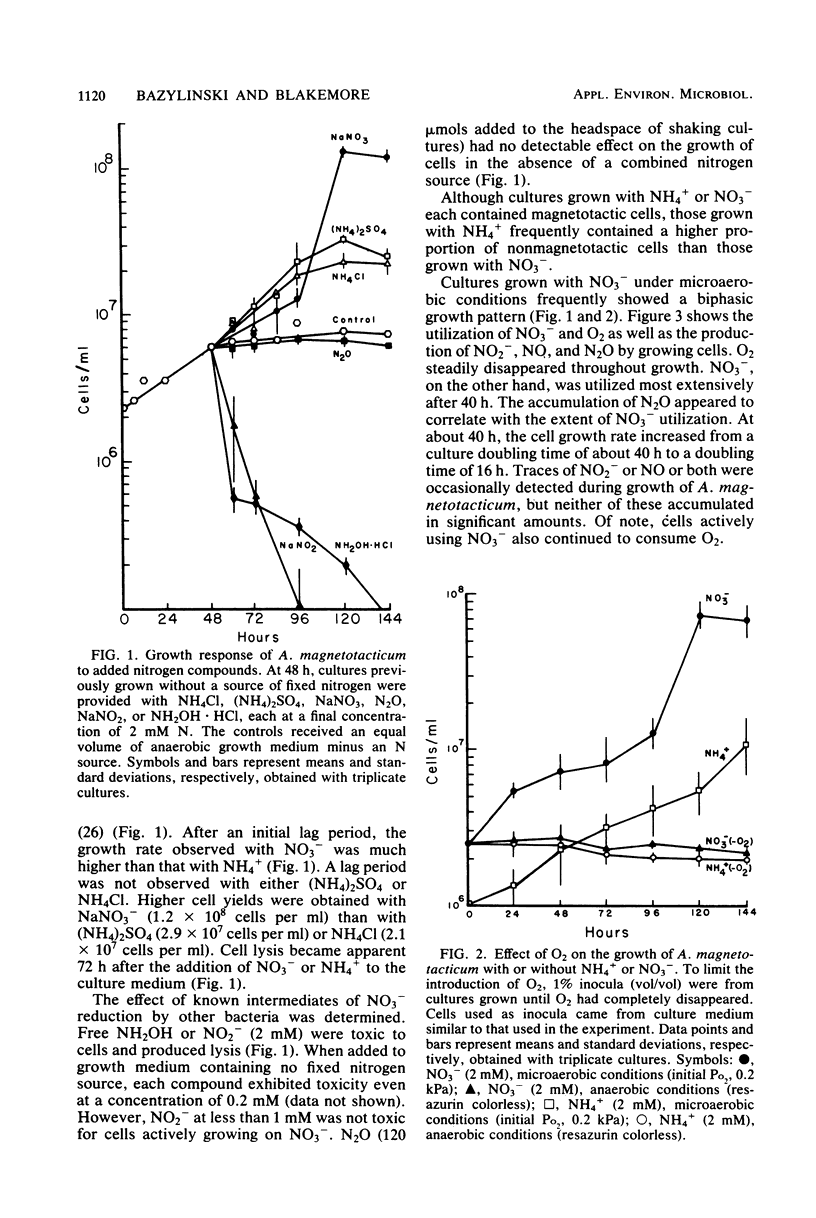
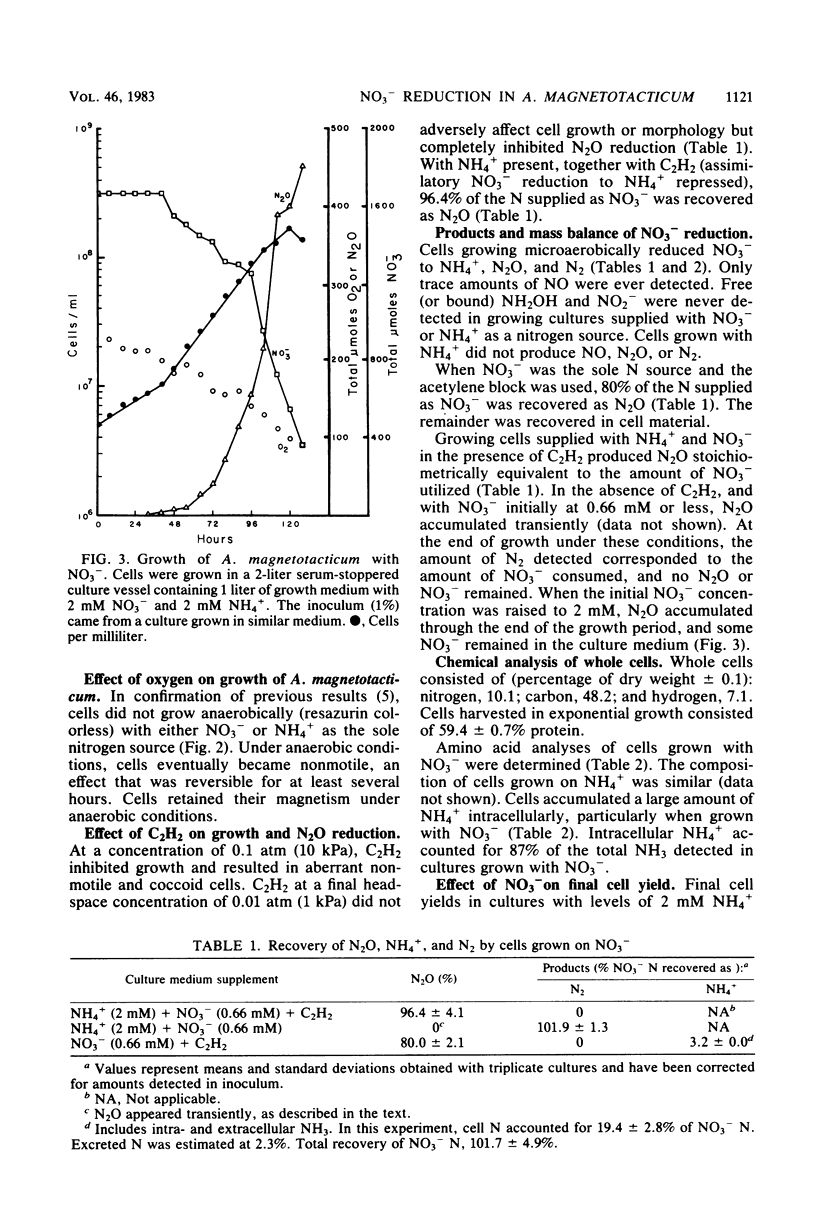
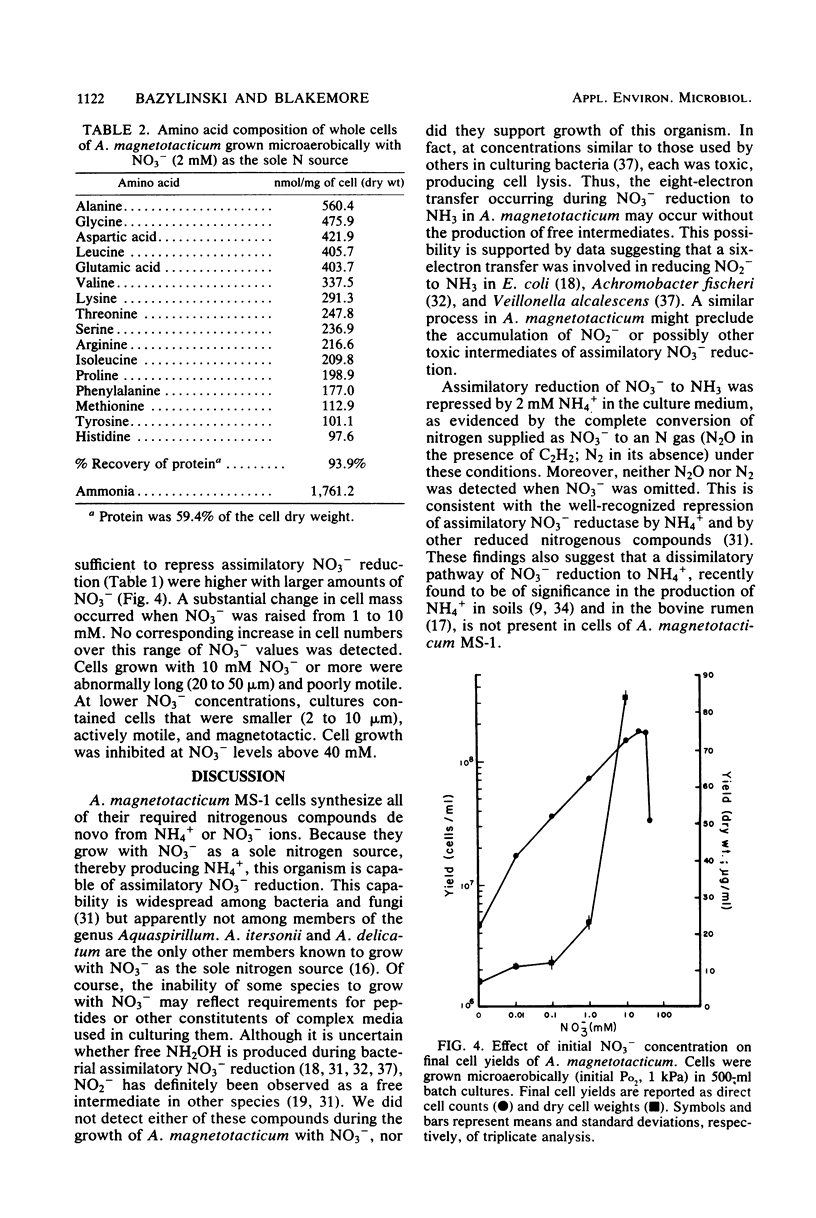
Aquaspirillum magnetotacticum MS-1 grew microaerobically but not anaerobically with NO3− or NH4+ as the sole nitrogen source. Nevertheless, cell yields varied directly with NO3− concentration under microaerobic conditions. Products of NO3− reduction included NH4+, N2O, NO, and N2. NO2− and NH2OH, each toxic to cells at 0.2 mM, were not detected as products of cells growing on NO3−. NO3− reduction to NH4+ was completely repressed by the addition of 2 mM NH4+ to the growth medium, whereas NO3− reduction to N2O or to N2 was not. C2H2 completely inhibited N2O reduction to N2 by growing cells. These results indicate that A. magnetotacticum is a microaerophilic denitrifier that is versatile in its nitrogen metabolism, concomitantly reducing NO3− by assimilatory and dissimilatory means. This bacterium appears to be the first described denitrifier with an absolute requirement for O2. The process of NO3− reduction appears well adapted for avoiding accumulation of several nitrogenous intermediates that are toxic to cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balch W. E., Wolfe R. S. New approach to the cultivation of methanogenic bacteria: 2-mercaptoethanesulfonic acid (HS-CoM)-dependent growth of Methanobacterium ruminantium in a pressureized atmosphere. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Dec;32(6):781–791. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.6.781-791.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balkwill D. L., Maratea D., Blakemore R. P. Ultrastructure of a magnetotactic spirillum. J Bacteriol. 1980 Mar;141(3):1399–1408. doi: 10.1128/jb.141.3.1399-1408.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakemore R. P., Maratea D., Wolfe R. S. Isolation and pure culture of a freshwater magnetic spirillum in chemically defined medium. J Bacteriol. 1979 Nov;140(2):720–729. doi: 10.1128/jb.140.2.720-729.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blakemore R. Magnetotactic bacteria. Science. 1975 Oct 24;190(4212):377–379. doi: 10.1126/science.170679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleakley B. H., Tiedje J. M. Nitrous oxide production by organisms other than nitrifiers or denitrifiers. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Dec;44(6):1342–1348. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.6.1342-1348.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Escalante-Semerena J. C., Blakemore R. P., Wolfe R. S. Nitrate dissimilation under microaerophilic conditions by a magnetic spirillum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Aug;40(2):429–430. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.2.429-430.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fedorova R. I., Milekhina E. I., Il'iukhina N. I. O vozmozhnosti metoda "gazoobmena" dlia obnaruzheniia zhizni vne zemli--identifikatsiia azotfiksiruiushchikh mikroorganizmov. Izv Akad Nauk SSSR Biol. 1973 Nov-Dec;6:797–806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel R. B., Blakemore R. P., Wolfe R. S. Magnetite in freshwater magnetotactic bacteria. Science. 1979 Mar 30;203(4387):1355–1356. doi: 10.1126/science.203.4387.1355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier D. K., Clark-Walker G. D., Garrard W. T., Jr, Lascelles J. Nitrate reductase and soluble cytochrome c in Spirillum itersonii. J Bacteriol. 1970 Jun;102(3):790–801. doi: 10.1128/jb.102.3.797-803.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaspar H. F., Tiedje J. M. Dissimilatory reduction of nitrate and nitrite in the bovine rumen: nitrous oxide production and effect of acetylene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Mar;41(3):705–709. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.3.705-709.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp J. D., Atkinson D. E. Nitrite reductase of Escherichia coli specific for reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. J Bacteriol. 1966 Sep;92(3):628–634. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.3.628-634.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg N. R. Biology of the chemoheterotrophic spirilla. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Mar;40(1):55–115. doi: 10.1128/br.40.1.55-115.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg N. R., Hylemon P. B. The taxonomy of the chemoheterotrophic spirilla. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1976;30:303–325. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.30.100176.001511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstam H. A. Minerals formed by organisms. Science. 1981 Mar 13;211(4487):1126–1131. doi: 10.1126/science.7008198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moench T. T., Konetzka W. A. A novel method for the isolation and study of a magnetotactic bacterium. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Nov 13;119(2):203–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00964274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottow J. C. Mechanism of iron-reduction by nitrate reductase inducible aerobic microorganisms. Naturwissenschaften. 1969 Jul;56(7):371–371. doi: 10.1007/BF00596937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottow J. C. Selection, characterization and iron-reducing capacity of nitrate reductaseless (nit-) mutants of iron-reducing bacteria. Z Allg Mikrobiol. 1970;10(1):55–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne W. J. Reduction of nitrogenous oxides by microorganisms. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Dec;37(4):409–452. doi: 10.1128/br.37.4.409-452.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash O. M., Sadana J. C. Purification, characterization and properties of nitrite reductase of Achromobacter fischeri. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Feb;148(2):614–632. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90181-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. S. Dissimilatory Reduction of NO(2) to NH(4) and N(2)O by a Soil Citrobacter sp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Apr;43(4):854–860. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.4.854-860.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen J. Reduction of ferric iron in anaerobic, marine sediment and interaction with reduction of nitrate and sulfate. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Feb;43(2):319–324. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.2.319-324.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOLIN E. A., WOLIN M. J., WOLFE R. S. FORMATION OF METHANE BY BACTERIAL EXTRACTS. J Biol Chem. 1963 Aug;238:2882–2886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yordy D. M., Delwiche E. A. Nitrite reduction in Veillonella alcalescens. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):905–911. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.905-911.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


