Abstract
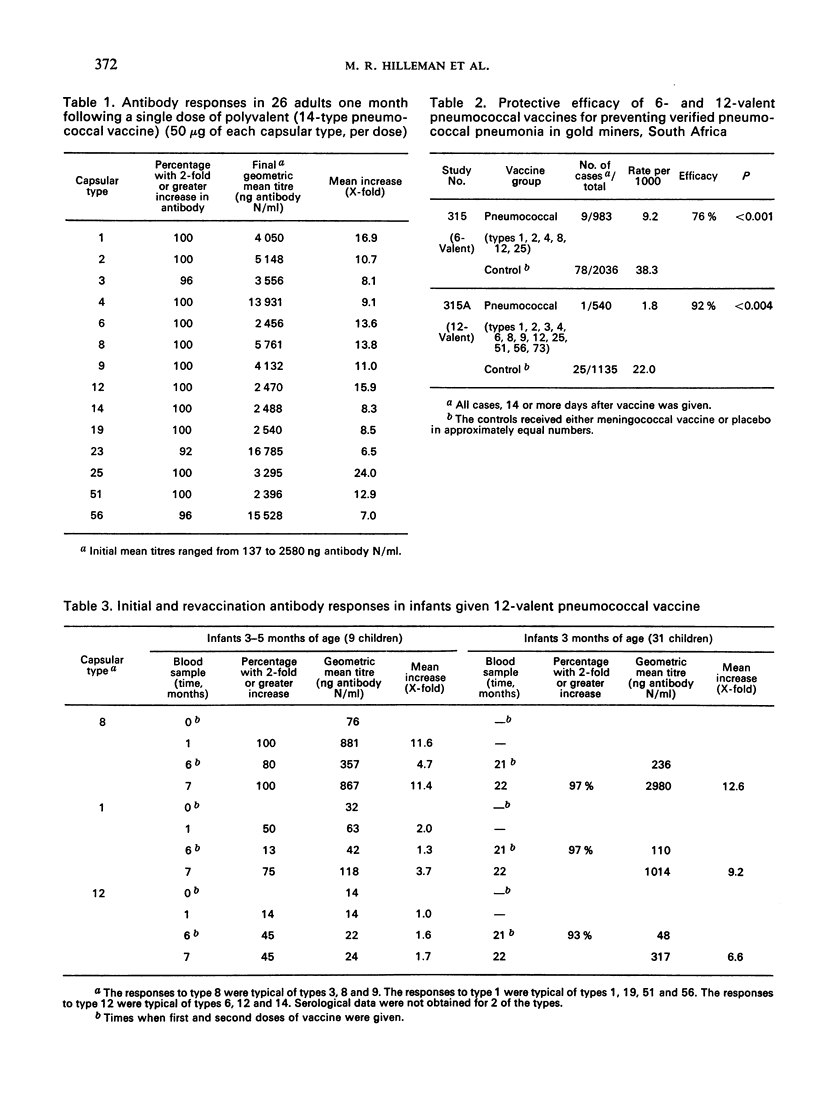
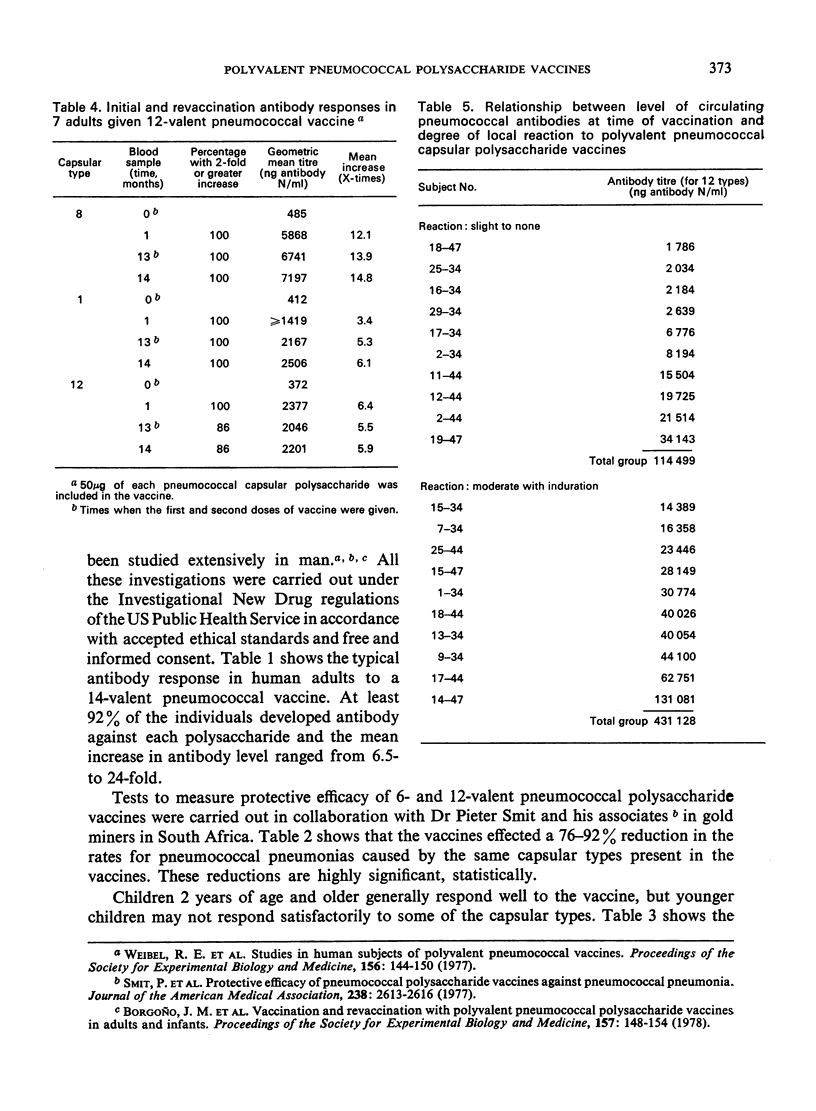
A 14-valent pneumococcal vaccine has recently been licensed for general use after extensive testing in human subjects. Antibody production was satisfactory in 92% of individuals and a highly significant (76-92%) reduction was found in the rates for pneumococcal pneumonias caused by the capsular types present in the vaccine. Children over 2 years of age respond well to the vaccine, but younger children may not respond satisfactorily to some capsular types. In adults, the duration of the protective effect is at present unknown, but no substantial booster response was seen after a second dose at 1 year. Such a booster dose, in fact, induced a marked increase in the degree of local reaction at the injection site.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austrian R., Douglas R. M., Schiffman G., Coetzee A. M., Koornhof H. J., Hayden-Smith S., Reid R. D. Prevention of pneumococcal pneumonia by vaccination. Trans Assoc Am Physicians. 1976;89:184–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit P., Oberholzer D., Hayden-Smith S., Koornhof H. J., Hilleman M. R. Protective efficacy of pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccines. JAMA. 1977 Dec 12;238(24):2613–2616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weibel R. E., Vella P. P., McLean A. A., Woodhour A. F., Davidson W. L., Hilleman M. R. Studies in human subjects of polyvalent pneumococcal vaccines (39894). Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1977 Oct;156(1):144–150. doi: 10.3181/00379727-156-39894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



