Abstract
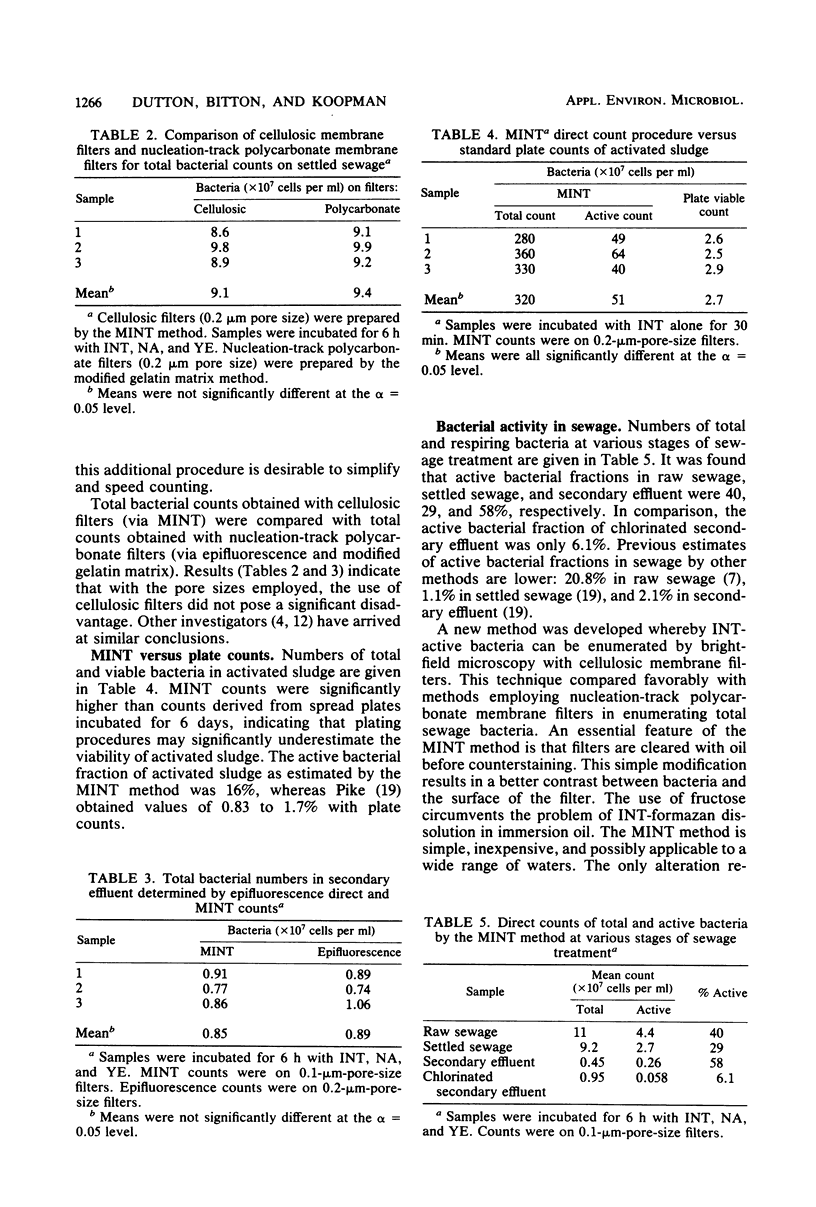
A membrane filtration method was developed to determine the proportion of active (respiring) bacteria at various stages of sewage treatment. Samples were incubated in the presence of 2-(p-iodophenyl)-3-(p-nitrophenyl)-5-phenyl tetrazolium chloride (INT) and, after fixation, passed through membrane filters. Filters were counterstained with malachite green and then were examined by bright-field microscopy. The contrast between bacteria and the filter background was greatly improved by drying and then clearing the filter before counterstaining. By this method, it was found that active bacterial fractions in raw sewage, settled sewage, and secondary effluent were 40, 29, and 58%, respectively, whereas the proportion of respiring bacteria in chlorinated secondary effluent was 6.1%. The active bacterial fraction of activated sludge was found to be 16%. The proposed method represents a significant improvement in speed and simplicity over existing methods for determining active bacteria in sewage.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bitton G., Koopman B. Tetrazolium reduction-malachite green method for assessing the viability of filamentous bacteria in activated sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Apr;43(4):964–966. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.4.964-966.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowden W. B. Comparison of two direct-count techniques for enumerating aquatic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1229–1232. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1229-1232.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bright J. J., Fletcher M. Amino Acid assimilation and electron transport system activity in attached and free-living marine bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):818–825. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.818-825.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbie J. E., Daley R. J., Jasper S. Use of nuclepore filters for counting bacteria by fluorescence microscopy. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1225–1228. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1225-1228.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horobin R. W. Structure-staining relationships in histochemistry and biological staining. I. Theoretical background and a general account of correlation of histochemical staining with the chemical structure of the reagents used. J Microsc. 1980 Aug;119(3):345–355. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1980.tb04106.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchman D., Sigda J., Kapuscinski R., Mitchell R. Statistical analysis of the direct count method for enumerating bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Aug;44(2):376–382. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.2.376-382.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogure K., Simidu U., Taga N. A tentative direct microscopic method for counting living marine bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Mar;25(3):415–420. doi: 10.1139/m79-063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maki J. S., Remsen C. C. Comparison of two direct-count methods for determining metabolizing bacteria in freshwater. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 May;41(5):1132–1138. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.5.1132-1138.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer-Reil L. A. Autoradiography and epifluorescence microscopy combined for the determination of number and spectrum of actively metabolizing bacteria in natural water. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Sep;36(3):506–512. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.3.506-512.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike E. B., Carrington E. G., Ashburner P. A. An evaluation of procedures for enumerating bacteria in activated sludge. J Appl Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;35(2):309–321. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1972.tb03703.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor P. S., Neihof R. A. Improved method for determination of respiring individual microorganisms in natural waters. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1249–1255. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1249-1255.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann R., Iturriaga R., Becker-Birck J. Simultaneous determination of the total number of aquatic bacteria and the number thereof involved in respiration. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Dec;36(6):926–935. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.6.926-935.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



