Abstract
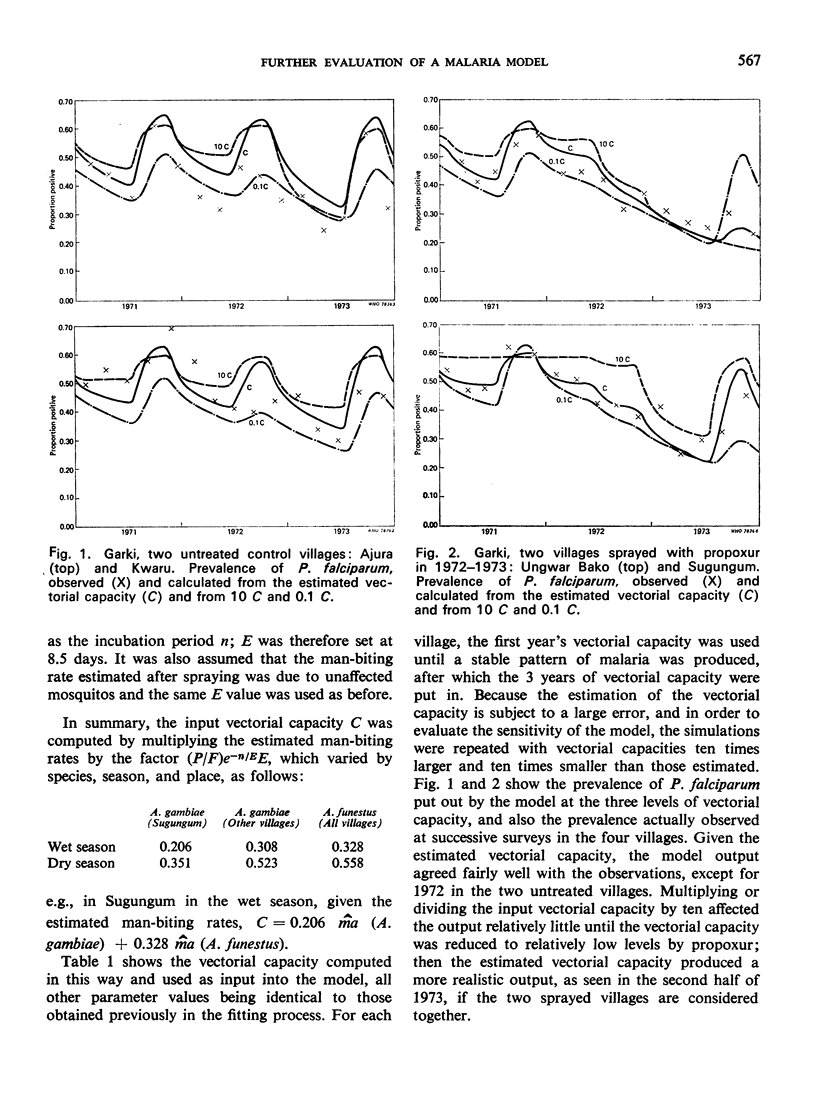
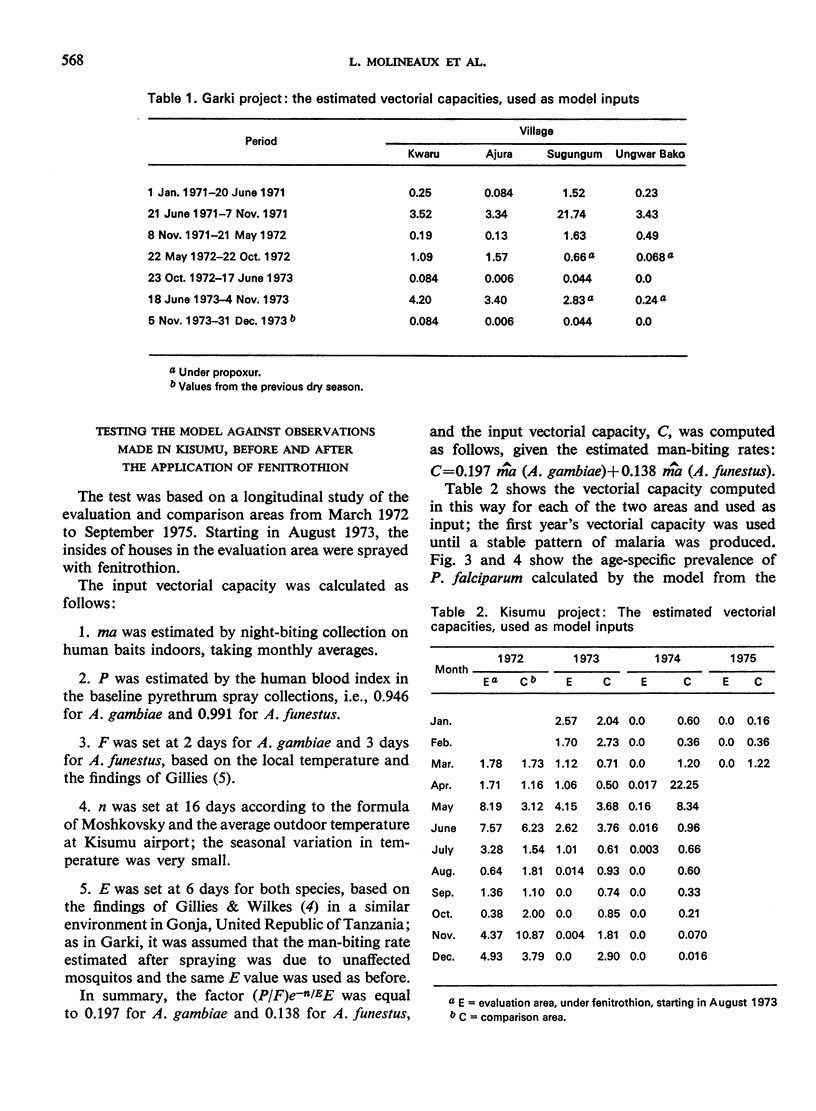
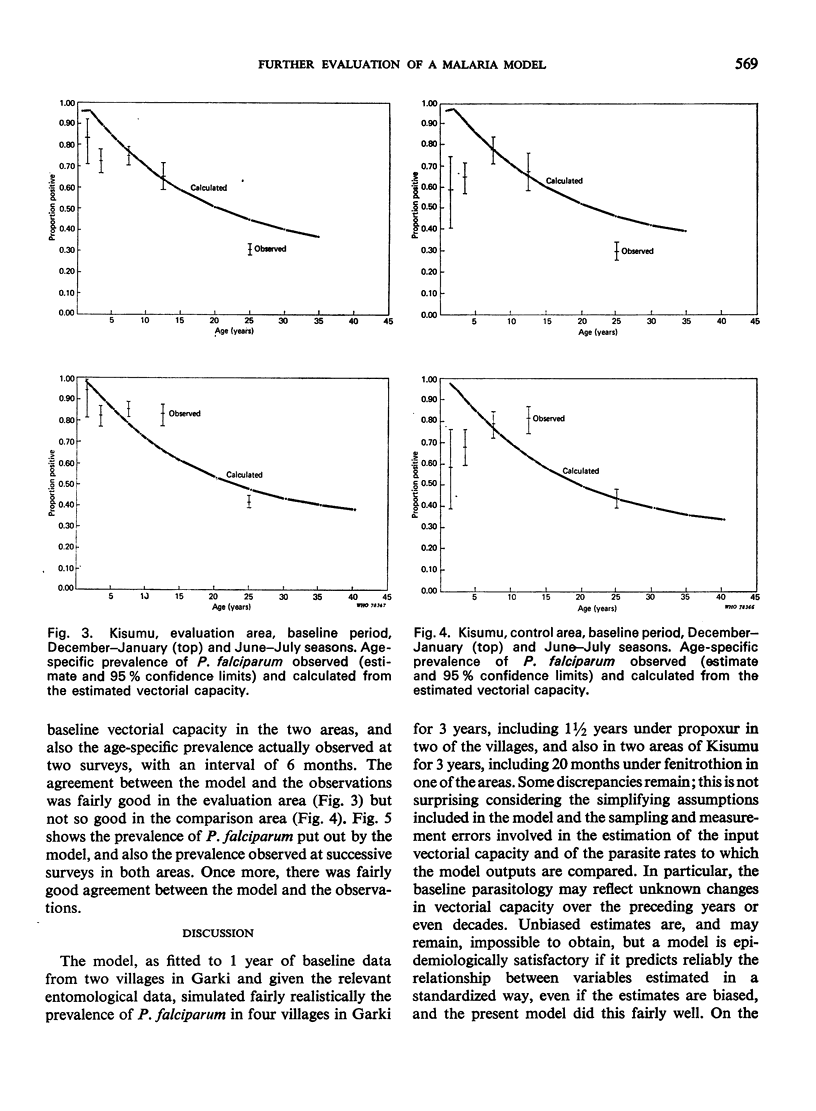
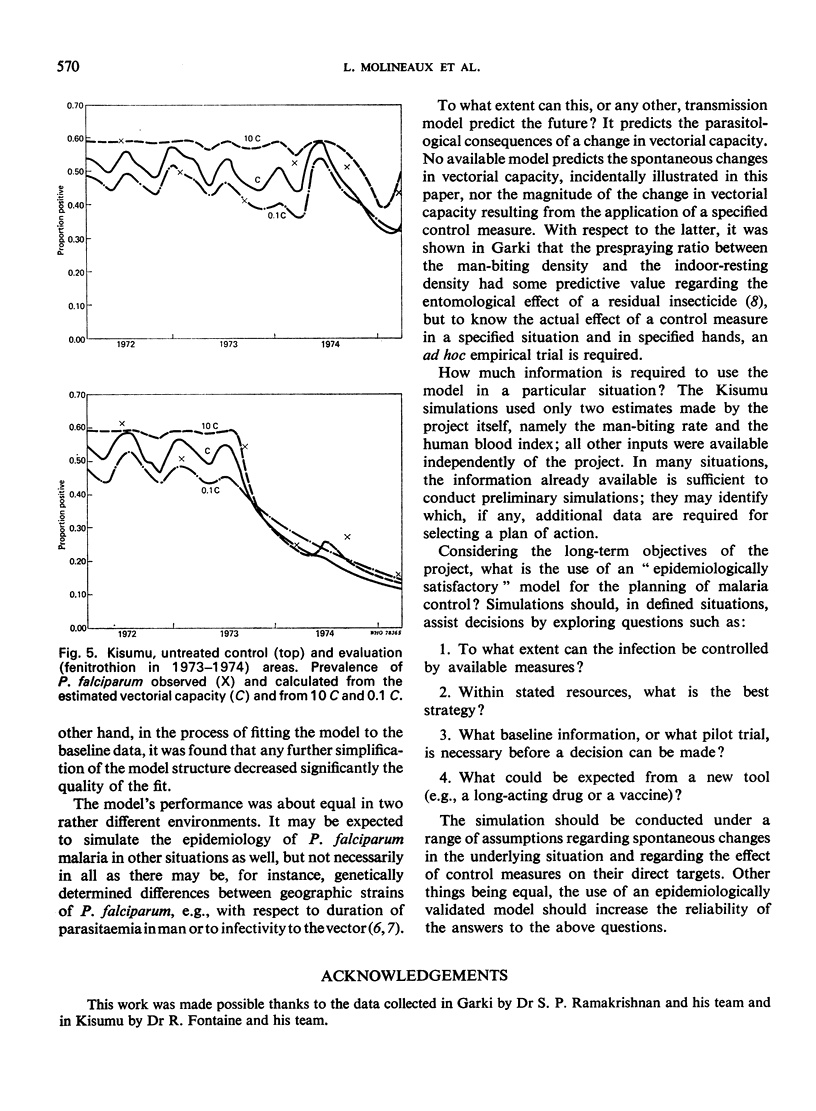
The malaria model previously fitted to 1 year of baseline data from the Garki District in the Sudan savanna of northern Nigeria was tested against data collected in the same area over a period of 3 years, including 1½ years during which the insides of houses in certain villages were sprayed with propoxur. It was also tested against data collected in Kisumu, Kenya, also over a period of 3 years, including 20 months during which the insides of houses in part of the area were sprayed with fenitrothion. The test consisted in using the vectorial capacity, calculated from the entomological observations made in the above places and periods, as input in the Garki model while keeping the other parameters as fitted to the Garki baseline data, and in comparing the prevalence of Plasmodium falciparum parasitaemia as estimated by the model to that actually observed. There was relatively good agreement and the model is considered epidemiologically satisfactory and fit for use in planning malaria control operations.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dietz K., Molineaux L., Thomas A. A malaria model tested in the African savannah. Bull World Health Organ. 1974;50(3-4):347–357. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARRETT-JONES C. THE HUMAN BLOOD INDEX OF MALARIA VECTORS IN RELATION TO EPIDEMIOLOGICAL ASSESSMENT. Bull World Health Organ. 1964;30:241–261. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLIES M. T. The duration of the gonotrophic cycle in Anopheles gambiae and Anopheles funestus, with a note on the efficiency of hand catching. East Afr Med J. 1953 Apr;30(4):129–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies M. T., Wilkes T. J. A study of the age-composition of populations of Anopheles gambiae Giles and A. funestus Giles in North-Eastern Tanzania. Bull Entomol Res. 1965 Dec;56(2):237–262. doi: 10.1017/s0007485300056339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James S. P., Nicol W. D., Shute P. G. A Study of Induced Malignant Tertian Malaria. Proc R Soc Med. 1932 Jun;25(8):1153–1186. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHUTE P. G., MARYON M. A contribution to the problem of strains of human plasmodium. Riv Malariol. 1954 Jun;33(1-3):1–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


