Abstract
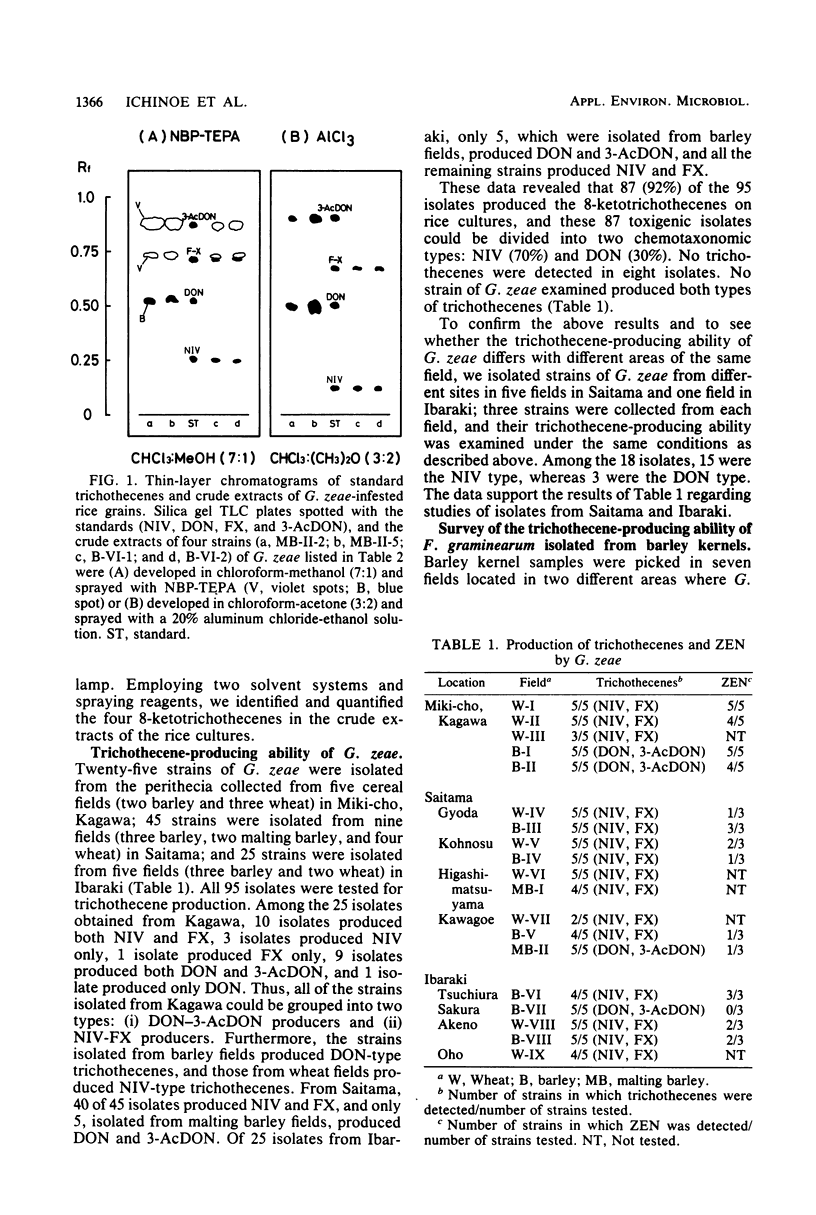
By adopting a single-spore isolation technique, 113 isolates of Gibberella zeae, the perfect stage of Fusarium graminearum, were isolated from rice stubbles in barley and wheat fields and tested for production of trichothecenes and zearalenone on rice grains. Of the isolates, 93% produced the trichothecenes, and they could be subdivided into two chemotaxonomic groups: nivalenol and fusarenon-X producers and deoxynivalenol and 3-acetyldeoxynivalenol producers. No cross production of these two types of trichothecenes was observed in these isolates. Zearalenone was detected in 68% of the isolates, but no clear relationship could be observed regarding its position with respect to the two chemotaxonomic groups.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Jemmali M., Ueno Y., Ishii K., Frayssinet C., Etienne M. Natural occurrence of trichothecenes (nivalenol, deoxynivalenol, T2) and zearalenone in corn. Experientia. 1978 Oct 15;34(10):1333–1334. doi: 10.1007/BF01981454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamimura H., Nishijima M., Yasuda K., Saito K., Ibe A., Nagayama T., Ushiyama H., Naoi Y. Simultaneous detection of several Fusarium mycotoxins in cereals, grains, and foodstuffs. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1981 Sep;64(5):1067–1073. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirocha C. J., Pathre S. V., Schauerhamer B., Christensen C. M. Natural occurrence of Fusarium toxins in feedstuff. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Oct;32(4):553–556. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.4.553-556.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta M., Ishii K., Ueno Y. Metabolism of trichothecene mycotoxins. I. Microsomal deacetylation of T-2 toxin in animal tissues. J Biochem. 1977 Dec;82(6):1591–1598. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STOB M., BALDWIN R. S., TUITE J., ANDREWS F. N., GILLETTE K. G. Isolation of an anabolic, uterotrophic compound from corn infected with Gibberella zeae. Nature. 1962 Dec 29;196:1318–1318. doi: 10.1038/1961318a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott P. M., Lau P. Y., Kanhere S. R. Gas chromatography with electron capture and mass spectrometric detection of deoxynivalenol in wheat and other grains. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1981 Nov;64(6):1364–1371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takitani S., Asabe Y., Kato T., Suzuki M., Ueno Y. Spectrodensitometric determination of trichothecene mycotoxins with 4-(p-nitrobenzyl)pyridine on silica gel thin-layer chromatograms. J Chromatogr. 1979 Apr 21;172:335–342. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(00)90970-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatsuno T., Saito M., Enomoto M., Tsunoda H. Nivalenol, a toxic principle of Fusarium nivale. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1968 Dec;16(12):2519–2520. doi: 10.1248/cpb.16.2519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno Y., Ishikawa Y., Saito-Amakai K., Tsunoda H. Environmental factors influencing the production of fusarenon-X, a cytotoxic mycotoxin of Fusarium nivale Fn 2B. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1970 Feb;18(2):304–312. doi: 10.1248/cpb.18.304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno Y., Ueno I., Tatsuno T., Ookubo K., Tsunoda H. Fusareon-X, a toxic principle of Fusarium nivale--culture filtrate. Experientia. 1969 Oct 15;25(10):1062–1062. doi: 10.1007/BF01901430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesonder R. F., Ciegler A., Jensen A. H. Isolation of the emetic principle from Fusarium-infected corn. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Dec;26(6):1008–1010. doi: 10.1128/am.26.6.1008-1010.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesonder R. F., Ciegler A., Rogers R. F., Burbridge K. A., Bothast R. J., Jensen A. H. Survey of 1977 crop year preharvest corn for vomitoxin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Dec;36(6):885–888. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.6.885-888.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vesonder R. F., Ciegler A., Rohwedder W. K., Eppley R. Re-examination of 1972 Midwest corn for vomitoxin. Toxicon. 1979;17(6):658–660. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(79)90244-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


