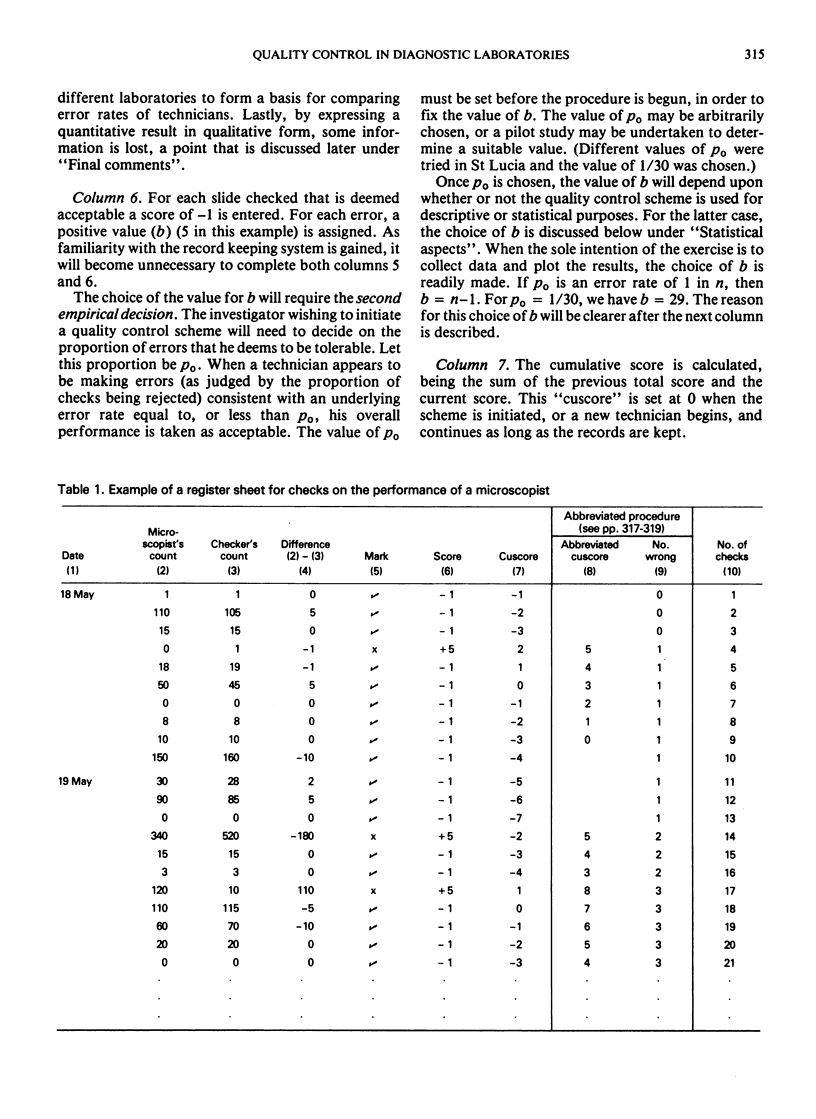
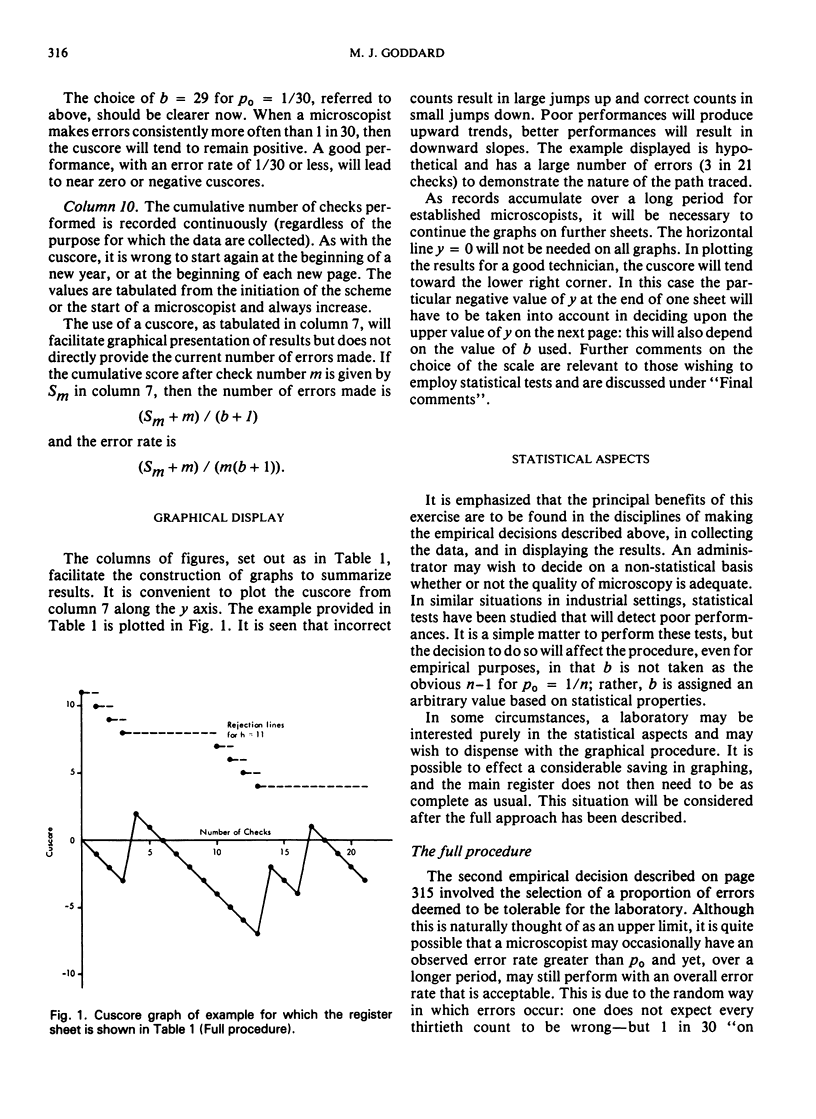
Abstract
The accuracy of results from any epidemiological project depends upon the performance of all stages of data collection and handling. One link in this chain may involve microscopic inspection of specimens and the purpose of this article is to describe means of assessing the accuracy of this stage. Two aspects merit consideration: the design of a sampling system and the collection and interpretation of the results. The importance of design is stressed, but the considerable variation in individual circumstances rules out a full treatment of the topic. A method of record keeping is described together with a method for graphical presentation of results. A procedure is outlined for detecting unacceptable performances and some of the statistical considerations are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartholomew R. K., Goddard M. J. Quality control in laboratory investigations on Schistosoma mansoni on St Lucia, West Indies: a staff assessment scheme. Bull World Health Organ. 1978;56(2):309–312. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis A. Comparative trials of antimonial drugs in urinary schistosomiasis. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;38(2):197–227. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



