Abstract
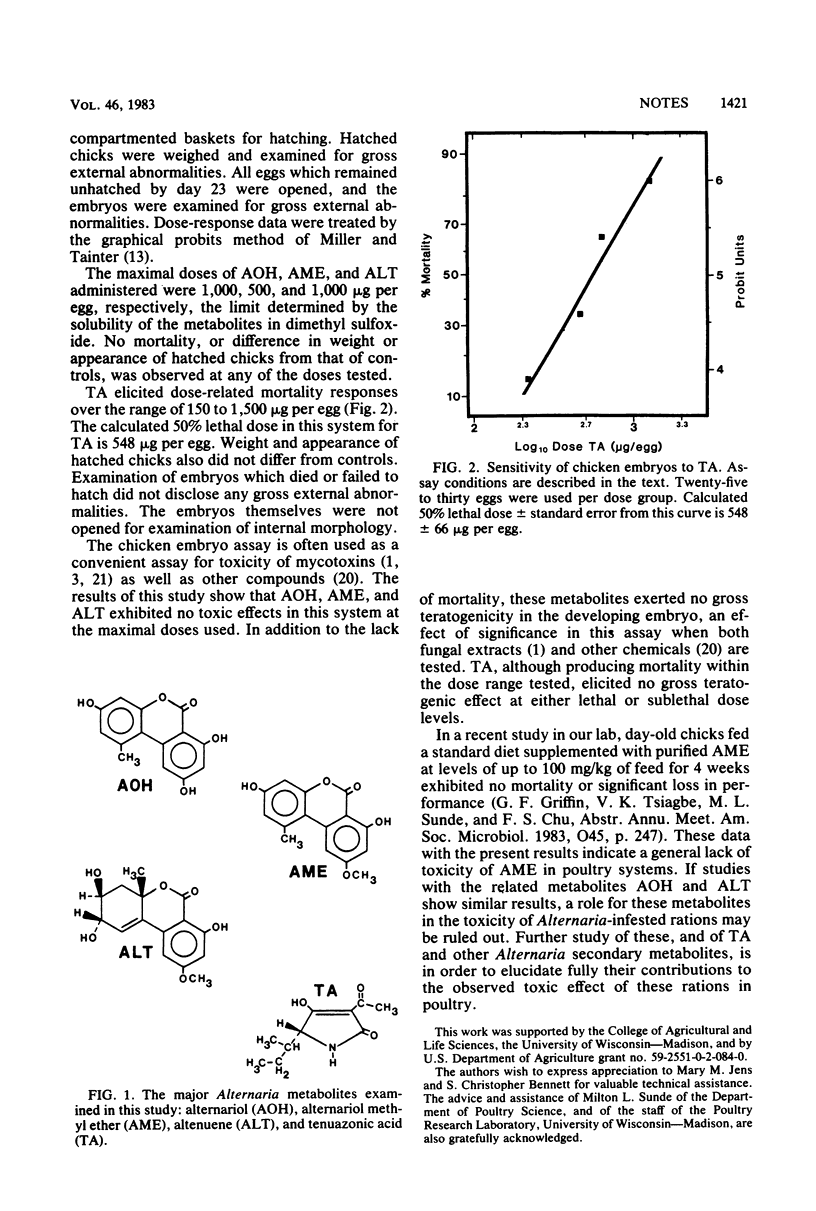
The effects in the chicken embryo assay of four Alternaria metabolites (alternariol [AOH], alternariol methyl ether [AME], altenuene [ALT], and tenuazonic acid [TA]) were investigated. Administered to 7-day-old chicken embryos by yolk sac injection, AOH, AME, and ALT caused no mortality or teratogenic effect at doses up to 1,000, 500, and 1,000 micrograms per egg, respectively. TA exhibited a calculated 50% lethal dose of 548 micrograms per egg, with no teratogenic effect observed at either lethal or sublethal doses.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer M. Detection of mycotoxins in foodstuffs by use of chick embryos. Mycopathol Mycol Appl. 1974 Dec 18;54(4):453–467. doi: 10.1007/BF02050051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N. D., Diener U. L., Morgan-Jones G. Tenuazonic acid production by Alternaria alternata and Alternaria tenuissima isolated from cotton. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Aug;34(2):155–157. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.2.155-157.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diener U. L., Morgan-Jones G., Wagener R. E., Davis N. D. Toxigenicity of fungi from grain sorghum. Mycopathologia. 1981 Jul 10;75(1):23–26. doi: 10.1007/BF00439062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doupnik B., Jr, Sobers E. K. Mycotoxicosis: toxicity to chicks of Alternaria longipes isolated from tobacco. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Oct;16(10):1596–1597. doi: 10.1128/am.16.10.1596-1597.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORGACS J., KOCH H., CARLL W. T., WHITE-STEVENS R. H. Additional studies on the relationship of mycotoxicoses to the poultry hemorrhagic syndrome. Am J Vet Res. 1958 Jul;19(72):744–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giambrone J. J., Davis N. D., Diener U. L. Effect of tenuazonic acid on young chickens. Poult Sci. 1978 Nov;57(6):1554–1558. doi: 10.3382/ps.0571554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwig J., Scott P. M., Stoltz D. R., Blanchfield B. J. Toxins of molds from decaying tomato fruit. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):267–274. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.2.267-274.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pero R. W., Posner H., Blois M., Harvan D., Spalding J. W. Toxicity of metabolites produced by the "Alternaria". Environ Health Perspect. 1973 Jun;4:87–94. doi: 10.1289/ehp.730487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauer D. B., Seitz L. M., Burroughs R., Mohr H. E., West J. L., Milleret R. J., Anthony H. D. Toxicity of Alternaria metabolites found in weathered sorghum grain at harvest. J Agric Food Chem. 1978 Nov-Dec;26(6):1380–1393. doi: 10.1021/jf60220a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson E. E., Bills D. D., Osman S. F., Siciliano J., Ceponis M. J., Heisler E. G. Mycotoxin production by Alternaria species grown on apples, tomatoes, and blueberries. J Agric Food Chem. 1980 Sep-Oct;28(5):960–963. doi: 10.1021/jf60231a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinson E. E., Osman S. F., Heisler E. G., Siciliano J., Bills D. D. Mycotoxin production in whole tomatoes, apples, oranges, and lemons. J Agric Food Chem. 1981 Jul-Aug;29(4):790–792. doi: 10.1021/jf00106a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrett M. J., Scott W. F., Reynaldo E. F., Alterman E. K., Thomas C. A. Toxicity and teratogenicity of food additive chemicals in the developing chicken embryo. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;56(2):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0041-008x(80)90298-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verrett M. J., Winbush J., Reynaldo E. F., Scott W. F. Collaborative study of the chicken embryo bioassay for aflatoxin B1. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1973 Jul;56(4):901–904. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


