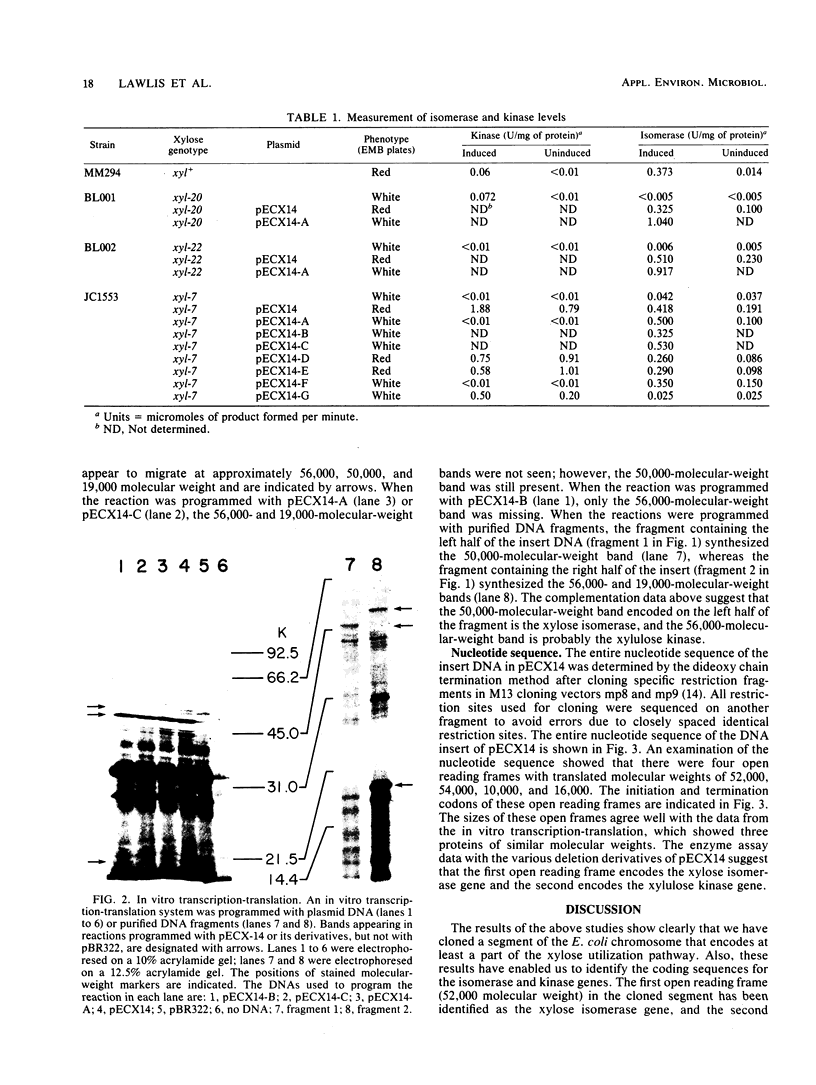
Abstract
A 4.2-kilobase-pair fragment of the Escherichia coli chromosome which contains the genes for xylose isomerase and xylulose kinase was cloned into plasmid pBR322. The hybrid plasmid (designated pECX14) complements strains deficient in either or both of the two enzymes. Deletion derivatives of pECX14 were used to localize the two genes on the cloned fragment. The entire nucleotide sequence of the cloned fragment was determined. Open reading frames which, if translated, would encode proteins of molecular weights 54,000 and 52,000 were found. These were identified as the isomerase and kinase structural genes, respectively.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Backman K., Ptashne M., Gilbert W. Construction of plasmids carrying the cI gene of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4174–4178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Effect of growth conditions on the formation of the relaxation complex of supercoiled ColE1 deoxyribonucleic acid and protein in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1972 Jun;110(3):1135–1146. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.3.1135-1146.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DISCHE Z. Spectrophotometric method for the determination of free pentose and pentose in nucleotides. J Biol Chem. 1949 Nov;181(1):379–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David J. D., Wiesmeyer H. Control of xylose metabolism in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Mar 24;201(3):497–499. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(70)90171-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershfield V., Boyer H. W., Yanofsky C., Lovett M. A., Helinski D. R. Plasmid ColEl as a molecular vehicle for cloning and amplification of DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3455–3459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Adelman J., Bock S. C., Franke A. E., Houck C. M., Najarian R. C., Seeburg P. H., Wion K. L. The sequence of human serum albumin cDNA and its expression in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 25;9(22):6103–6114. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.22.6103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legerski R. J., Hodnett J. L., Gray H. B., Jr Extracellular nucleases of pseudomonas BAL 31. III. Use of the double-strand deoxyriboexonuclease activity as the basis of a convenient method for the mapping of fragments of DNA produced by cleavage with restriction enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 May;5(5):1445–1464. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.5.1445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maleszka R., Wang P. Y., Schneider H. A Col E1 hybrid plasmid containing Escherichia coli genes complementing d-xylose negative mutants of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. Can J Biochem. 1982 Feb;60(2):144–151. doi: 10.1139/o82-020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maloy S. R., Nunn W. D. Selection for loss of tetracycline resistance by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Feb;145(2):1110–1111. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.2.1110-1111.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills D. R., Kramer F. R. Structure-independent nucleotide sequence analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2232–2235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAITO H., MIURA K. I. PREPARATION OF TRANSFORMING DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID BY PHENOL TREATMENT. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 Aug 20;72:619–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamanna D. K., Sanderson K. E. Genetics and regulation of D-xylose utilization in Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):71–79. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.71-79.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamanna D. K., Sanderson K. E. Uptake and catabolism of D-xylose in Salmonella typhimurium LT2. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jul;139(1):64–70. doi: 10.1128/jb.139.1.64-70.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. A. Carbohydrate metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1966;35:521–558. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.35.070166.002513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wovcha M. G., Steuerwald D. L., Brooks K. E. Amplification of D-xylose and D-glucose isomerase activities in Escherichia coli by gene cloning. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Apr;45(4):1402–1404. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.4.1402-1404.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]