Abstract
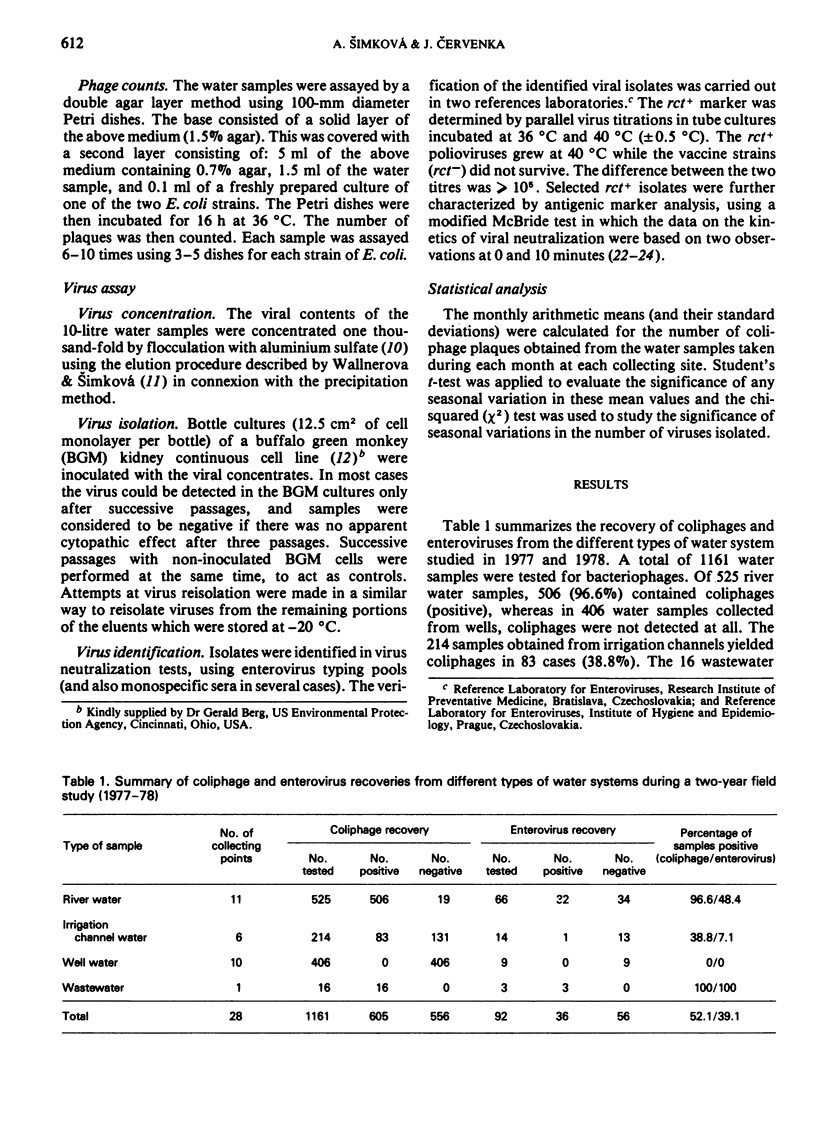
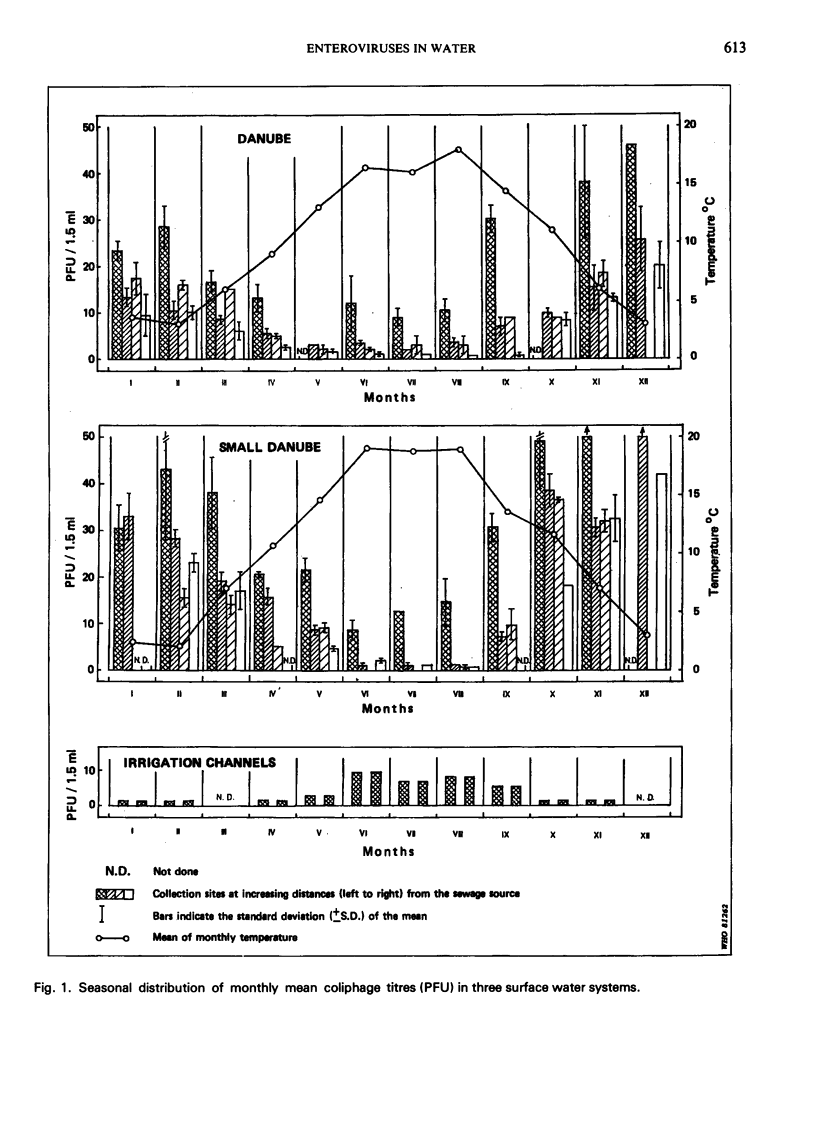
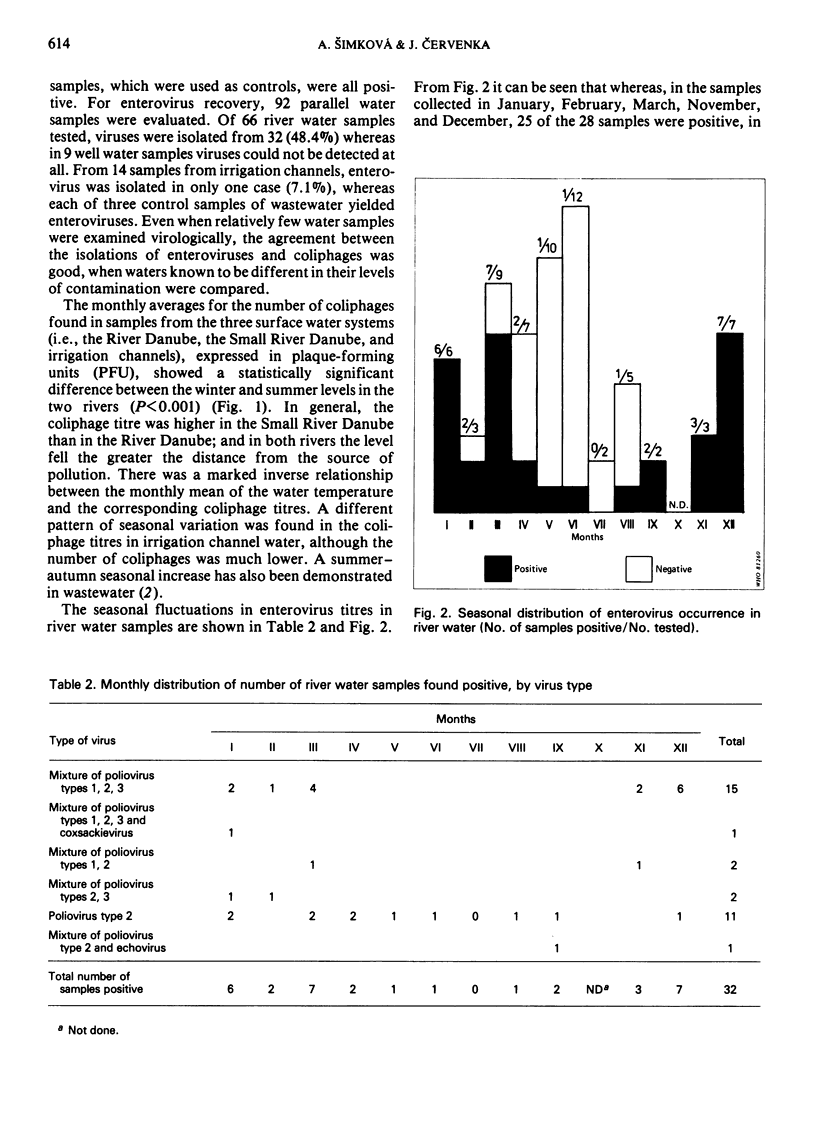
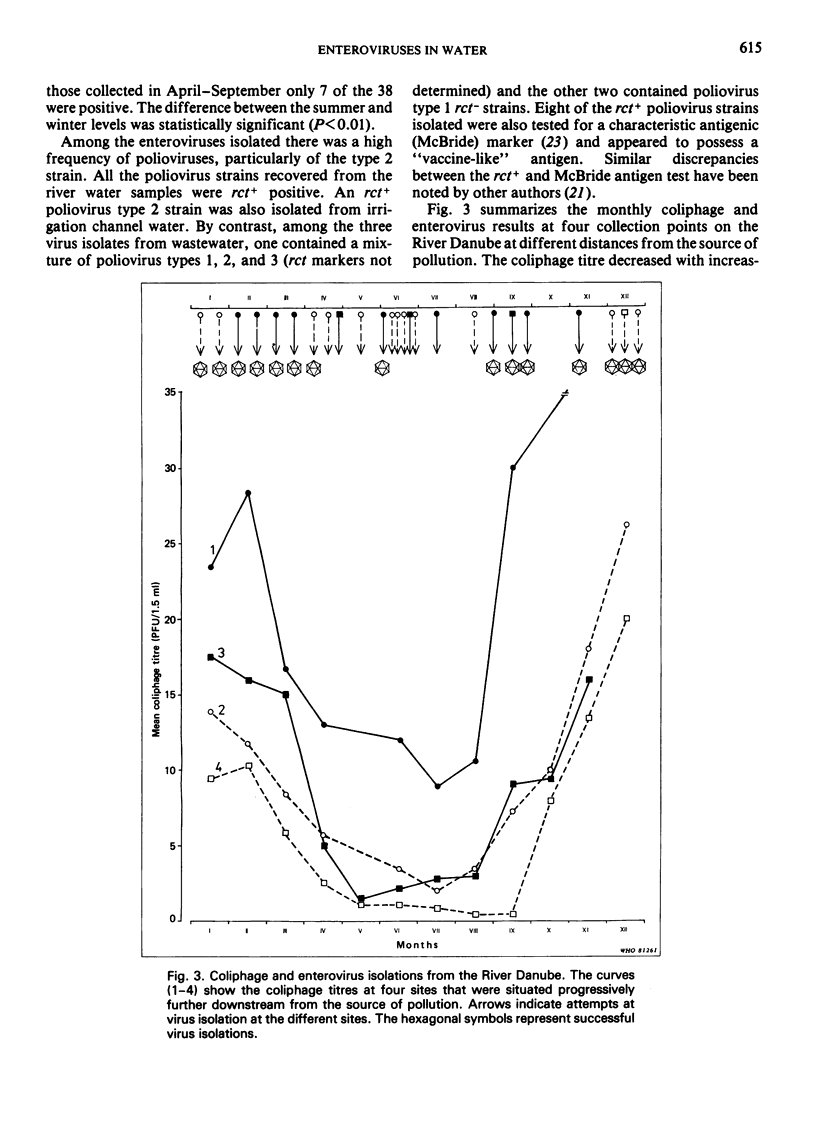
The occurrence of coliphages and enteroviruses in a variety of water systems in Czechoslovakia was monitored for two years. Two host strains of Escherichia coli bacteria were used to test 1161 water samples for the presence of bacteriophages. These strains were polyvalent hosts for a broad spectrum of morphologically distinct coliphages, and their use thus gave quantitative data on the degree of viral pollution in any given water sample. Ninety-two water samples were tested in parallel for the presence of enteroviruses, by using a flocculation method to concentrate the viruses followed by isolation in cultures of a buffalo green monkey (BGM) kidney continuous cell line. The enterovirus and coliphage recovery rates showed similar differences when waters with different levels of pollution were compared. Seasonal fluctuations of both the coliphage and enterovirus (mostly poliovirus) levels in river water were demonstrated by statistical analysis of the data collected. The levels increased in the winter and sharply declined in the summer months as the river water temperature increased. Chemical pollution did not seem to influence the survival of either the coliphages or the enteroviruses in the observed rivers.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg G., Dahling D. R., Brown G. A., Berman D. Validity of fecal coliforms, total coliforms, and fecal streptococci as indicators of viruses in chlorinated primary sewage effluents. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Dec;36(6):880–884. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.6.880-884.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahling D. R., Berg G., Berman D. BGM, a continuous cell line more sensitive than primary rhesus and African green kidney cells for the recovery of viruses from water. Health Lab Sci. 1974 Oct;11(4):275–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahling D. R., Safferman R. S. Survival of enteric viruses under natural conditions in a subarctic river. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Dec;38(6):1103–1110. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.6.1103-1110.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURESZ J., ARMSTRONG R. E., YAROSH W., NAGLER F. P. GENETIC MARKERS OF POLIOVIRUS STRAINS ISOLATED FROM PARALYTIC PATIENTS PRIOR TO AND AFTER SABIN VACCINATION PROGRAMS. I. STUDIES ON TYPE 1 STRAINS. Am J Hyg. 1964 Jul;80:45–54. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grabow W. O., Middendorff I. G., Basson N. C. Role of lime treatment in the removal of bacteria, enteric viruses, and coliphages in a wastewater reclamation plant. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Apr;35(4):663–669. doi: 10.1128/aem.35.4.663-669.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LWOFF A., LWOFF M. Remarques sur les facteurs aspécifiques gouvernant l'évolution des infections virales; la notion d'état critique. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1959 Jan 5;248(1):154–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBRIDE W. D. Antigenic analysis of polioviruses by kinetic studies of serum neutralization. Virology. 1959 Jan;7(1):45–58. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(59)90176-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nestor I., Costin L., Sovrea D., Ionescu N. Enteric viruses in the Danube river water and sludge. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1978;22(2):144–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Ho H. H., Riggs J. L., Lennette E. H. Comparative sensitivity of various cell culture systems for isolation of viruses from wastewater and fecal samples. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Sep;36(3):480–486. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.3.480-486.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simková A., Wallnerová Z. Isolations of coxsackie viruses from Danube river water. Acta Virol. 1973 Jul;17(4):363–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simková A., Wallnerová Z. Survival of small amounts of Coxsackie A4 virus in Danube river water under laboratory conditions. Acta Virol. 1973 Nov;17(6):505–506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. M., Landry E. F., Baranosky L. J., Beckwith C. A., Dahl M. C., Delihas N. C. Survey of human virus occurrence in wastewater-recharged groundwater on Long Island. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Jul;36(1):47–51. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.1.47-51.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaughn J. M., Landry E. F., Thomas M. Z., Vicale T. J., Penello W. F. Survey of human enterovirus occurrence in fresh and marine surface waters on Long Island. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Aug;38(2):290–296. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.2.290-296.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallnerová Z., Simková A. Comparison of the efficiency of two methods for virus concentration from river water environment in a model experiment. J Hyg Epidemiol Microbiol Immunol. 1978;22(2):152–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



