Abstract
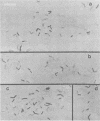
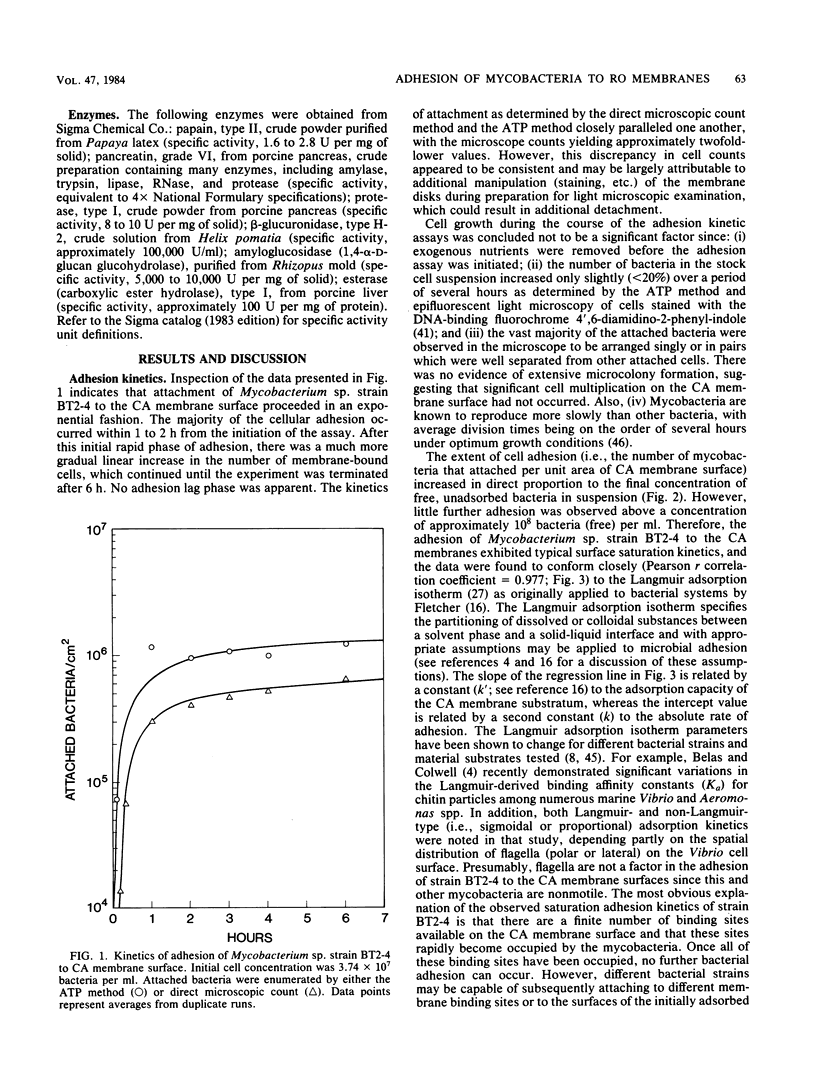
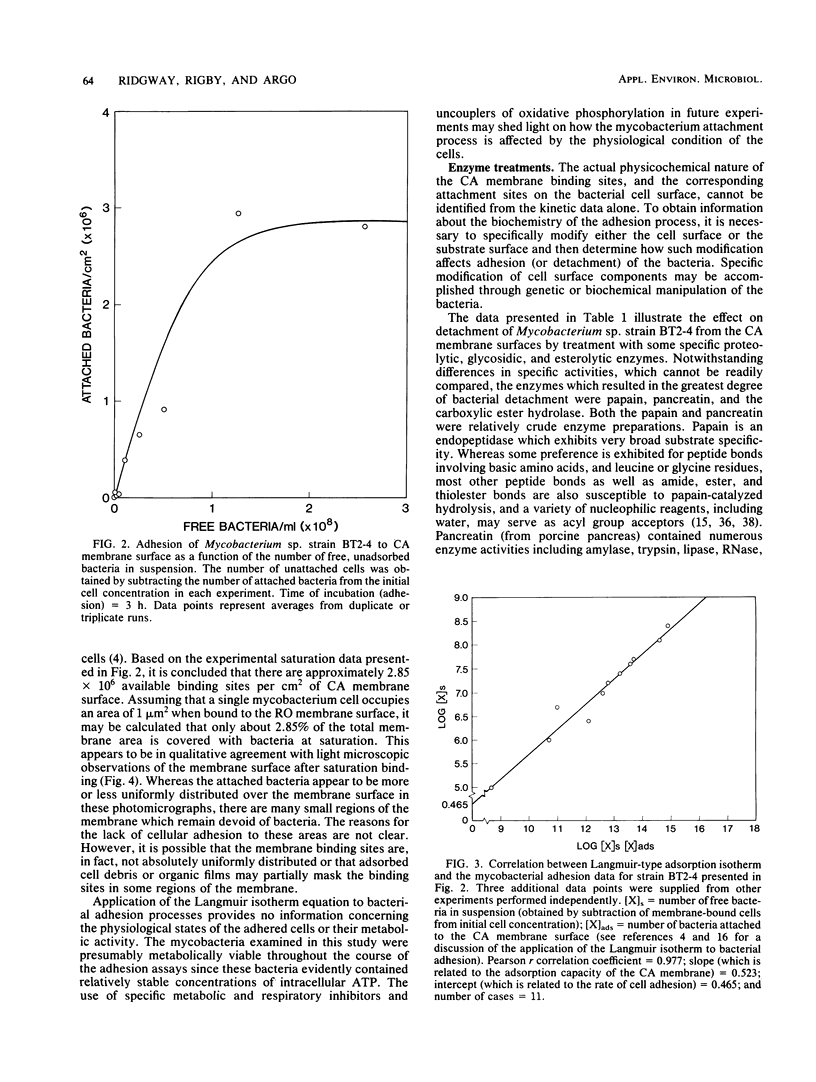
The kinetics of adhesion of a Mycobacterium sp. to cellulose diacetate reverse-osmosis membranes is described. This Mycobacterium sp. (strain BT2-4) was previously implicated in the initial stages of reverse-osmosis membrane biofouling at a wastewater reclamation facility. Adhesion of BT2-4 cells to the cellulose diacetate membrane surfaces occurred within 1 to 2 h at 30 degrees C and exhibited saturation-type kinetics which conformed closely to the Langmuir adsorption isotherm (Pearson r correlation coefficient = 0.977), a mathematical expression describing the partitioning of substances between a solution and solid-liquid interface. This suggests that the cellulose diacetate membrane surfaces may possess a finite number of available binding sites to which the mycobacteria can adhere. Treatment of the attached mycobacteria with different enzymes suggested that cell surface polypeptides, alpha-1, 4- or alpha-1,6-linked glucan polymers, and carboxyl ester bond-containing substances (possibly peptidoglycolipids) may be involved in mycobacterial adhesion. The possible implication of these findings for reverse-osmosis membrane biofouling are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azuma I., Yamamura Y., Misaki A. Isolation and characterization of arabinose mycolate from firmly bound lipids of mycobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1969 Apr;98(1):331–333. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.1.331-333.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baier R. E., Shafrin E. G., Zisman W. A. Adhesion: mechanisms that assist or impede it. Science. 1968 Dec 20;162(3860):1360–1368. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3860.1360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belas M. R., Colwell R. R. Adsorption kinetics of laterally and polarly flagellated Vibrio. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1568–1580. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1568-1580.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum S. E., Affronti L. F. Mycobacterial polysaccharides. II. Comparison of polysaccharides from strains of four species of mycobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):58–63. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.58-63.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celesk R. A., London J. Attachment of oral Cytophaga species to hydroxyapatite-containing surfaces. Infect Immun. 1980 Aug;29(2):768–777. doi: 10.1128/iai.29.2.768-777.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Irvin R. T., Costerton J. W. Autochthonous and pathogenic colonization of animal tissues by bacteria. Can J Microbiol. 1981 May;27(5):461–490. doi: 10.1139/m81-071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas C. J., Halperin W., Nester E. W. Agrobacterium tumefaciens mutants affected in attachment to plant cells. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):1265–1275. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.1265-1275.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher M., Loeb G. I. Influence of substratum characteristics on the attachment of a marine pseudomonad to solid surfaces. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jan;37(1):67–72. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.1.67-72.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher M., Marshall K. C. Bubble contact angle method for evaluating substratum interfacial characteristics and its relevance to bacterial attachment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jul;44(1):184–192. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.1.184-192.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., van Houte J. Dental caries. Annu Rev Med. 1975;26:121–136. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.26.020175.001005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOLLES P., SMOUR D., LEDERER E. Analytical studies on wax D, a macromolecular peptidoglycoplied fraction from humn strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosos. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Sep;Suppl 1:283–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marszalek D. S., Gerchakov S. M., Udey L. R. Influence of substrate composition on marine microfouling. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Nov;38(5):987–995. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.5.987-995.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCoy W. F., Bryers J. D., Robbins J., Costerton J. W. Observations of fouling biofilm formation. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Sep;27(9):910–917. doi: 10.1139/m81-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickels J. S., Bobbie R. J., Lott D. F., Martz R. F., Benson P. H., White D. C. Effect of manual brush cleaning on biomass and community structure of microfouling film formed on aluminum and titanium surfaces exposed to rapidly flowing seawater. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jun;41(6):1442–1453. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.6.1442-1453.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K. Factors regulating microbial biofilm development in a system with slowly flowing seawater. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Nov;44(5):1196–1204. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.5.1196-1204.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K. Method for studying microbial biofilms in flowing-water systems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jan;43(1):6–13. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.6-13.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway H. F., Kelly A., Justice C., Olson B. H. Microbial fouling of reverse-osmosis membranes used in advanced wastewater treatment technology: chemical, bacteriological, and ultrastructural analyses. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1066–1084. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.3.1066-1084.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway H. F., Olson B. H. Chlorine resistance patterns of bacteria from two drinking water distribution systems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):972–987. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.972-987.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridgway H. F., Olson B. H. Scanning electron microscope evidence for bacterial colonization of a drinking-water distribution system. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):274–287. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.274-287.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler T. T., Clark W. B., Birdsell D. C. Adherence of Actinomyces viscosus T14V and T14AV to hydroxyapatite surfaces in vitro and human teeth in vivo. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):1066–1074. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.1066-1074.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]