Abstract
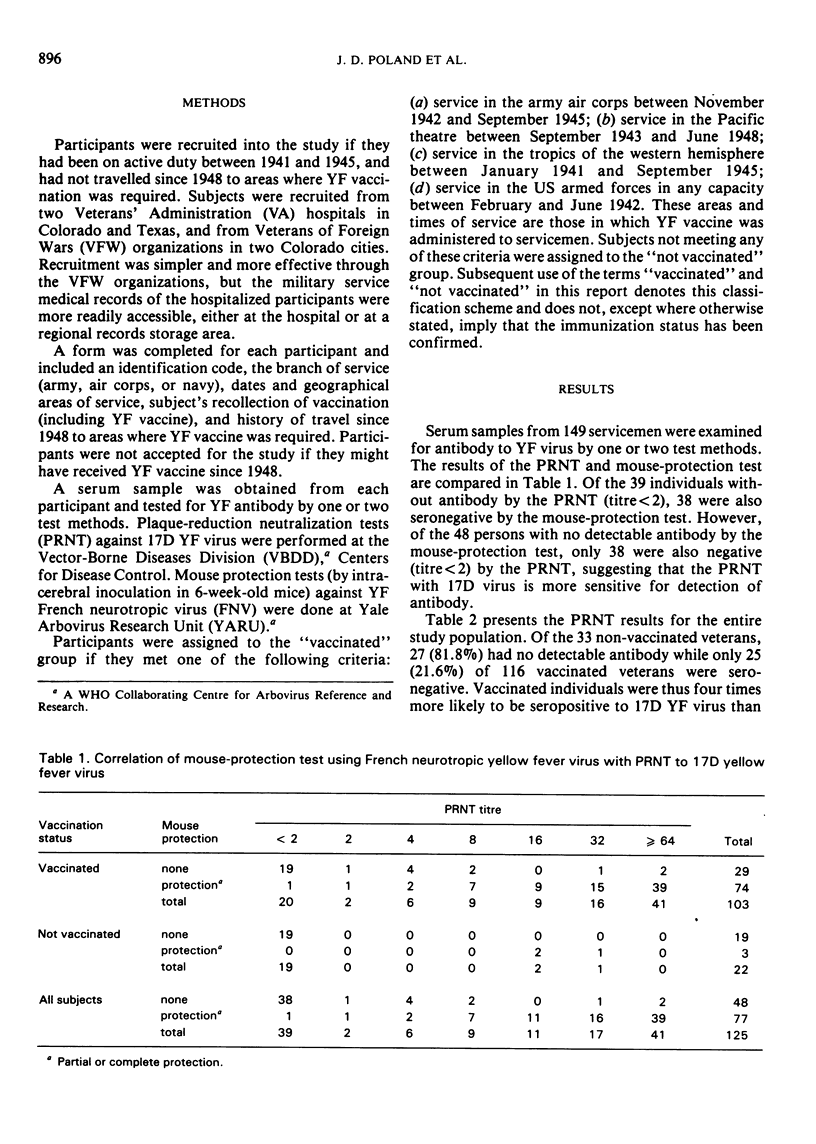
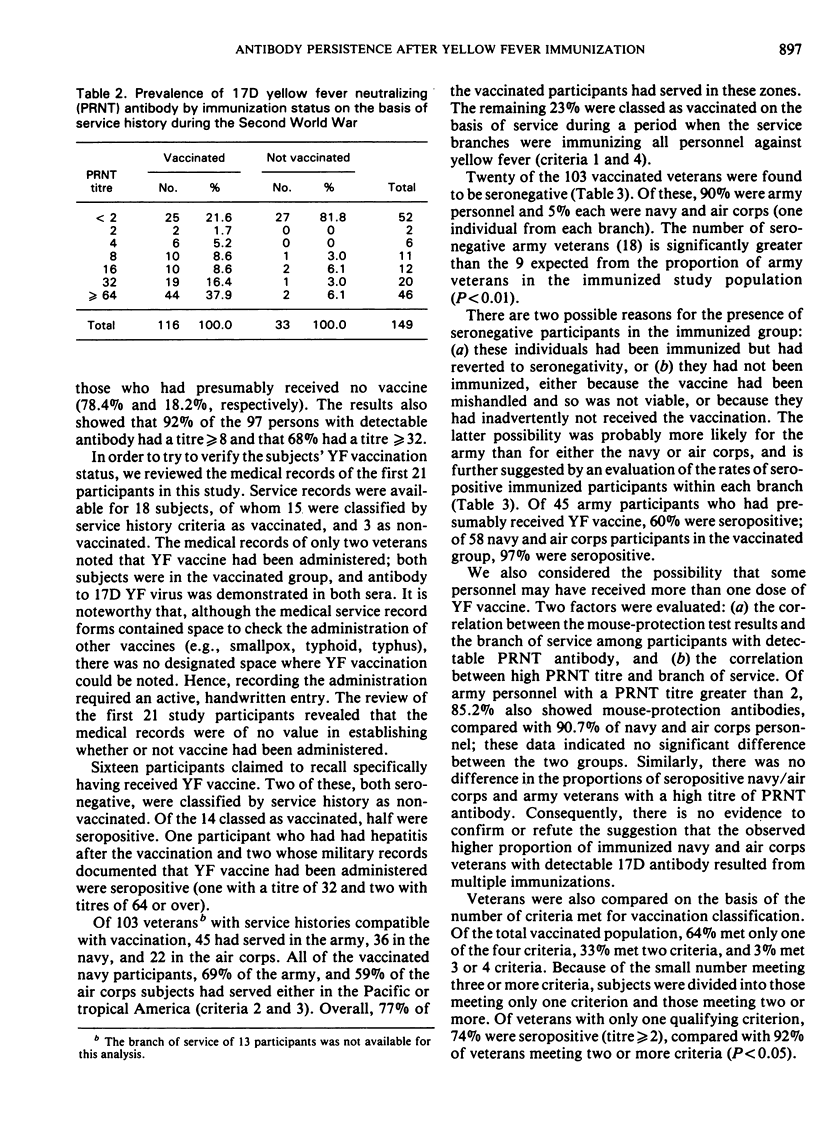
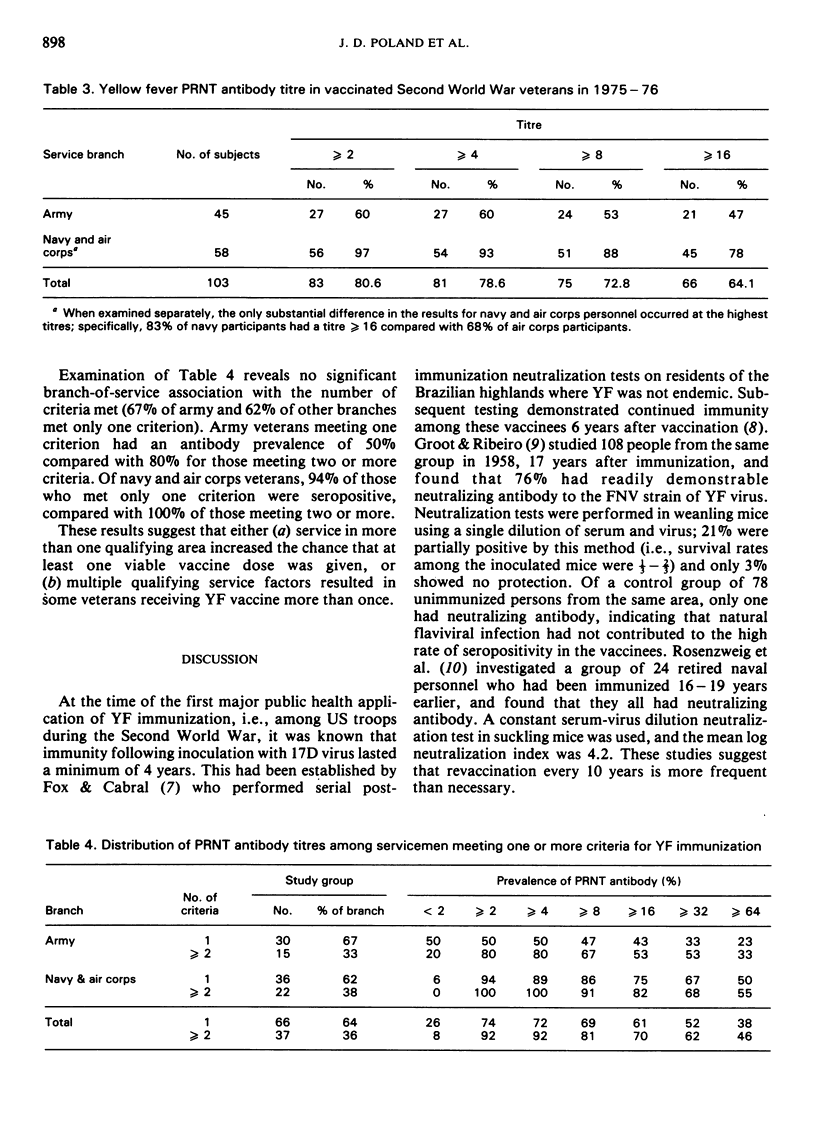
Previous studies on the duration of antibody following vaccination with 17D yellow fever (17D YF) virus vaccine have indicated that immunity persists for at least 17 years and suggest that the vaccine may provide lifelong immunity. We studied sera obtained from 149 veterans of the Second World War, 30 - 35 years after military service during which YF vaccination was required for defined groups. A significantly high proportion of ”vaccinated” subjects was found to be seropositive to 17D YF virus. The highest proportion of seropositive ”vaccinated” veterans (97%) was among navy and air corps personnel, while only 60% of ”vaccinated” army personnel and 19% of ”unvaccinated” personnel were seropositive. This study suggests that (i) antibody to 17D YF virus, as measured by the plaque-reduction neutralization test (PRNT), persists for 30 years or more following administration of a potent vaccine; (ii) army personnel often had not received potent vaccine, even though their service history indicated that they should have been vaccinated; (iii) some personnel were vaccinated, although their service did not include vaccination-designated areas; and (iv) 88% of veterans with persistent PRNT antibody to 17D YF virus also had mouse-protective antibody against French neurotropic YF virus.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GROOT H., RIBERIRO R. B. Neutralizing and haemagglutination-inhibiting antibodies to yellow fever 17 years after vaccination with 17D vaccine. Bull World Health Organ. 1962;27:699–707. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENZWEIG E. C., BABIONE R. W., WISSEMAN C. L., Jr Immunological studies with group B arthropod-borne viruses. IV. Persistence of yellow fever antibodies following vaccination with 17D strain yellow fever vaccine. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1963 Mar;12:230–235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH C. E., TURNER L. H., ARMITAGE P. Yellow fever vaccination in Malaya by subcutaneous injection and multiple puncture. Neutralizing antibody responses in persons with and without pre-existing antibody to related viruses. Bull World Health Organ. 1962;27:717–727. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


