Abstract
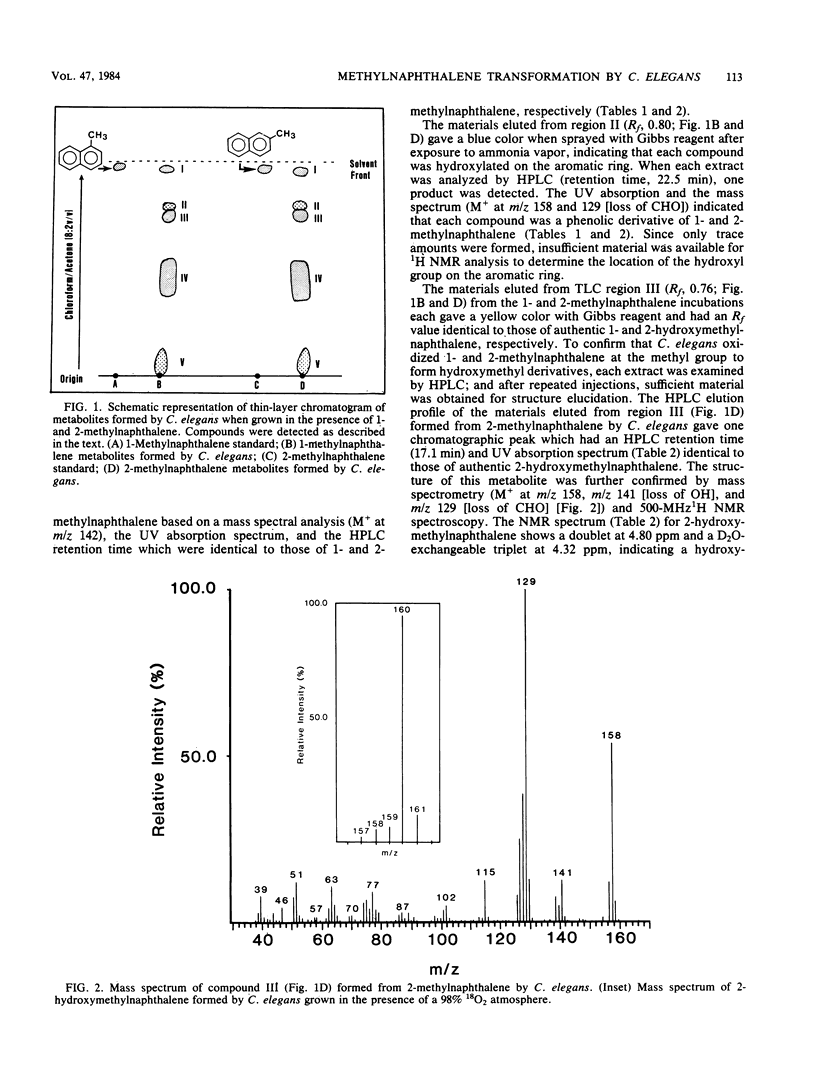
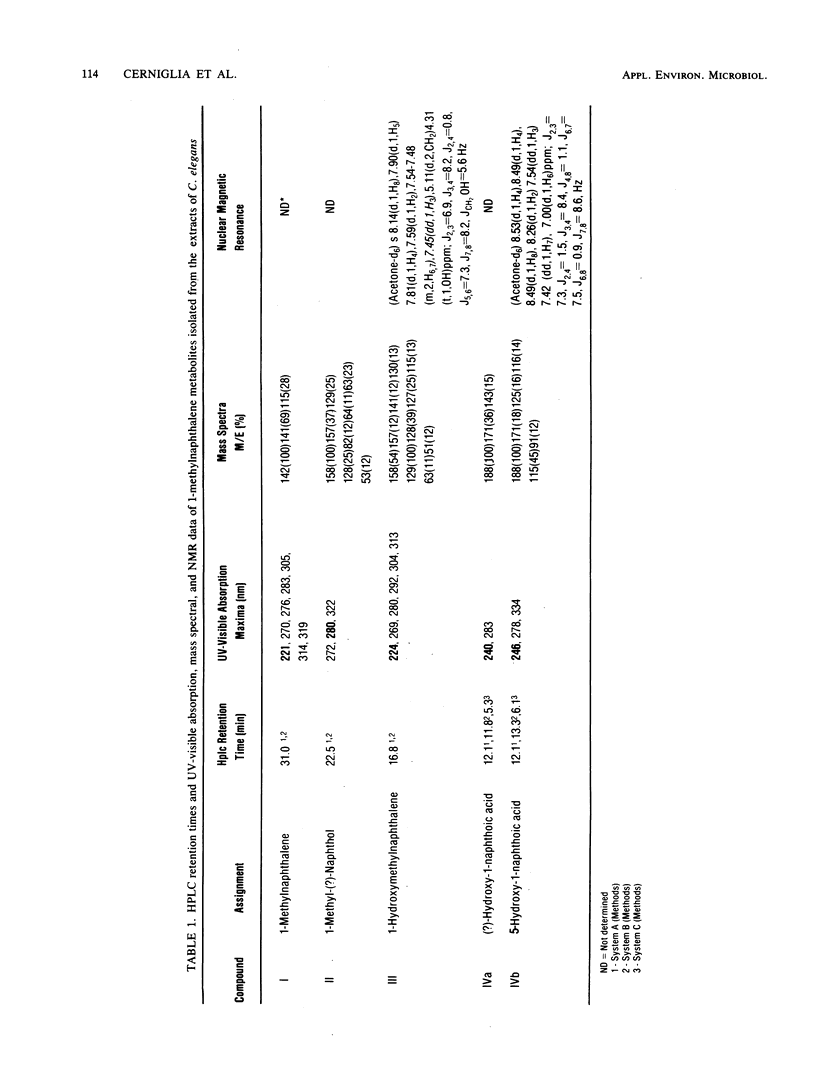
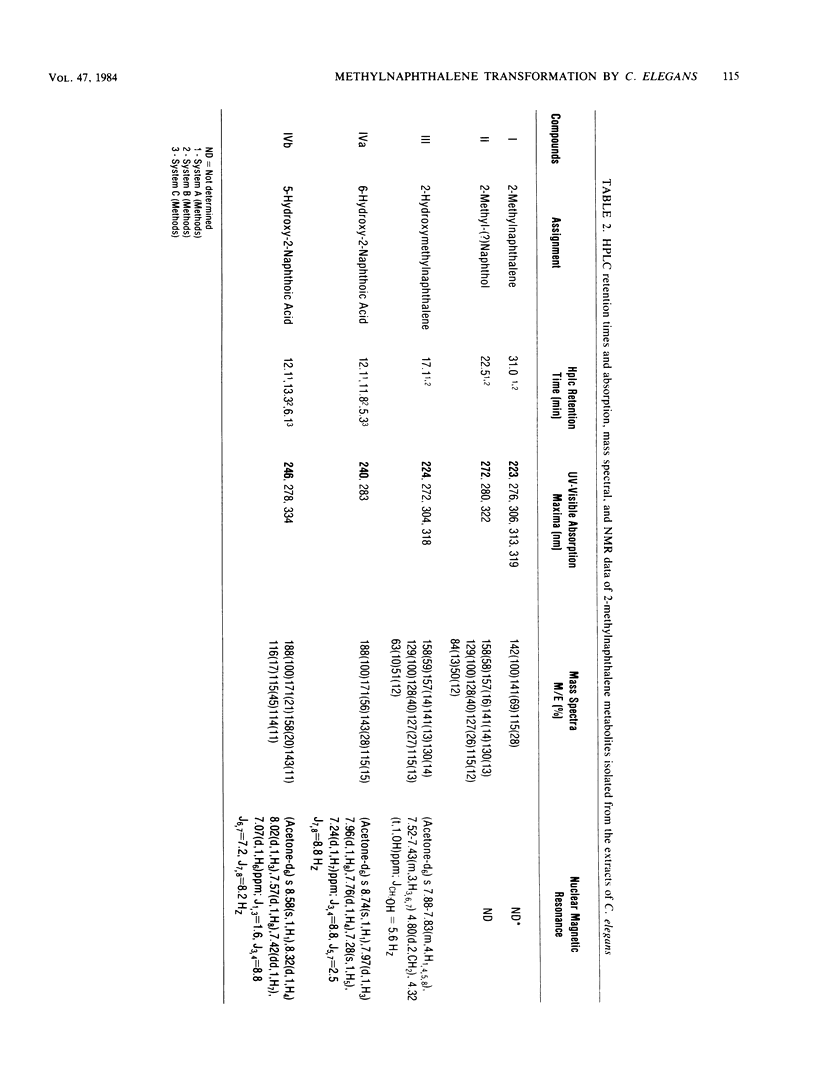
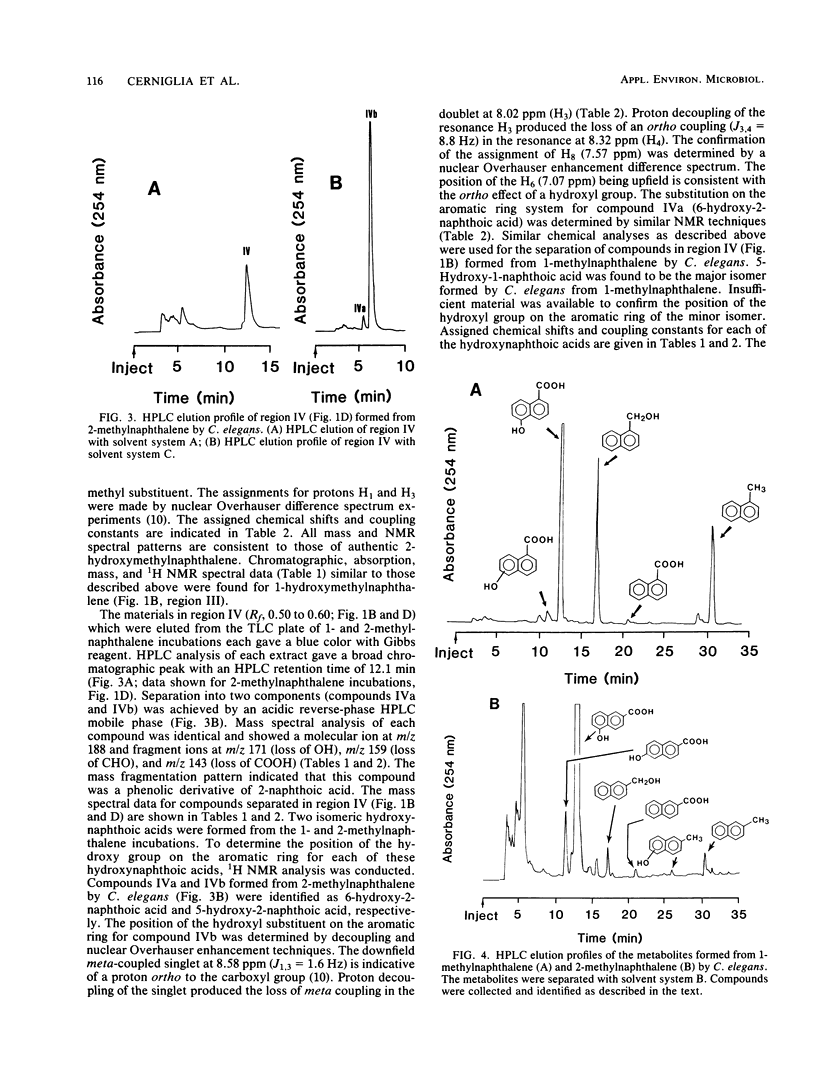
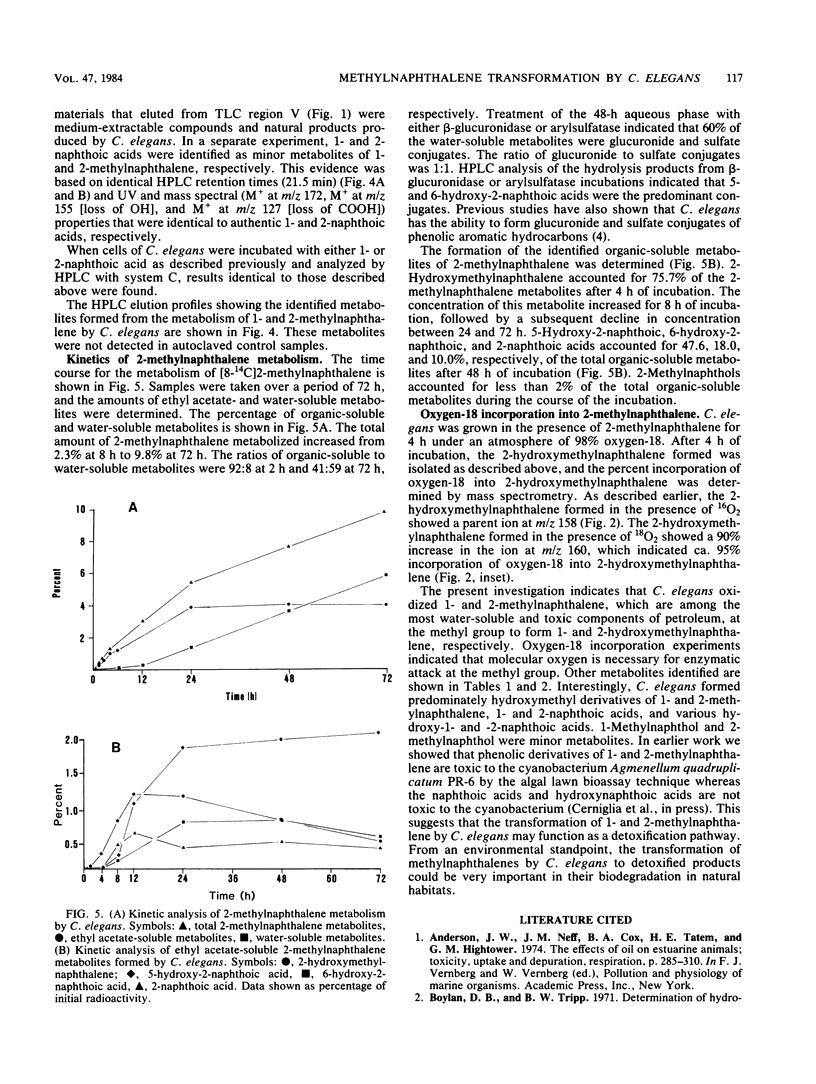
Cunninghamella elegans metabolized 1- and 2-methylnaphthalene primarily at the methyl group to form 1- and 2-hydroxymethylnaphthalene, respectively. Other compounds isolated and identified were 1- and 2-naphthoic acids, 5-hydroxy-1-naphthoic acid, 5-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid, 6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid, and phenolic derivatives of 1- and 2-methylnaphthalene. The metabolites were isolated by thin-layer and reverse-phase high-pressure liquid chromatography and characterized by the application of UV-visible absorption, 1H nuclear magnetic resonance, and mass spectral techniques. Experiments with [8-14C]2-methylnaphthalene indicated that over a 72-h period, 9.8% of 2-methylnaphthalene was oxidized to metabolic products. The ratio of organic-soluble in water-soluble metabolites at 2 h was 92:8, and at 72 h it was 41:59. Enzymatic treatment of the 48-h aqueous phase with either beta-glucuronidase or arylsulfatase released 60% of the metabolites of 2-methylnaphthalene that were extractable with ethyl acetate. In both cases, the major conjugates released were 5-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid and 6-hydroxy-2-naphthoic acid. The ratio of the water-soluble glucuronide conjugates to sulfate conjugates was 1:1. Incubation of C. elegans with 2-methylnaphthalene under an 18O2 atmosphere and subsequent mass spectral analysis of 2-hydroxymethylnaphthalene indicated that hydroxylation of the methyl group is catalyzed by a monooxygenase.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Breger R. K., Franklin R. B., Lech J. J. Metabolism of 2-methylnaphthalene to isomeric dihydrodiols by hepatic microsomes of rat and rainbow trout. Drug Metab Dispos. 1981 Mar-Apr;9(2):88–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerniglia C. E., Gibson D. T. Metabolism of naphthalene by Cunninghamella elegans. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Oct;34(4):363–370. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.4.363-370.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerniglia C. E., Gibson D. T. Metabolism of naphthalene by cell extracts of Cunninghamella elegans. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Feb;186(1):121–127. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90471-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerniglia C. E., Hebert R. L., Szaniszlo P. J., Gibson D. T. Fungal transformation of naphthalene. Arch Microbiol. 1978 May 30;117(2):135–143. doi: 10.1007/BF00402301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferris J. P., Fasco M. J., Stylianopoulou F. L., Jerina D. M., Daly J. W., Jeffrey A. M. Monooxygenase activity in Cunninghamella bainieri: evidence for a fungal system similar to liver microsomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 May;156(1):97–103. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90345-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaubisch N., Daly J. W., Jerina D. M. Arene oxides as intermediates in the oxidative metabolism of aromatic compounds. Isomerization of methyl-substituted arene oxides. Biochemistry. 1972 Aug 1;11(16):3080–3088. doi: 10.1021/bi00766a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. C., Craig W. K., Smith P. J. Water-soluble hydrocarbons from crude oil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1974 Aug;12(2):212–217. doi: 10.1007/BF01684964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melancon M. J., Jr, Lech J. J. Distribution and elimination of naphthalene and 2-methylnaphthalene in rainbow trout during short- and long-term exposures. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol. 1978;7(2):207–220. doi: 10.1007/BF02332049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGOFF M. H., WENDER I. Methylnaphthalene oxidations by pseudomonads. J Bacteriol. 1959 Jun;77(6):783–788. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.6.783-788.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. V., Rosazza J. P. Microbial models of mammalian metabolism. Aromatic hydroxylation. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Apr 2;161(2):551–558. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90338-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. A., Catterall F. A., Murray K. Metabolism of naphthalene, 2-methylnaphthalene, salicylate, and benzoate by Pseudomonas PG: regulation of tangential pathways. J Bacteriol. 1975 Nov;124(2):679–685. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.2.679-685.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirtz R. A., Turrentine J. D., Jr, Fox R. C. Area repellents for mosquitoes (Diptera: culicidae): identification of the active ingredients in a petroleum oil fraction. J Med Entomol. 1981 Apr;18(2):126–128. doi: 10.1093/jmedent/18.2.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


