Abstract
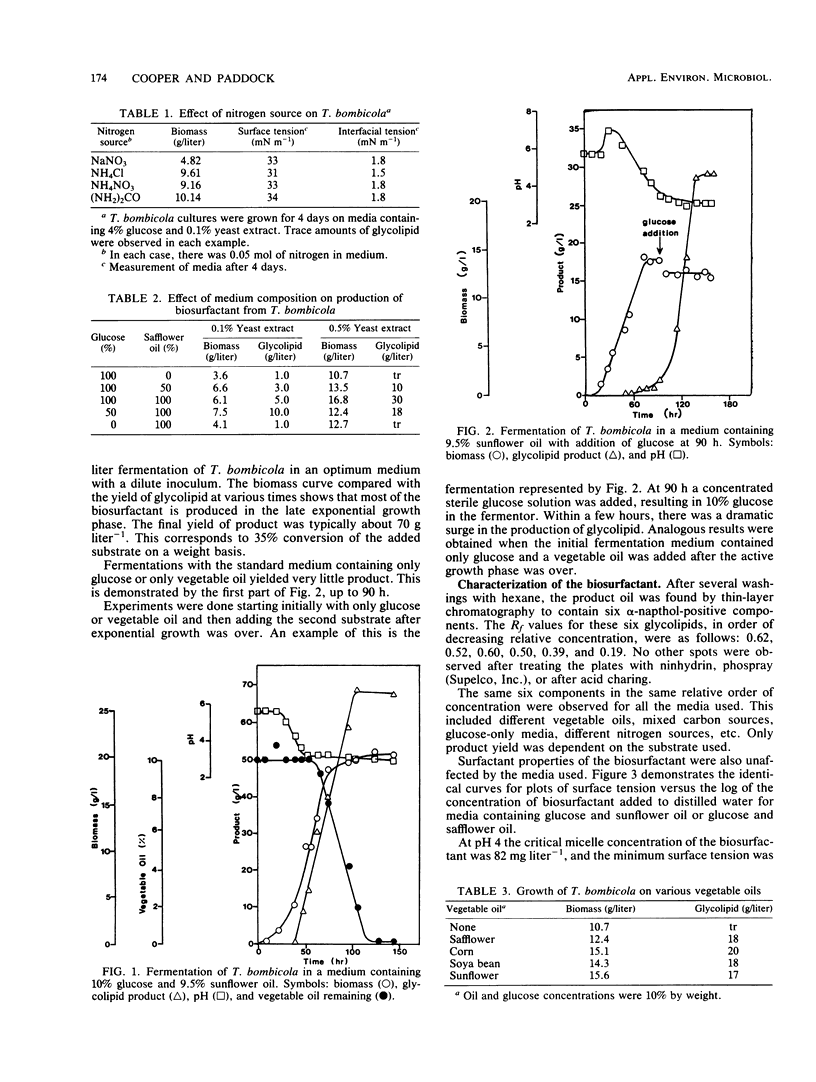
Two types of carbon sources—carbohydrate and vegetable oil—are necessary to obtain large yields of biosurfactant from Torulopsis bombicola ATCC 22214. Most of the surfactant is produced in the late exponential phase of growth. It is possible to grow the yeast on a single carbon source and then add the other type of substrate, after the exponential growth phase, and cause a burst of surfactant production. This product is a mixture of glycolipids. The maximum yield is 70 g liter−1, or 35% of the weight of the substrate used. An economic comparison demonstrated that this biosurfactant could be produced significantly more cheaply than any of the previously reported microbial surfactants.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cooper D. G., Macdonald C. R., Duff S. J., Kosaric N. Enhanced Production of Surfactin from Bacillus subtilis by Continuous Product Removal and Metal Cation Additions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Sep;42(3):408–412. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.3.408-412.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. G., Zajic J. E., Gerson D. F. Production of surface-active lipids by Corynebacterium lepus. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jan;37(1):4–10. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.1.4-10.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper D. G., Zajic J. E., Gracey D. E. Analysis of corynomycolic acids and other fatty acids produced by Corynebacterium lepus grown on kerosene. J Bacteriol. 1979 Feb;137(2):795–801. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.2.795-801.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez J. R., Erickson L. E. Hydrocarbon uptake in hydrocarbon fermentations. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1977 Sep;19(9):1331–1349. doi: 10.1002/bit.260190907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito S., Inoue S. Sophorolipids from Torulopsis bombicola: possible relation to alkane uptake. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1278–1283. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1278-1283.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. F., Howe R. Microbiological oxidation of long-chain aliphatic compounds. I. Alkanes and alk-1-enes. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1968;22:2801–2808. doi: 10.1039/j39680002801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretschmer A., Bock H., Wagner F. Chemical and Physical Characterization of Interfacial-Active Lipids from Rhodococcus erythropolis Grown on n-Alkanes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Oct;44(4):864–870. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.4.864-870.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


