Abstract
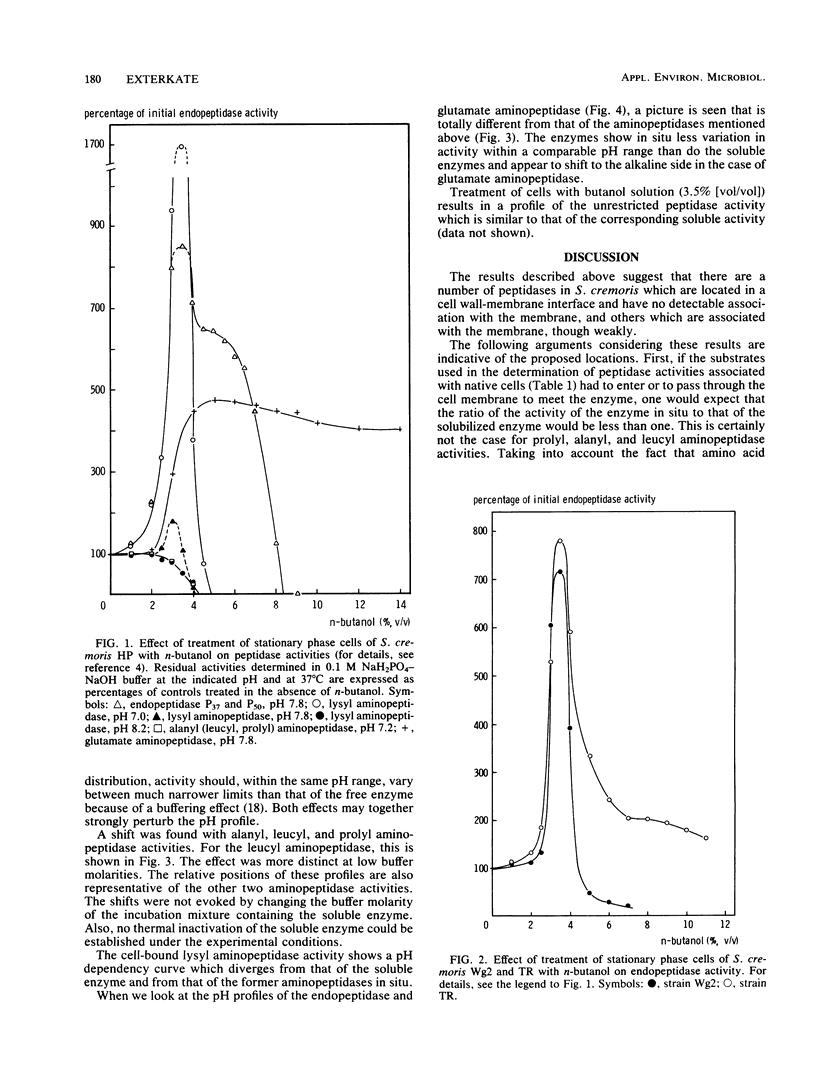
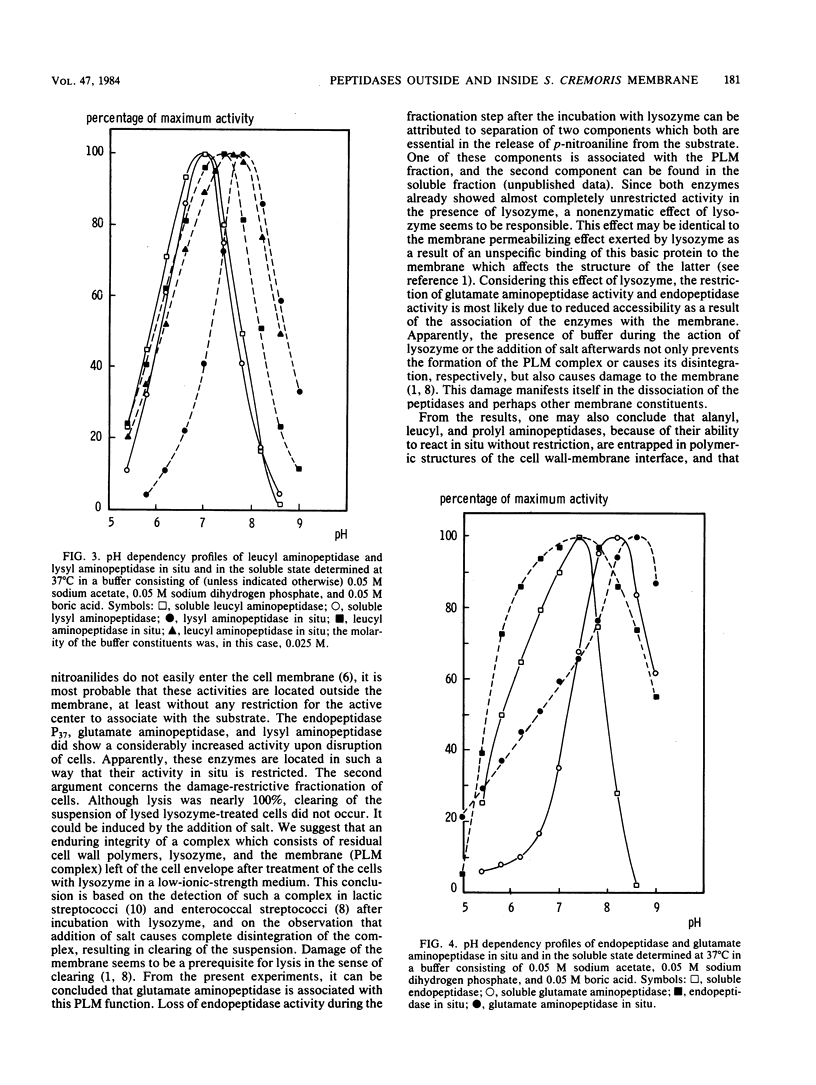
Peptidase activity determinations involving native cells of Streptococcus cremoris and completely disrupted cell preparations, as well as experiments concerned with peptidase activity distribution among cell fractions obtained by a damage-restrictive removal of the cell wall and release of intracellular material, suggest the presence of peptidases with distinguishable locations. Alanyl, leucyl, and prolyl aminopeptidase activities are most likely located in the cell wall-membrane interface, showing no detectable association with the membrane. Lysyl aminopeptidase is present not only in this location, but also as an intracellular enzyme. Endopeptidase activity and glutamate aminopeptidase activity appear to be weakly associated with the membrane. The locations of these two peptidase activities, unlike those of the former aminopeptidase activities, impose a restriction on their expression. Results of experiments concerned with permeabilization of the membrane and findings regarding an effect of the local environment of the enzymes on their pH activity profiles are evaluated and considered as being indicative of the proposed location. The possible implications of these findings with respect to protein utilization during growth of the organism in milk are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cho M. I., Holt S. C., Iacono V. J., Pollock J. J. Effects of lysozyme and inorganic anions on the morphology of Streptococcus mutans BHT: electron microscopic examination. J Bacteriol. 1982 Sep;151(3):1498–1507. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.3.1498-1507.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exterkate F. A. Pyrrolidone carboxylyl peptidase in Streptococcus cremoris: dependence on an interaction with membrane components. J Bacteriol. 1977 Mar;129(3):1281–1288. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.3.1281-1288.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frey J., Röhm K. H. External and internal forms of yeast aminopeptidase II. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun;97(1):169–173. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13099.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman H., Pollock J. J., Iacono V. J., Wong W., Shockman G. D. Peptidoglycan loss during hen egg white lysozyme-inorganic salt lysis of Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):755–763. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.755-763.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman H., Pollock J. J., Katona L. I., Iacono V. J., Cho M. I., Thomas E. Lysis of Streptococcus mutans by hen egg white lysozyme and inorganic sodium salts. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):764–774. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.764-774.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain M. K., Gleeson J., Upreti A., Upreti G. C. Intrinsic perturbing ability of alkanols in lipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 May 4;509(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruse H., Hurst A. Preparation of spheroplasts from Streptococcus lactis. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Jun;18(6):825–831. doi: 10.1139/m72-128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. P., Weppner W. A., Neuhaus F. C. Initial membrane reaction in peptidoglycan synthesis: perturbation of lipid-phospho-N-acetylmuramyl-pentapeptide translocase interactions by n-butanol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Apr 24;597(3):603–613. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90231-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenaz G., Bertoli E., Curatola G., Mazzanti L., Bigi A. Lipid protein interactions in mitochondria. Spin and fluorescence probe studies on the effect of n-alkanols on phospholipid vesicles and mitochondrial membranes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jan;172(1):278–288. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90077-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenaz G., Parenti-Castelli G., Sechi A. M. Lipid-protein interactions in mitochondria. Changes in mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase activity induced by n-butyl alcohol. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Mar;167(1):72–79. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90442-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurel P., Douzou P., Waldmann J., Yonetani T. Enzyme behaviour and molecular environment. The effects of ionic strength, detergents, linear polyanions and phospholipids on the pH profile of soluble cytochrome oxidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 7;525(2):314–324. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(78)90226-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf R. H., Deibel R. H. Effect of lysozyme on enterococcal viability in low ionic environments. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jan;113(1):278–286. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.1.278-286.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otto R., Lageveen R. G., Veldkamp H., Konings W. N. Lactate efflux-induced electrical potential in membrane vesicles of Streptococcus cremoris. J Bacteriol. 1982 Feb;149(2):733–738. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.2.733-738.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. B. Teichoic and teichuronic acids: biosynthesis, assembly, and location. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Jun;45(2):211–243. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.2.211-243.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


