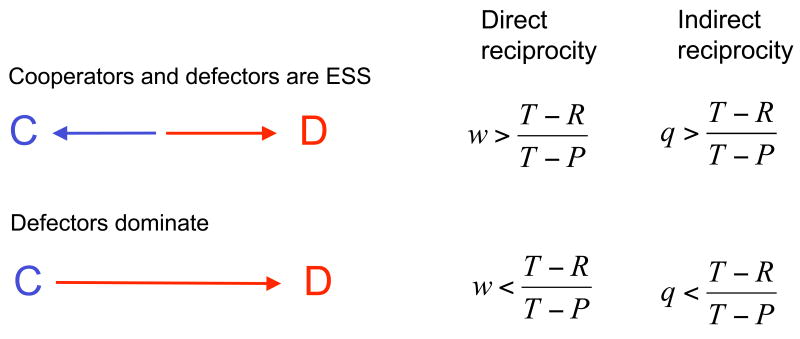
Figure 2. Direct and indirect reciprocity can lead to the evolution of cooperation.
While direct reciprocity is based on repeated encounters between the same two individuals, indirect reciprocity uses the experience of others. Defectors are always ESS. Cooperators are ESS if w or q exceed (T − R)/(T − P), where w is the probability of another round in direct reciprocity, and q is the coefficient of social acquaintanceship under indirect reciprocity.