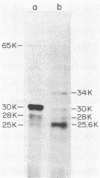
Abstract
The gene responsible for the malolactic fermentation of wine was cloned from the bacterium Lactobacillus delbrueckii into Escherichia coli and the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. This gene codes for the malolactic enzyme which catalyzes the conversion of l-malate to l-lactate. A genetically engineered yeast strain with this enzymatic capability would be of considerable value to winemakers. L. delbrueckii DNA was cloned in E. coli on the plasmid pBR322, and two E. coll clones able to convert l-malate to l-lactate were selected. Both clones contained the same 5-kilobase segment of L. delbrueckii DNA. The DNA segment was transferred to E. coli-yeast shuttle vectors, and gene expression was analyzed in both hosts by using enzymatic assays for l-lactate and l-malate. When grown nonaerobically for 5 days, E. coli cells harboring the malolactic gene converted about 10% of the l-malate in the medium to l-lactate. The best expression in S. cerevisiae was attained by transfer of the gene to a shuttle vector containing both a yeast 2-μm plasmid and yeast chromosomal origin of DNA replication. When yeast cells harboring this plasmid were grown nonaerobically for 5 days, ca. 1.0% of the l-malate present in the medium was converted to l-lactate. The L. delbrueckii controls grown under these same conditions converted about 25%. A laboratory yeast strain containing the cloned malolactic gene was used to make wine in a trial fermentation, and about 1.5% of the l-malate in the grape must was converted to l-lactate. Increased expression of the malolactic gene in wine yeast will be required for its use in winemaking. This will require an increased understanding of the factors governing the expression of this gene in yeasts.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. Codon selection in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3026–3031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochner B. R., Huang H. C., Schieven G. L., Ames B. N. Positive selection for loss of tetracycline resistance. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):926–933. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.926-933.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspritz G., Radler F. Malolactic enzyme of Lactobacillus plantarum. Purification, properties, and distribution among bacteria. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):4907–4910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. Isolation of a yeast centromere and construction of functional small circular chromosomes. Nature. 1980 Oct 9;287(5782):504–509. doi: 10.1038/287504a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke L., Carbon J. Isolation of the centromere-linked CDC10 gene by complementation in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2173–2177. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson J., Groppe J. C., Reed S. I. Construction and characterization of three yeast-Escherichia coli shuttle vectors designed for rapid subcloning of yeast genes on small DNA fragments. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):191–197. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90075-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitzeman R. A., Hagie F. E., Levine H. L., Goeddel D. V., Ammerer G., Hall B. D. Expression of a human gene for interferon in yeast. Nature. 1981 Oct 29;293(5835):717–722. doi: 10.1038/293717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. P., Holland M. J. Structural comparison of two nontandemly repeated yeast glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase genes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2596–2605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkee R. E. Malo-lactic fermentation. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1967;9:235–279. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70530-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langridge J., Langridge P., Bergquist P. L. Extraction of nucleic acids from agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Apr;103(2):264–271. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90266-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonvaud-Funel A., de Saad A. M. Purification and Properties of a Malolactic Enzyme from a Strain of Leuconostoc mesenteroides Isolated from Grapes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Feb;43(2):357–361. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.2.357-361.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W., Rothstein R. J. Yeast transformation: a model system for the study of recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6354–6358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilone G. J., Kunkee R. E., Webb A. D. Chemical characterization of wines fermented with various malo-lactic bacteria. Appl Microbiol. 1966 Jul;14(4):608–615. doi: 10.1128/am.14.4.608-615.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütz M., Radler F. Das Vorkommen von Malatenzym und Malo-Lactat-Enzym bei verschiedenen Milchsäurebakterien. Arch Mikrobiol. 1974 Mar 28;96(4):329–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soberon X., Covarrubias L., Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. IV. Deletion derivatives of pBR322 and pBR325. Gene. 1980 May;9(3-4):287–305. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90328-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tschumper G., Carbon J. Sequence of a yeast DNA fragment containing a chromosomal replicator and the TRP1 gene. Gene. 1980 Jul;10(2):157–166. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90133-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]