Abstract
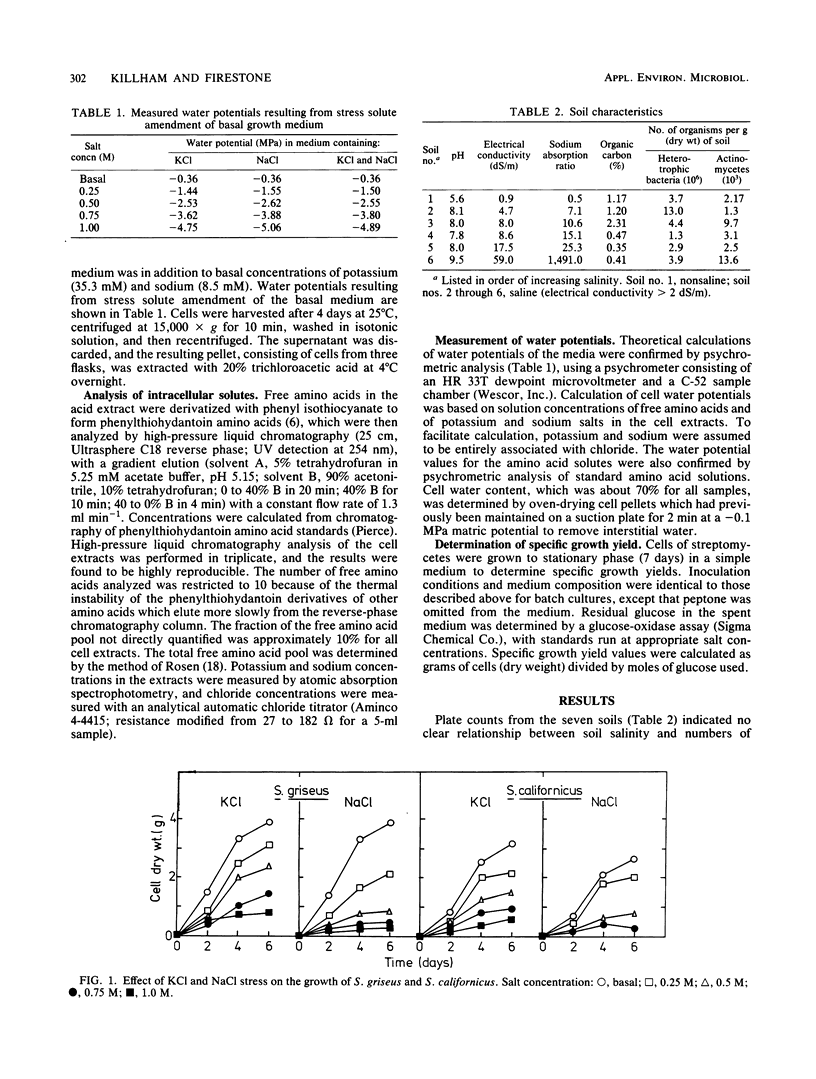
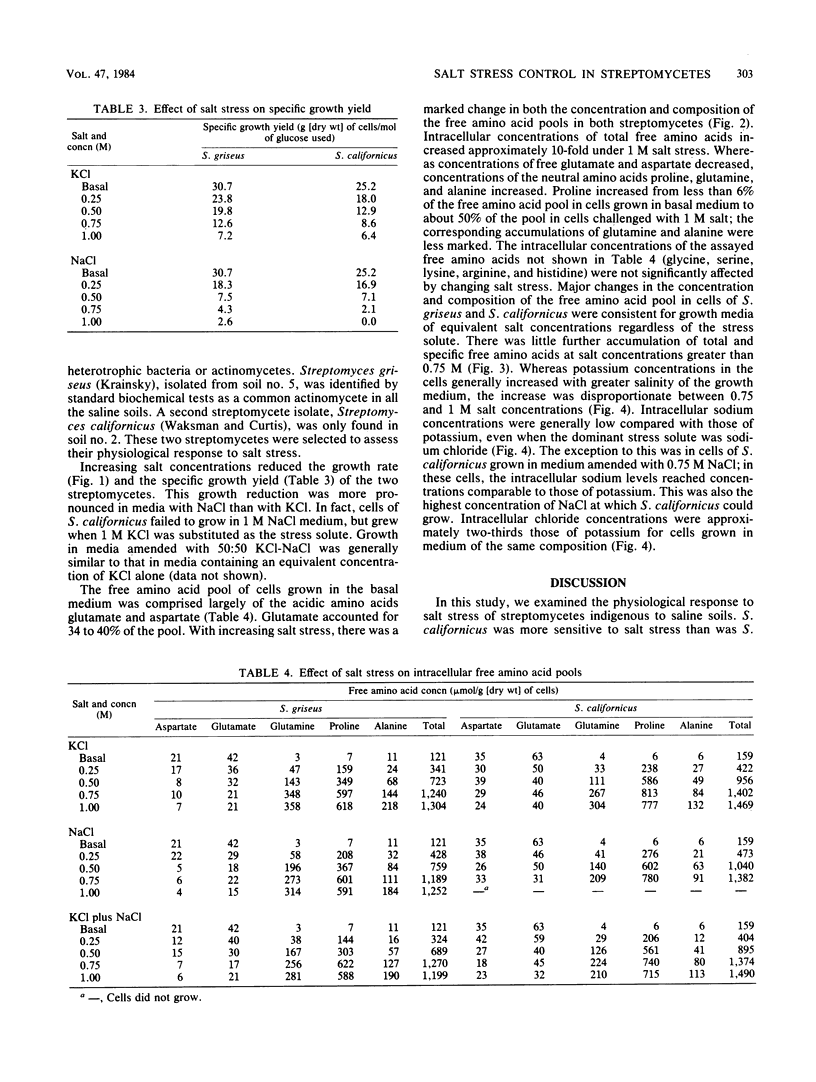
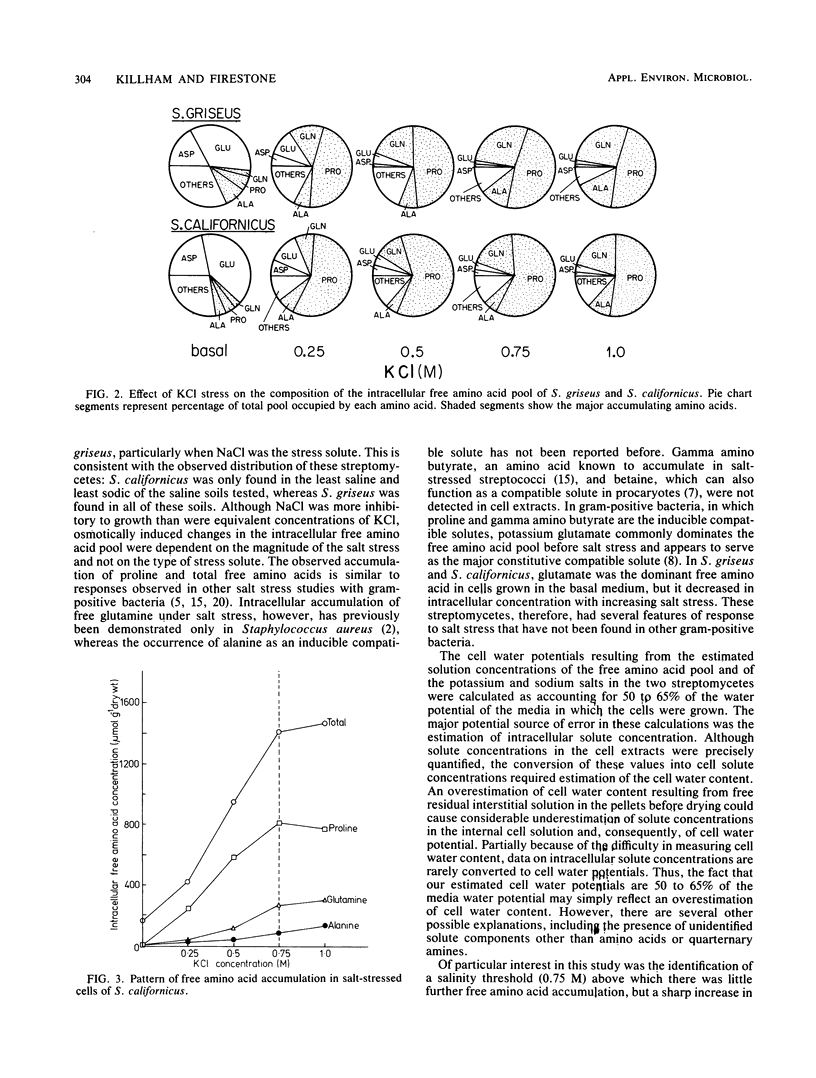
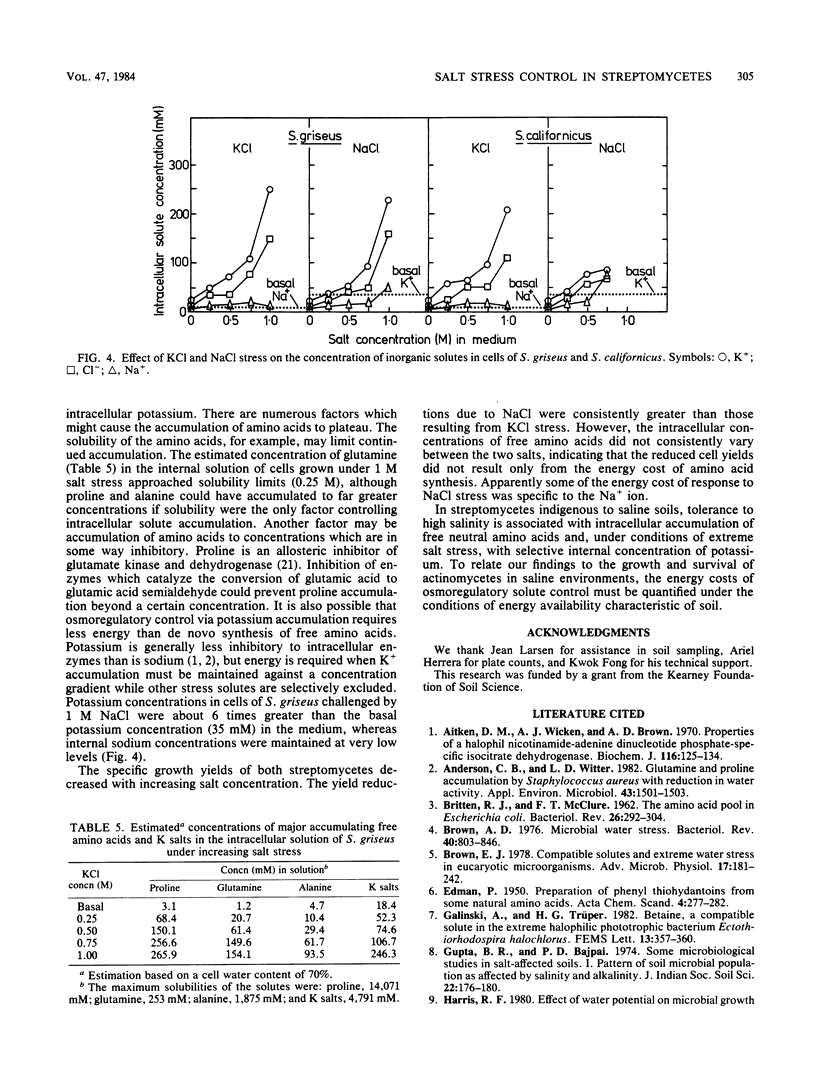
Actinomycetes were isolated from a number of saline and saline-sodic California soils. From these isolates, two species of Streptomyces (S. griseus and S. californicus) were selected to assess their physiological response to salinity. NaCl was more inhibitory to growth rates and specific growth yields than were equivalent concentrations of KCl. Intracellular concentrations of the free amino acid pool increased in response to salt stress. Whereas the neutral free amino acids proline, glutamine, and alanine accumulated as salinity increased, concentrations of the acidic free amino acids glutamate and aspartate were reduced. Accumulation of free amino acids by streptomycetes under salt stress suggests a response typical of procaryotes, although the specific amino acids involved differ from those associated with other gram-positive bacteria. Above a salinity threshold of about 0.75 M (−3.8 MPa), there was little further intracellular accumulation of free amino acids, whereas accumulation of K+ salts sharply increased.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken D. M., Wicken A. J., Brown A. D. Properties of a halophil nicotinamide--adenine dinucleotide phosphate-specific isocitrate dehydrogenase. Preliminary studies of the salt relations and kinetics of the crude enzyme. Biochem J. 1970 Jan;116(1):125–134. doi: 10.1042/bj1160125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. B., Witter L. D. Glutamine and proline accumulation by Staphylococcus aureus with reduction in water activity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jun;43(6):1501–1503. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.6.1501-1503.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRITTEN R. J., McCLURE F. T. The amino acid pool in Escherichia coli. Bacteriol Rev. 1962 Sep;26:292–335. doi: 10.1128/br.26.3.292-335.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. D. Compatible solutes and extreme water stress in eukaryotic micro-organisms. Adv Microb Physiol. 1978;17:181–242. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60058-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. D. Microbial water stress. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Dec;40(4):803–846. doi: 10.1128/br.40.4.803-846.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hua S. S., Tsai V. Y., Lichens G. M., Noma A. T. Accumulation of Amino Acids in Rhizobium sp. Strain WR1001 in Response to Sodium Chloride Salinity. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jul;44(1):135–140. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.1.135-140.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINGAPPA Y., LOCKWOOD J. L. A chitin medium for isolation, growth and maintenance of actinomycetes. Nature. 1961 Jan 14;189:158–159. doi: 10.1038/189158a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makemson J. C., Hastings J. W. Glutamate functions in osmoregulation in a marine bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jul;38(1):178–180. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.1.178-180.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Measures J. C. Role of amino acids in osmoregulation of non-halophilic bacteria. Nature. 1975 Oct 2;257(5525):398–400. doi: 10.1038/257398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEN H. A modified ninhydrin colorimetric analysis for amino acids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Mar;67(1):10–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schobert B. Is there an osmotic regulatory mechanism in algae and higher plants? J Theor Biol. 1977 Sep 7;68(1):17–26. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(77)90224-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempest D. W., Meers J. L., Brown C. M. Influence of environment on the content and composition of microbial free amino acid pools. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(2):171–185. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



