Abstract
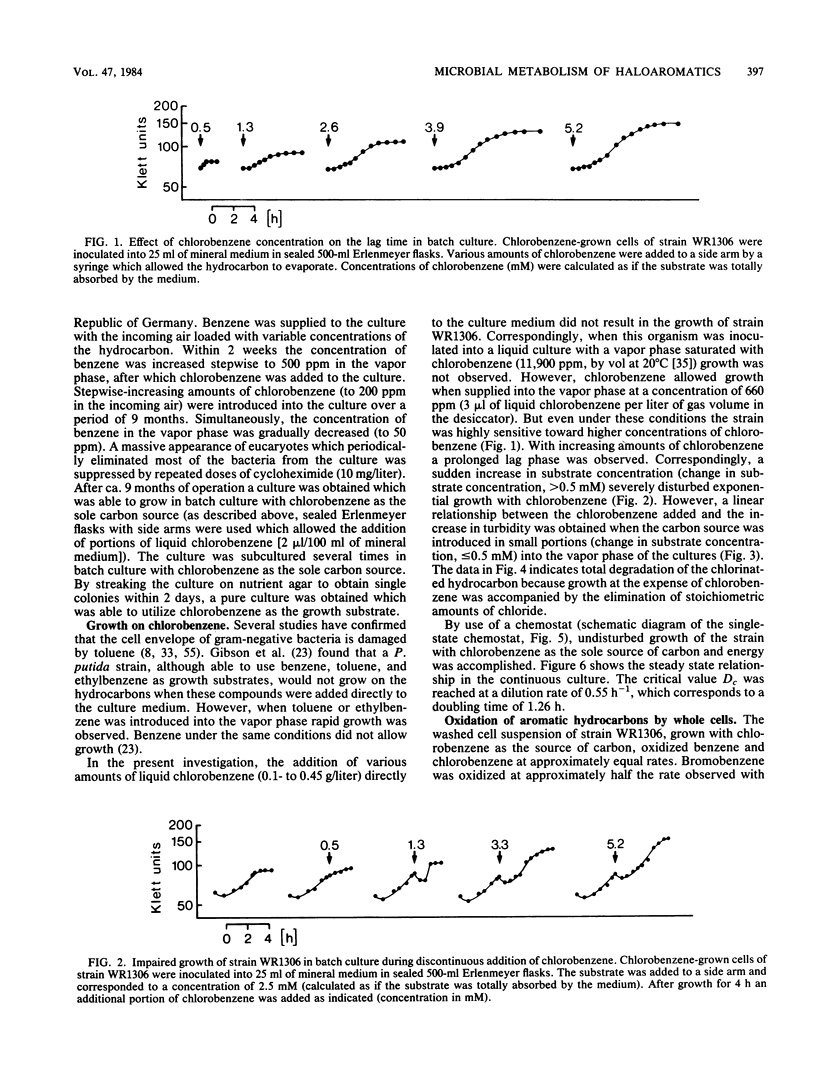
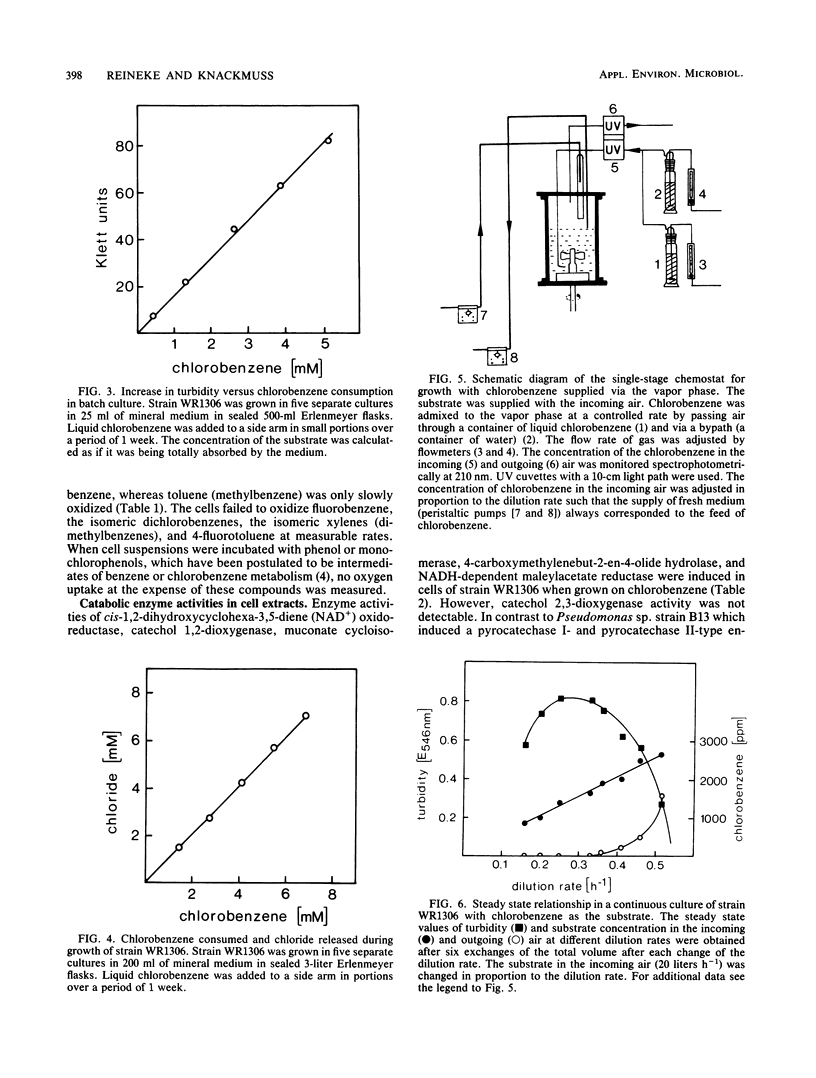
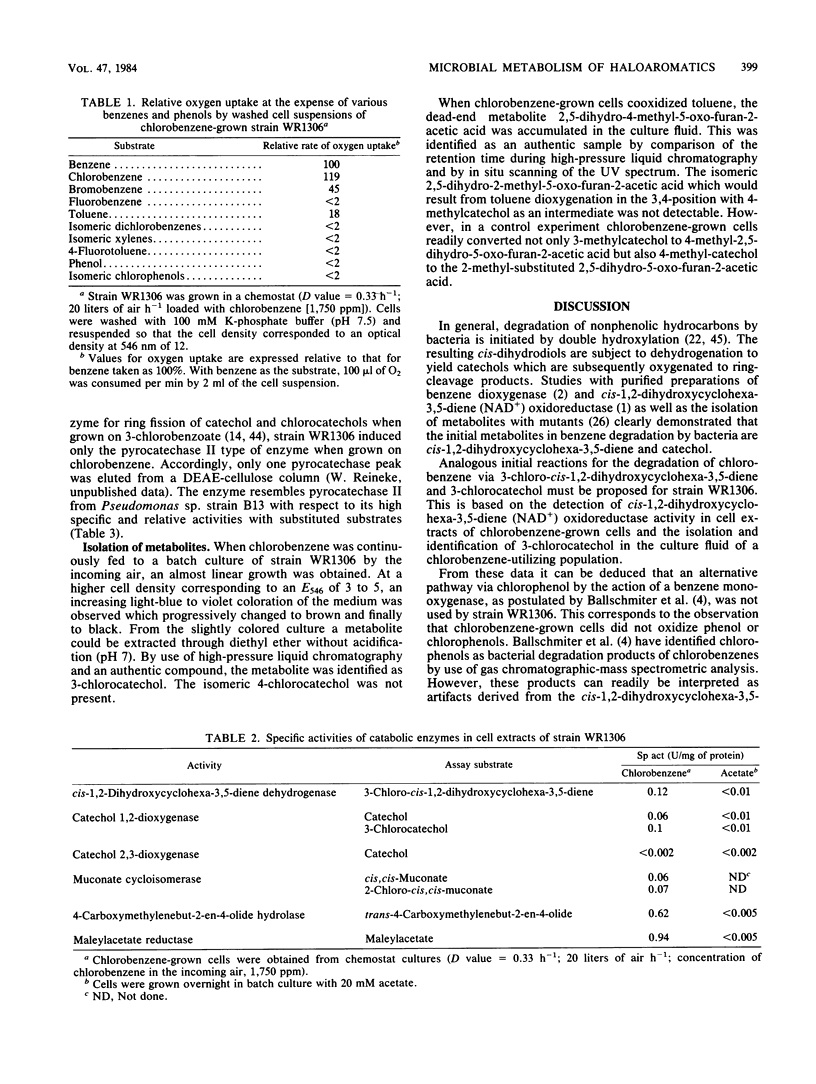
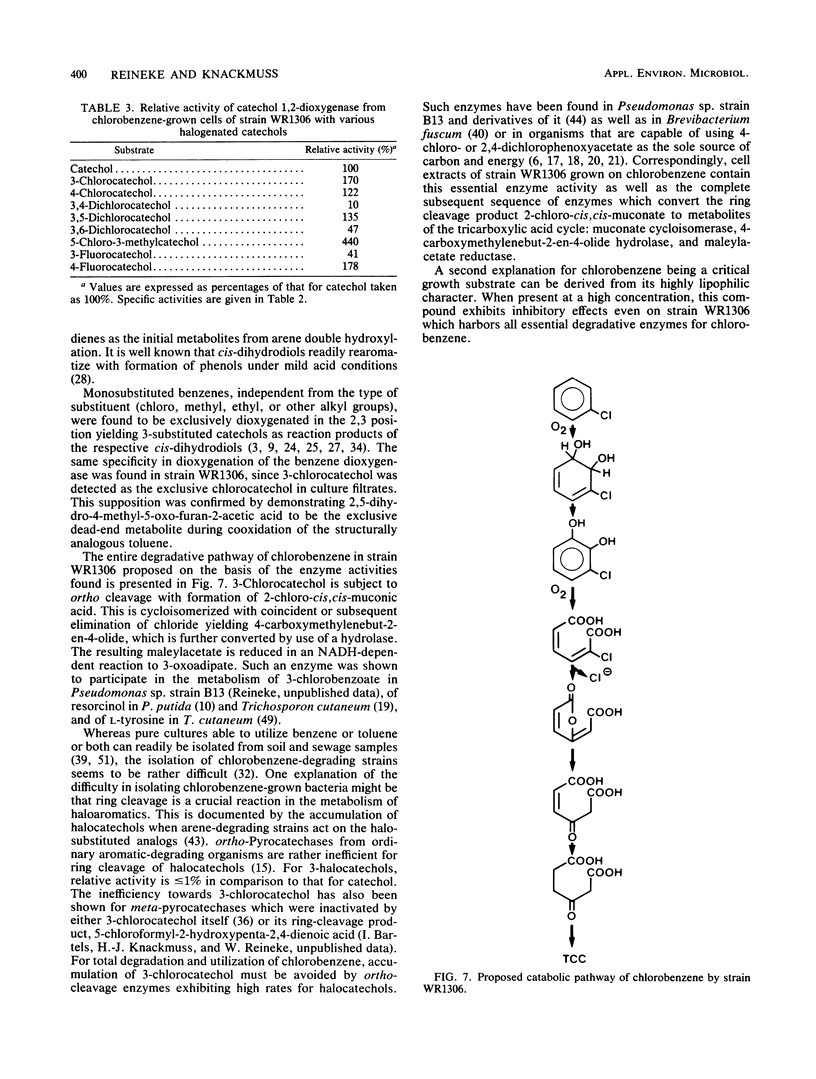
A chlorobenzene-degrading bacterium was isolated by continuous enrichment from a mixture of soil and sewage samples. This organism, strain WR1306, was grown in a chemostat on a mineral medium with chlorobenzene being supplied through the vapor phase with a critical Dc value at a dilution rate of 0.55 h-1. Maximum growth rates in batch culture were accomplished at substrate concentrations of less than or equal to 0.5 mM in the culture medium. During growth on chlorobenzene, stoichiometric amounts of chloride were released. Respiration data and enzyme activities in cell extracts as well as the isolation of 3-chlorocatechol from the culture fluid are consistent with the degradation of chlorobenzene via 3-chloro-cis-1,2-dihydroxycyclohexa-3,5-diene, 3-chlorocatechol, 2-chloro-cis,cis-muconate, trans-4-carboxymethylenebut-2-en-4-olide, maleylacetate, and 3-oxoadipate.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Axcell B. C., Geary P. J. Purification and some properties of a soluble benzene-oxidizing system from a strain of Pseudomonas. Biochem J. 1975 Jan;146(1):173–183. doi: 10.1042/bj1460173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Axcell B. C., Geary P. J. The metabolism of benzene by bacteria. Purification and some properties of the enzyme cis-1,2-dihydroxycyclohexa-3,5-diene (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) oxidoreductase (cis-benzene glycol dehydrogenase). Biochem J. 1973 Dec;136(4):927–934. doi: 10.1042/bj1360927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baggi G., Catelani D., Galli E., Treccani V. The microbial degradation of phenylalkanes. 2-Phenylbutane, 3-phenylpentane, 3-phenyldodecane and 4-phenylheptane. Biochem J. 1972 Mar;126(5):1091–1097. doi: 10.1042/bj1261091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAUS D., WALKER N. THE DECOMPOSITION OF TOLUENE BY SOIL BACTERIA. J Gen Microbiol. 1964 Jul;36:107–122. doi: 10.1099/00221287-36-1-107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catelani D., Colombi A., Sorlini C., Treccani V. Metabolism of quaternary carbon compounds: 2,2-dimethylheptane and tertbutylbenzene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 Oct;34(4):351–354. doi: 10.1128/aem.34.4.351-354.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman P. J., Ribbons D. W. Metabolism of resorcinylic compounds by bacteria: alternative pathways for resorcinol catabolism in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1976 Mar;125(3):985–998. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.3.985-998.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn E., Hellwig M., Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Isolation and characterization of a 3-chlorobenzoate degrading pseudomonad. Arch Microbiol. 1974;99(1):61–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00696222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn E., Knackmuss H. J. Chemical structure and biodegradability of halogenated aromatic compounds. Substituent effects on 1,2-dioxygenation of catechol. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 15;174(1):85–94. doi: 10.1042/bj1740085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn E., Knackmuss H. J. Chemical structure and biodegradability of halogenated aromatic compounds. Two catechol 1,2-dioxygenases from a 3-chlorobenzoate-grown pseudomonad. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 15;174(1):73–84. doi: 10.1042/bj1740073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson D. Studies on Some Lake-Mud Strains of Micromonospora. J Bacteriol. 1941 Mar;41(3):277–300. doi: 10.1128/jb.41.3.277-300.1941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. C., Smith B. S., Fernley H. N., Davies J. I. Bacterial metabolism of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):543–551. doi: 10.1042/bj1220543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. C., Smith B. S., Moss P., Fernley H. N. Bacterial metabolism of 4-chlorophenoxyacetate. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):509–517. doi: 10.1042/bj1220509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaal A., Neujahr H. Y. Metabolism of phenol and resorcinol in Trichosporon cutaneum. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):13–21. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.13-21.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaunt J. K., Evans W. C. Metabolism of 4-chloro-2-methylphenoxyacetate by a soil pseudomonad. Preliminary evidence for the metabolic pathway. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):519–526. doi: 10.1042/bj1220519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaunt J. K., Evans W. C. Metabolism of 4-chloro-2-methylphenoxyacetate by a soil pseudomonad. Ring-fission, lactonizing and delactonizing enzymes. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):533–542. doi: 10.1042/bj1220533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Cardini G. E., Maseles F. C., Kallio R. E. Incorporation of oxygen-18 into benzene by Pseudomonas putida. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 31;9(7):1631–1635. doi: 10.1021/bi00809a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Gschwendt B., Yeh W. K., Kobal V. M. Initial reactions in the oxidation of ethylbenzene by Pseudomonas putida. Biochemistry. 1973 Apr 10;12(8):1520–1528. doi: 10.1021/bi00732a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Hensley M., Yoshioka H., Mabry T. J. Formation of (+)-cis-2,3-dihydroxy-1-methylcyclohexa-4,6-diene from toluene by Pseudomonas putida. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 31;9(7):1626–1630. doi: 10.1021/bi00809a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Koch J. R., Kallio R. E. Oxidative degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons by microorganisms. I. Enzymatic formation of catechol from benzene. Biochemistry. 1968 Jul;7(7):2653–2662. doi: 10.1021/bi00847a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Koch J. R., Schuld C. L., Kallio R. E. Oxidative degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons by microorganisms. II. Metabolism of halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons. Biochemistry. 1968 Nov;7(11):3795–3802. doi: 10.1021/bi00851a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Mahadevan V., Jerina D. M., Yogi H., Yeh H. J. Oxidation of the carcinogens benzo [a] pyrene and benzo [a] anthracene to dihydrodiols by a bacterium. Science. 1975 Jul 25;189(4199):295–297. doi: 10.1126/science.1145203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haider K., Jagnow G., Kohnen R., Lim S. U. Abbau chlorierter Benzole, Phenole und Cyclohexan-Derivate durch Benzol und Phenol verwertende Bodenbakterien unter aeroben Bedingungen. Arch Microbiol. 1974 Mar 7;96(3):183–200. doi: 10.1007/BF00590175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann J., Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Metabolism of 3-chloro-, 4-chloro-, and 3,5-dichlorobenzoate by a pseudomonad. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):421–428. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.421-428.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Högn T., Jaenicke L. Benzene metabolism of Moraxella species. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Oct;30(2):369–375. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb02107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson R. W., DeMoss J. A. Effects of toluene on Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1965 Nov;90(5):1420–1425. doi: 10.1128/jb.90.5.1420-1425.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klecka G. M., Gibson D. T. Inhibition of catechol 2,3-dioxygenase from Pseudomonas putida by 3-chlorocatechol. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 May;41(5):1159–1165. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.5.1159-1165.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARR E. K., STONE R. W. Bacterial oxidation of benzene. J Bacteriol. 1961 Mar;81:425–430. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.3.425-430.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenna E. J., Kallio R. E. The biology of hydrocarbons. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1965;19:183–208. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.19.100165.001151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAKAGAWA H., INOUE H., TAKEDA Y. CHARACTERISTICS OF CATECHOL OXYGENASE FROM BREVIBACTERIUM FUSCUM. J Biochem. 1963 Jul;54:65–74. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reineke W., Jeenes D. J., Williams P. A., Knackmuss H. J. TOL plasmid pWW0 in constructed halobenzoate-degrading Pseudomonas strains: prevention of meta pathway. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):195–201. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.195-201.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Construction of haloaromatics utilising bacteria. Nature. 1979 Feb 1;277(5695):385–386. doi: 10.1038/277385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Hybrid pathway for chlorobenzoate metabolism in Pseudomonas sp. B13 derivatives. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):467–473. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.467-473.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt E., Knackmuss H. J. Chemical structure and biodegradability of halogenated aromatic compounds. Conversion of chlorinated muconic acids into maleoylacetic acid. Biochem J. 1980 Oct 15;192(1):339–347. doi: 10.1042/bj1920339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A., Hellwig M., Dorn E., Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Critical Reactions in Fluorobenzoic Acid Degradation by Pseudomonas sp. B13. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jan;39(1):58–67. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.1.58-67.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparnins V. L., Burbee D. G., Dagley S. Catabolism of L-tyrosine in Trichosporon cutaneum. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):425–430. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.425-430.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIELAND T., GRISS G., HACCIUS B. Un tersuchungen zur mikrobiellen Benzoloxydation. I. Nachweis und Chemismus des Benzolabbaus. Arch Mikrobiol. 1958;28(4):383–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woldringh C. L. Effects of toluene and phenethyl alcohol on the ultrastructure of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Jun;114(3):1359–1361. doi: 10.1128/jb.114.3.1359-1361.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Linden A. C., Thijsse G. J. The mechanisms of microbial oxidations of petroleum hydrocarbons. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1965;27:469–546. doi: 10.1002/9780470122723.ch10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



