Abstract
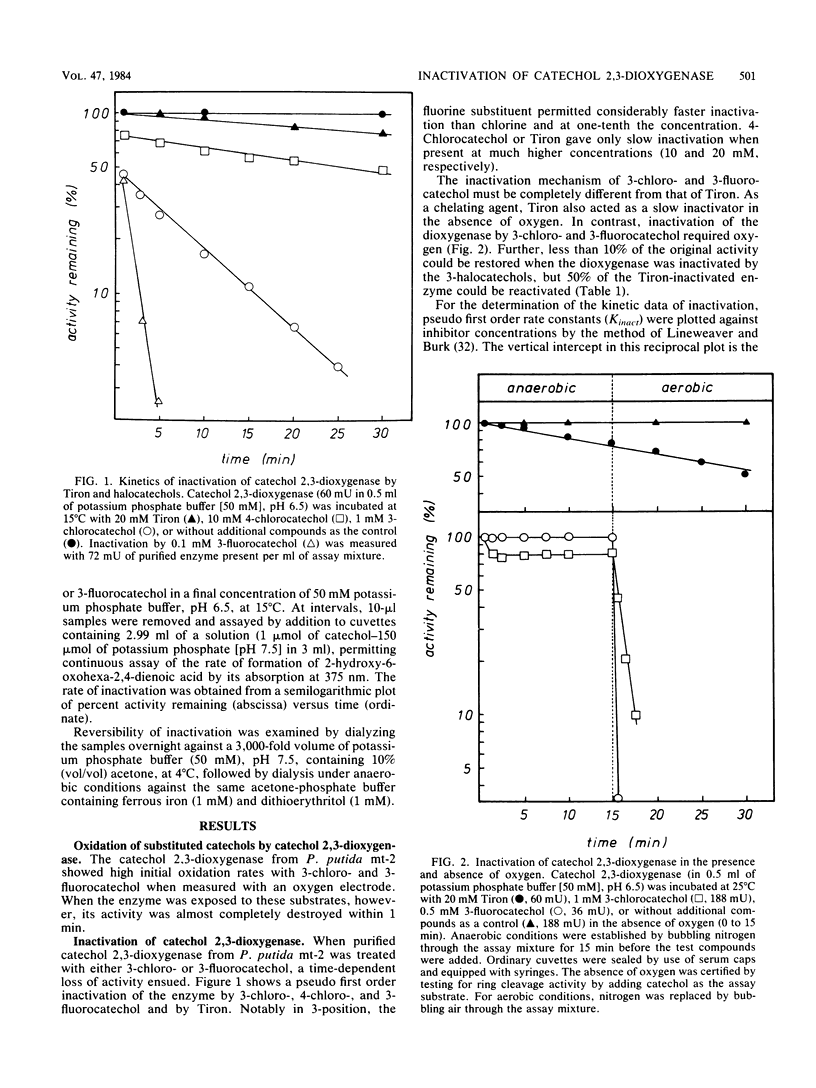
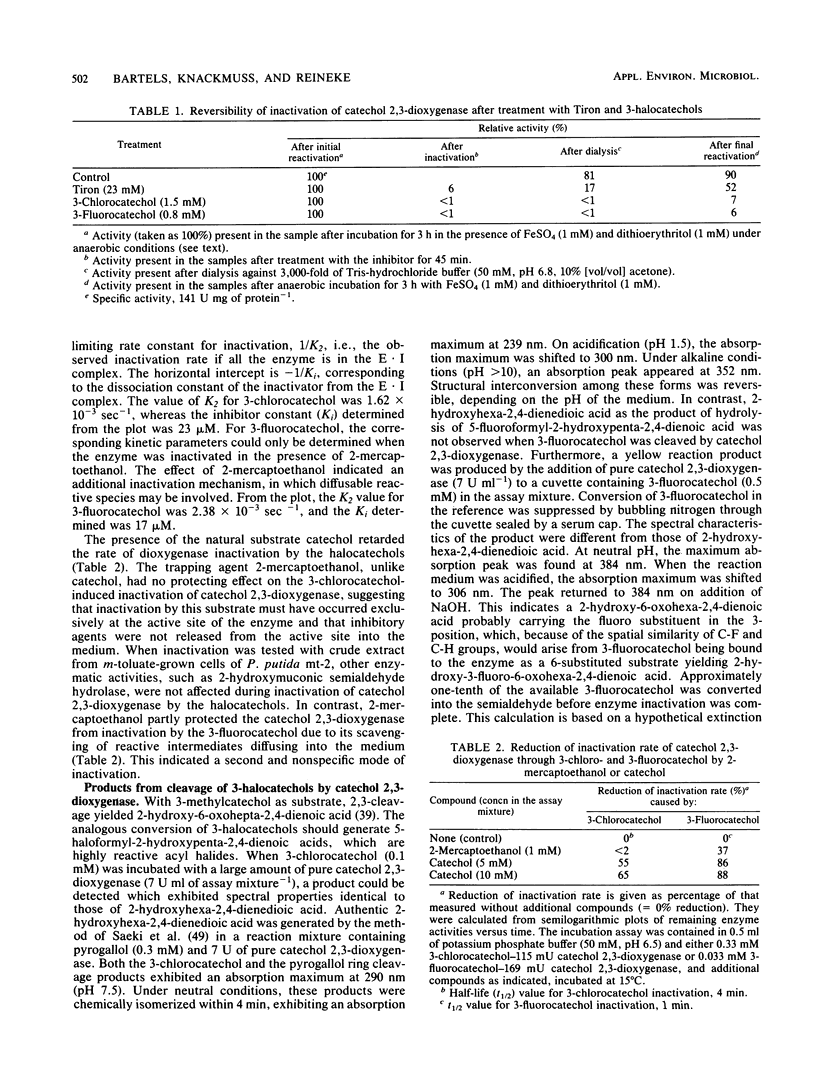
The inactivation of catechol 2,3-dioxygenase from Pseudomonas putida mt-2 by 3-chloro- and 3-fluorocatechol and the iron-chelating agent Tiron (catechol-3,5-disulfonate) was studied. Whereas inactivation by Tiron is an oxygen-independent and mostly reversible process, inactivation by the 3-halocatechols was only observed in the presence of oxygen and was largely irreversible. The rate constants for inactivation (K2) were 1.62 × 10−3 sec−1 for 3-chlorocatechol and 2.38 × 10−3 sec−1 for 3-fluorocatechol. The inhibitor constants (Ki) were 23 μM for 3-chlorocatechol and 17 μM for 3-fluorocatechol. The kinetic data for 3-fluorocatechol could only be obtained in the presence of 2-mercaptoethanol. Besides inactivated enzyme, some 2-hydroxyhexa-2,4-diendioic acid was formed from 3-chlorocatechol, suggesting 5-chloroformyl-2-hydroxypenta-2,4-dienoic acid as the actual suicide product of meta-cleavage. A side product of 3-fluorocatechol cleavage is a yellow compound with the spectral characteristics of a 2-hydroxy-6-oxohexa-2,4-dienoic acid indicating 1,6-cleavage. Rates of inactivation by 3-fluorocatechol were reduced in the presence of superoxide dismutase, catalase, formate, and mannitol, which implies that superoxide anion, hydrogen peroxide, and hydroxyl radical exhibit additional inactivation.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong D. A., Buchanan J. D. Reactions of O-.2, H2O2 and other oxidants with sulfhydryl enzymes. Photochem Photobiol. 1978 Oct-Nov;28(4-5):743–755. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1978.tb07011.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayly R. C., Dagley S. Oxoenoic acids as metabolites in the bacterial degradation of catechols. Biochem J. 1969 Feb;111(3):303–307. doi: 10.1042/bj1110303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bird J. A., Cain R. B. Microbial degradation of alkylbenzenesulphonates. Metabolism of homologues of short alkyl-chain length by an Alcaligenes sp. Biochem J. 1974 May;140(2):121–134. doi: 10.1042/bj1400121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn E., Hellwig M., Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Isolation and characterization of a 3-chlorobenzoate degrading pseudomonad. Arch Microbiol. 1974;99(1):61–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00696222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn E., Knackmuss H. J. Chemical structure and biodegradability of halogenated aromatic compounds. Substituent effects on 1,2-dioxygenation of catechol. Biochem J. 1978 Jul 15;174(1):85–94. doi: 10.1042/bj1740085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. C., Smith B. S., Fernley H. N., Davies J. I. Bacterial metabolism of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):543–551. doi: 10.1042/bj1220543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. C., Smith B. S., Moss P., Fernley H. N. Bacterial metabolism of 4-chlorophenoxyacetate. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):509–517. doi: 10.1042/bj1220509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaunt J. K., Evans W. C. Metabolism of 4-chloro-2-methylphenoxyacetate by a soil pseudomonad. Preliminary evidence for the metabolic pathway. Biochem J. 1971 May;122(4):519–526. doi: 10.1042/bj1220519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. T., Koch J. R., Schuld C. L., Kallio R. E. Oxidative degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons by microorganisms. II. Metabolism of halogenated aromatic hydrocarbons. Biochemistry. 1968 Nov;7(11):3795–3802. doi: 10.1021/bi00851a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann J., Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Metabolism of 3-chloro-, 4-chloro-, and 3,5-dichlorobenzoate by a pseudomonad. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Mar;37(3):421–428. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.3.421-428.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Nakazawa A., Nozaki M., Hayaishi O. Studies on metapyrocatechase. IV. Circular dichroism and optical rotatory dispersion. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 10;246(19):5882–5887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori K., Hashimoto T., Nozaki M. Kinetic studies on the reaction mechanism of dioxygenases. J Biochem. 1973 Aug;74(2):375–384. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath R. S., Alexander M. Cometabolism of m-chlorobenzoate by an Arthrobacter. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Aug;20(2):254–258. doi: 10.1128/am.20.2.254-258.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath R. S. Cometabolism of the herbicide 2,3,6-trichlorobenzoate. J Agric Food Chem. 1971 Mar-Apr;19(2):291–293. doi: 10.1021/jf60174a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ICHIHARA A., ADACHI K., HOSOKAWA K., TAKEDA Y. The enzymatic hydroxylation of aromatic carboxylic acids; substrate specificities of anthranilate and benzoate oxidases. J Biol Chem. 1962 Jul;237:2296–2302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klecka G. M., Gibson D. T. Inhibition of catechol 2,3-dioxygenase from Pseudomonas putida by 3-chlorocatechol. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 May;41(5):1159–1165. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.5.1159-1165.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lal M., Lin W. S., Gaucher G. M., Armstrong D. A. The repair, protection and sensitization of papain with respect to inactivation by H2O2 and OH: effects of dithiothreitol, penicillamine, cystine and penicillamine disulphide. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1975 Dec;28(6):549–564. doi: 10.1080/09553007514551411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin W. S., Armstrong D. A. Glutathione mediation of papain inactivation by hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl radicals. Radiat Res. 1977 Mar;69(3):434–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matheson I. B., Etheridge R. D., Kratowich N. R., Lee J. The quenching of singlet oxygen by amino acids and proteins. Photochem Photobiol. 1975 Mar;21(3):165–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1975.tb06647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra H. P. Generation of superoxide free radical during the autoxidation of thiols. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2151–2155. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOZAKI M., KAGAMIYAMA H., HAYAISHI O. METAPYROCATECHASE. I. PURIFICATION, CRYSTALLIZATION AND SOME PROPERTIES. Biochem Z. 1963;338:582–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki M., Kotani S., Ono K., Seno S. Metapyrocatechase. 3. Substrate specificity and mode of ring fission. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 11;220(2):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki M., Ono K., Nakazawa T., Kotani S., Hayaishi O. Metapyrocatechase. II. The role of iron and sulfhydryl groups. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 25;243(10):2682–2690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki M. Oxygenases and dioxygenases. Top Curr Chem. 1979;78:145–186. doi: 10.1007/BFb0048193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERS R. A. Mechanism of the toxicity of the active constituent of Dichapetalum cymosum and related compounds. Adv Enzymol Relat Subj Biochem. 1957;18:113–159. doi: 10.1002/9780470122631.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando R. R. Chemistry and enzymology of kcat inhibitors. Science. 1974 Jul 26;185(4148):320–324. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4148.320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando R. R. Mechanism-based irreversible enzyme inhibitors. Methods Enzymol. 1977;46:28–41. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(77)46007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reineke W., Jeenes D. J., Williams P. A., Knackmuss H. J. TOL plasmid pWW0 in constructed halobenzoate-degrading Pseudomonas strains: prevention of meta pathway. J Bacteriol. 1982 Apr;150(1):195–201. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.1.195-201.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Hybrid pathway for chlorobenzoate metabolism in Pseudomonas sp. B13 derivatives. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):467–473. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.467-473.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saeki Y., Nozaki M., Senoh S. Cleavage of pyrogallol by non-heme iron-containing dioxygenases. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8465–8471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A., Hellwig M., Dorn E., Reineke W., Knackmuss H. J. Critical Reactions in Fluorobenzoic Acid Degradation by Pseudomonas sp. B13. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Jan;39(1):58–67. doi: 10.1128/aem.39.1.58-67.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spokes J. R., Walker N. Chlorophenol and chlorobenzoic acid co-metabolism by different genera of soil bacteria. Arch Mikrobiol. 1974 Mar 4;96(2):125–134. doi: 10.1007/BF00590169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomita M., Irie M., Ukita T. Sensitized photooxidation of histidine and its derivatives. Products and mechanism of the reaction. Biochemistry. 1969 Dec;8(12):5149–5160. doi: 10.1021/bi00840a069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C., Cromartie T., Marcotte P., Spencer R. Suicide substrates for flavoprotein enzymes. Methods Enzymol. 1978;53:437–448. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)53048-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh C. Recent developments in suicide substrates and other active site-directed inactivating agents of specific target enzymes. Horiz Biochem Biophys. 1977;3:36–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigmore G. J., Ribbons D. W. Selective enrichment of Pseudomonas spp. defective in catabolism after exposure to halogenated substrates. J Bacteriol. 1981 Jun;146(3):920–927. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.3.920-927.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigmore G. J., Ribbons D. W. p-Cymene pathway in Pseudomonas putida: selective enrichment of defective mutants by using halogenated substrate analogs. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):816–824. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.816-824.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



