Abstract
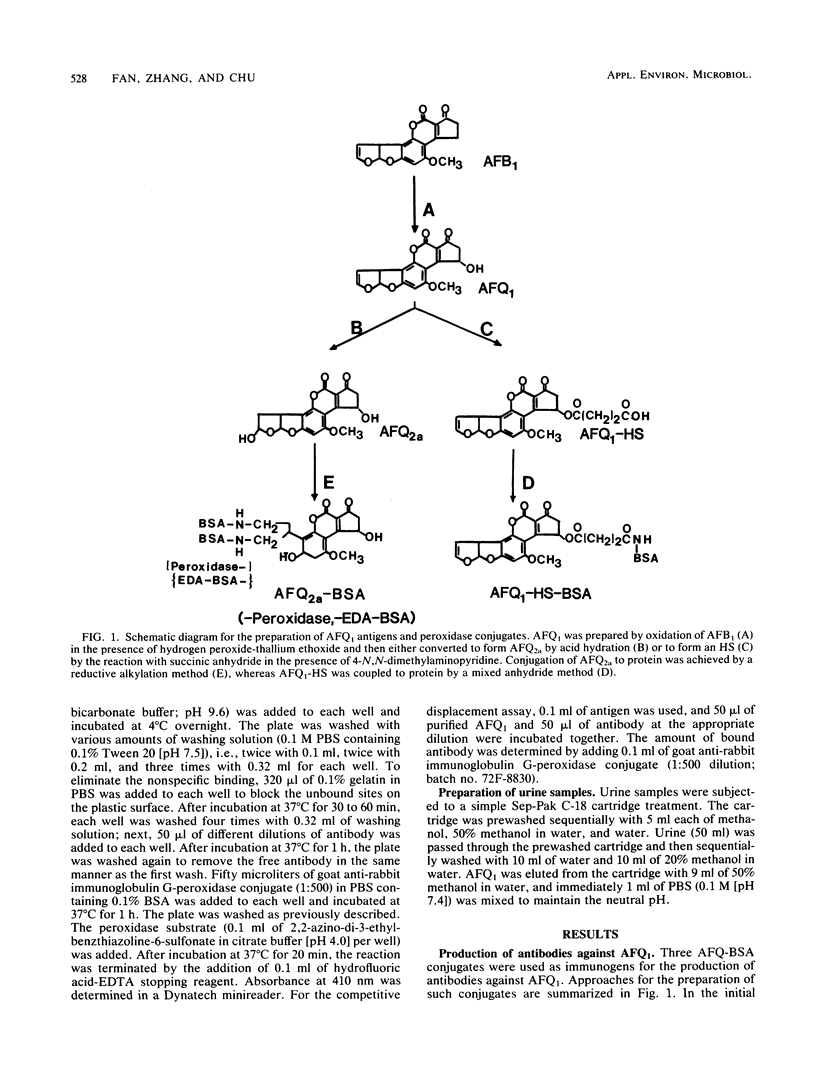
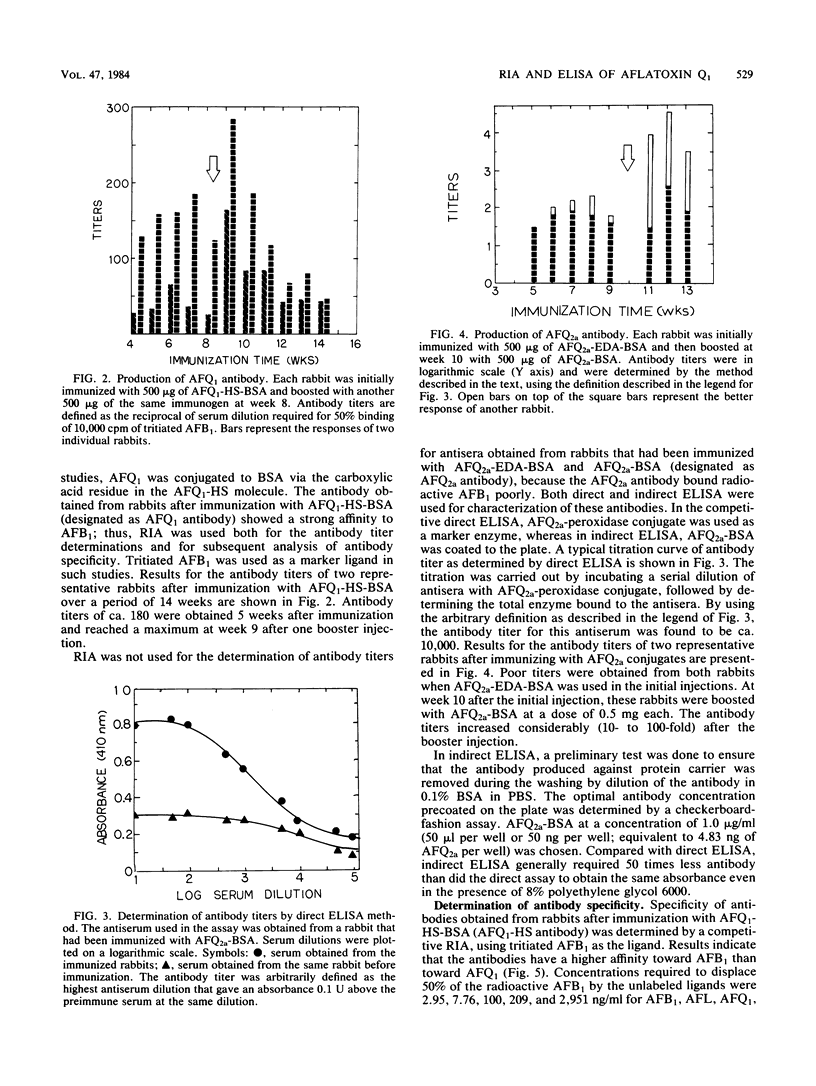
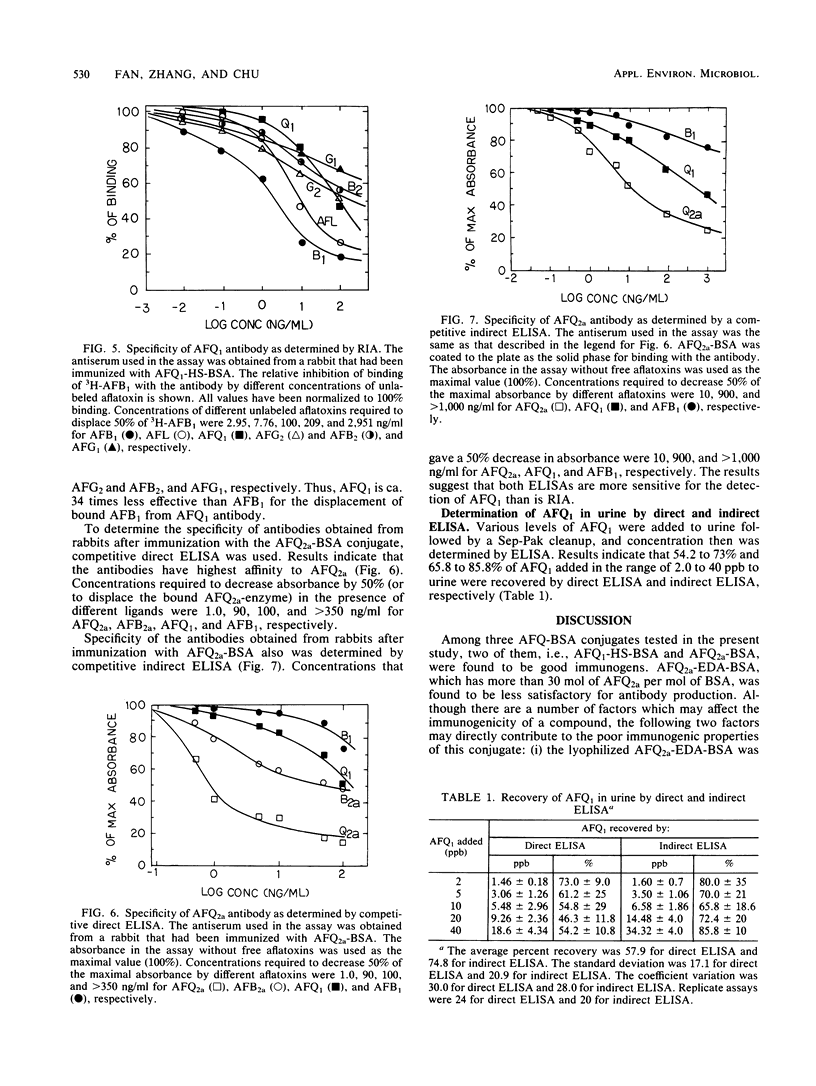
Antibodies against aflatoxin Q1 (AFQ1) were obtained from rabbits after immunization of either AFQ1-hemisuccinate or AFQ2a conjugated to bovine serum albumin. Both radioimmunoassay and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assaY (ELISA) were used for the determination of antibody titers and specificities. Antibodies obtained from rabbits after immunization with AFQ1-hemisuccinate-bovine serum albumin had the highest affinity to aflatoxin B1, whereas antibodies obtained from rabbits after immunization with AFQ2a-bovine serum albumin bound most effectively with AFQ2a. AFQ2a antibody was selected for the subsequent direct and indirect ELISA for the detection of AFQ1 in biological fluids. When AFQ2a-peroxidase and AFQ2a antibody were used, direct ELISA was able to detect as low as 2 ppb (ng/ml) of AFQ1 spiked in the urine samples that had been subjected to a Sep-Pak cleanup treatment. In indirect ELISA in which the antigen (AFQ2a-bovine serum albumin) was coated to the solid phase followed by reaction with rabbit antibody and goat anti-rabbit immunoglobulin G-peroxidase conjugate, 50-fold less antibody was used without sacrificing sensitivity. Recoveries of AFQ1 added to urine samples (2 to 40 ppb) were 46.3 to 73% and 65.8 to 85.8% for direct and indirect ELISA, respectively.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Büchi G. H., Müller P. M., Roebuck B. D., Wogan G. N. Aflatoxin Q1: a major metabolite of aflatoxin B1 produced by human liver. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1974 Aug;8(4):585–592. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Büchi G., Luk K., Müller P. M. Synthesis of aflatoxin Q1. J Org Chem. 1975 Nov 14;40(23):3458–3459. doi: 10.1021/jo00911a040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu F. S., Chang F. C., Hinsdill R. D. Production of antibody against ochratoxin A. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jun;31(6):831–835. doi: 10.1128/aem.31.6.831-835.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu F. S. Chromatography of crude aflatoxins on adsorbosil-5. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1971 Nov;54(6):1304–1306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu F. S., Grossman S., Wei R. D., Mirocha C. J. Production of antibody against T-2 toxin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jan;37(1):104–108. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.1.104-108.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu F. S., Ueno I. Production of antibody against aflatoxin B1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1977 May;33(5):1125–1128. doi: 10.1128/aem.33.5.1125-1128.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalezios J. I., Hsieh D. P., Wogan G. N. Excretion and metabolism of orally administered aflatoxin B1 by rhesus monkeys. Food Cosmet Toxicol. 1973 Aug;11(4):605–616. doi: 10.1016/s0015-6264(73)80331-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Nakib O., Pestka J. J., Chu F. S. Determination of aflatoxin B1 in corn, wheat, and peanut butter by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and solid phase radioimmunoassay. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1981 Sep;64(5):1077–1082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaur P. K., Lau H. P., Pestka J. J., Chu F. S. Production and characterization of aflatoxin B2a antiserum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Feb;41(2):478–482. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.2.478-482.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder W. O., Chu F. S. Production and characterization of antibody against aflatoxin M1. Experientia. 1979 Aug 15;35(8):1104–1107. doi: 10.1007/BF01949970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebert G. A., Pelham P. L., Pittman B. Determination of the optimal ammonium sulfate concentration for the fractionation of rabbit, sheep, horse, and goat antisera. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Jan;25(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/am.25.1.26-36.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsia M. T., Chu F. S. Reduction of aflatoxin B1 with zinc borohydride: an efficient preparation of aflatoxicol. Experientia. 1977 Sep 15;33(9):1132–1133. doi: 10.1007/BF01922282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh D. P., Dalezios J. I., Krieger R. I., Masri M. S., Haddon W. F. Use of monkey liver microsomes in production of aflatoxin Q1. J Agric Food Chem. 1974 May-Jun;22(3):515–517. doi: 10.1021/jf60193a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh D. P., Fitzell D. L., Miller J. L., Seiber J. N. High-pressure liquid chromatography of oxidative aflatoxin metabolites. J Chromatogr. 1976 Feb 18;117(2):474–479. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(76)80031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langone J. J., Van Vunakis H. Aflatoxin B; specific antibodies and their use in radioimmunoassay. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Mar;56(3):591–595. doi: 10.1093/jnci/56.3.591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masri M. S., Booth A. N., Hsieh D. P. Comparative metabolic conversion of aflatoxin B1 to M1 and Q1 by monkey, rat and chicken liver. Life Sci. 1974 Jul 15;15(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90208-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masri M. S., Haddon W. F., Lundin R. E., Hsieh D. P. Aflatoxin Q1. A newly identified major metabolite of aflatoxin B1 in monkey liver. J Agric Food Chem. 1974 May-Jun;22(3):512–515. doi: 10.1021/jf60193a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe S. A., Colley P. J., Neal G. E. A comparison of the effects of pretreatment with phenobarbitone and 3-methylcholanthrene on the metabolism of aflatoxin B1 by rat liver microsomes and isolated hepatocytes in vitro. Chem Biol Interact. 1981 May;35(2):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(81)90139-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neal G. E., Colley P. J. Some high-performance liquid-chromatographic studies of the metabolism of aflatoxins by rat liver microsomal preparations. Biochem J. 1978 Sep 15;174(3):839–851. doi: 10.1042/bj1740839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka J. J., Gaur P. K., Chu F. S. Quantitation of aflatoxin B1 and aflatoxin B1 antibody by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent microassay. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1980 Dec;40(6):1027–1031. doi: 10.1128/aem.40.6.1027-1031.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka J. J., Li Y., Harder W. O., Chu F. S. Comparison of radioimmunoassay and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for determining aflatoxin M1 in milk. J Assoc Off Anal Chem. 1981 Mar;64(2):294–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roebuck B. D., Wogan G. N. Species comparison of in vitro metabolism of aflatoxin B1. Cancer Res. 1977 Jun;37(6):1649–1656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salonen E. M., Vaheri A. Rapid solid-phase enzyme immunoassay for antibodies to viruses and other microbes: effects of polyethylene glycol. J Immunol Methods. 1981;41(1):95–103. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90277-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steyn P. S., Vleggaar R., Pitout M. J., Steyn M., Thiel P. G. 3-Hydroxyaflatoxin B1: a new metabolite of in vitro aflatoxin B1 metabolism by Vervet monkey (Cercopithecus aethiops) liver. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1974;(22):2551–2552. doi: 10.1039/p19740002551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stubblefield R. D., Shannon G. M., Shotwell O. L. Aflatoxins M1 and M2: preparation and purification. J Am Oil Chem Soc. 1970 Oct;47(10):389–390. doi: 10.1007/BF02632471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizawa H., Uchimaru R., Ueno Y. Metabolism of aflatoxin B1 in the isolated nuclei of rat liver. J Biochem. 1981 Feb;89(2):443–452. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



