Abstract
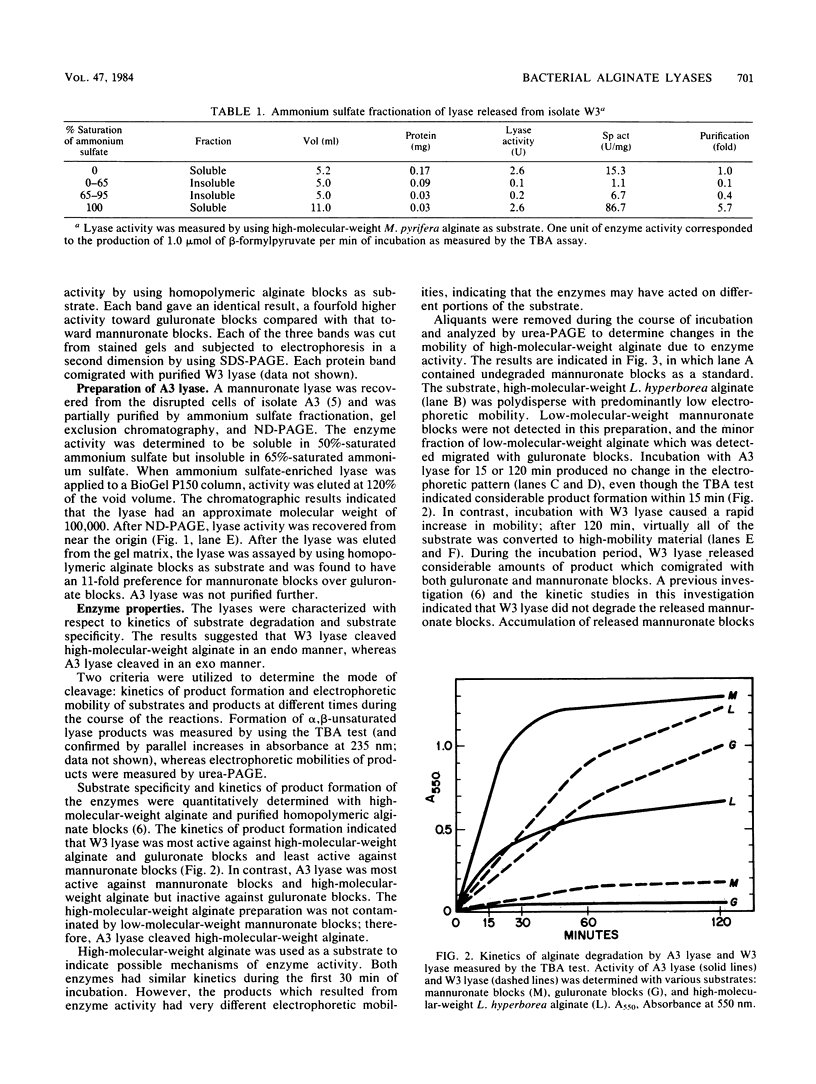
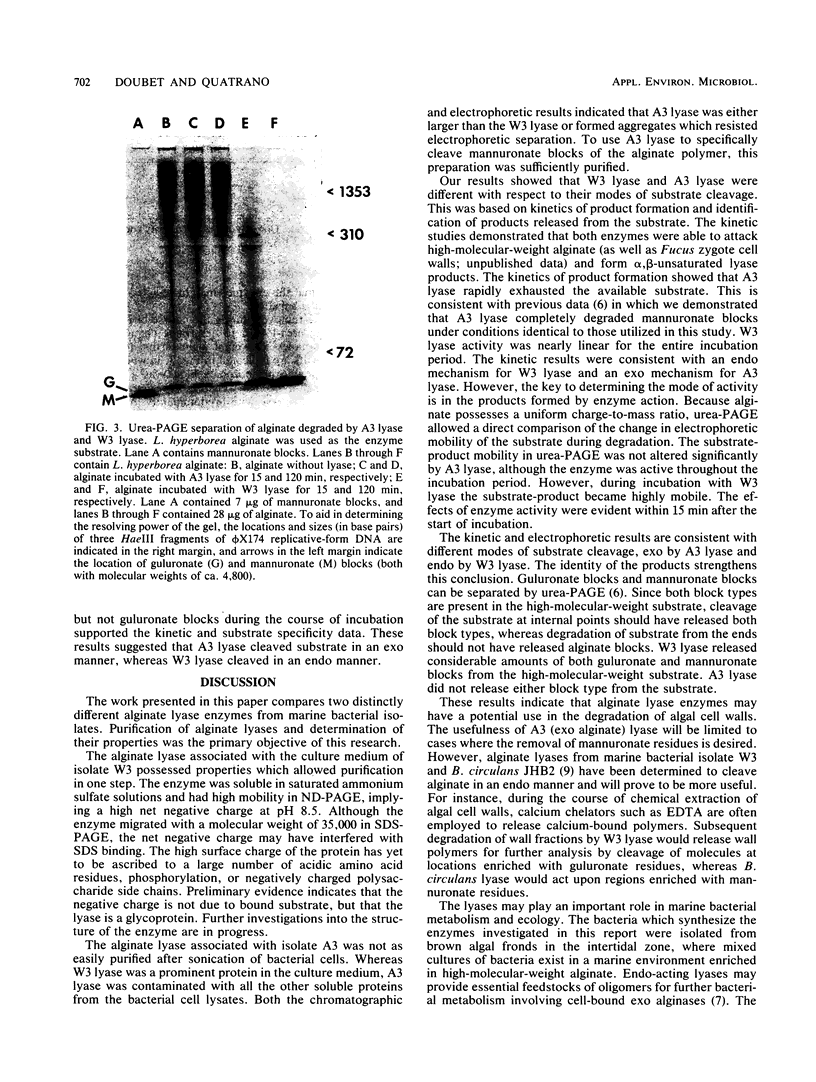
Alginate lyases (EC 4.2.2.3) from two marine bacteria were isolated and partially characterized. A cell-bound lyase from isolate A3 had a molecular weight of approximately 100,000 and cleaved mannuronate blocks, apparently in an exo manner. A lyase recovered from the culture medium of isolate W3 was soluble in saturated ammonium sulfate, cleaved guluronate blocks, apparently in an endo manner, and had a molecular weight of 35,000. The thiobarbiturate test and urea-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis were used to determine substrate specificity and mode of substrate cleavage by the enzymes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bearden J. C., Jr Quantitation of submicrogram quantities of protein by an improved protein-dye binding assay. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Apr 26;533(2):525–529. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90398-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd J., Turvey J. R. Isolation of poly-alpha-L-guluronate lyase from Klebsiella aerogenes. Carbohydr Res. 1977 Aug;57:163–171. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6215(00)81928-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucke C. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis of alginic acid. J Chromatogr. 1974 Feb 13;89(1):99–102. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)84167-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson I. W., Lawson C. J., Sutherland I. W. An alginate lysate from Azotobacter vinelandii phage. J Gen Microbiol. 1977 Jan;98(1):223–229. doi: 10.1099/00221287-98-1-223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doubet R. S., Quatrano R. S. Isolation of marine bacteria capable of producing specific lyases for alginate degradation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Sep;44(3):754–756. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.3.754-756.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Min K. H., Sasaki S., Kashiwabara Y., Nisizawa K. Substrate specificity of endo-polyguluronide lyases from Pseudomonas sp. on the basis of their kinetic properties. J Biochem. 1977 Mar;81(3):547–553. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakada H. I., Sweeny P. C. Alginic acid degradation by eliminases from abalone hepatopancreas. J Biol Chem. 1967 Mar 10;242(5):845–851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PREISS J., ASHWELL G. Alginic acid metabolism in bacteria. I. Enzymatic formation of unsaturated oligosac-charides and 4-deoxy-L-erythro-5-hexoseulose uronic acid. J Biol Chem. 1962 Feb;237:309–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quatrano R. S., Caldwell B. A. Isolation of a unique marine bacterium capable of growth on a wide variety of polysaccharides from macroalgae. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Dec;36(6):979–981. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.6.979-981.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quatrano R. S., Stevens P. T. Cell wall assembly in fucus zygotes: I. Characterization of the polysaccharide components. Plant Physiol. 1976 Aug;58(2):224–231. doi: 10.1104/pp.58.2.224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISSBACH A., HURWITZ J. The formation of 2-keto-3-deoxyheptonic acid in extracts of Escherichia coli B. I. Identification. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):705–709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]