Abstract
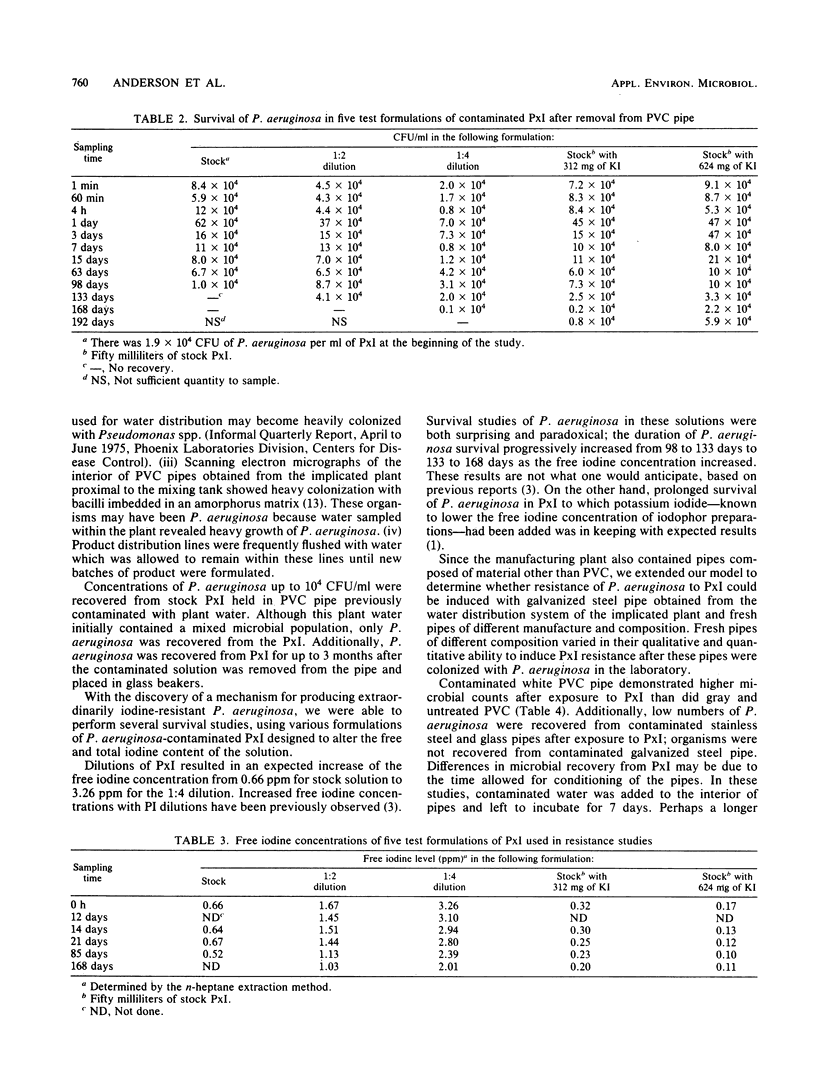
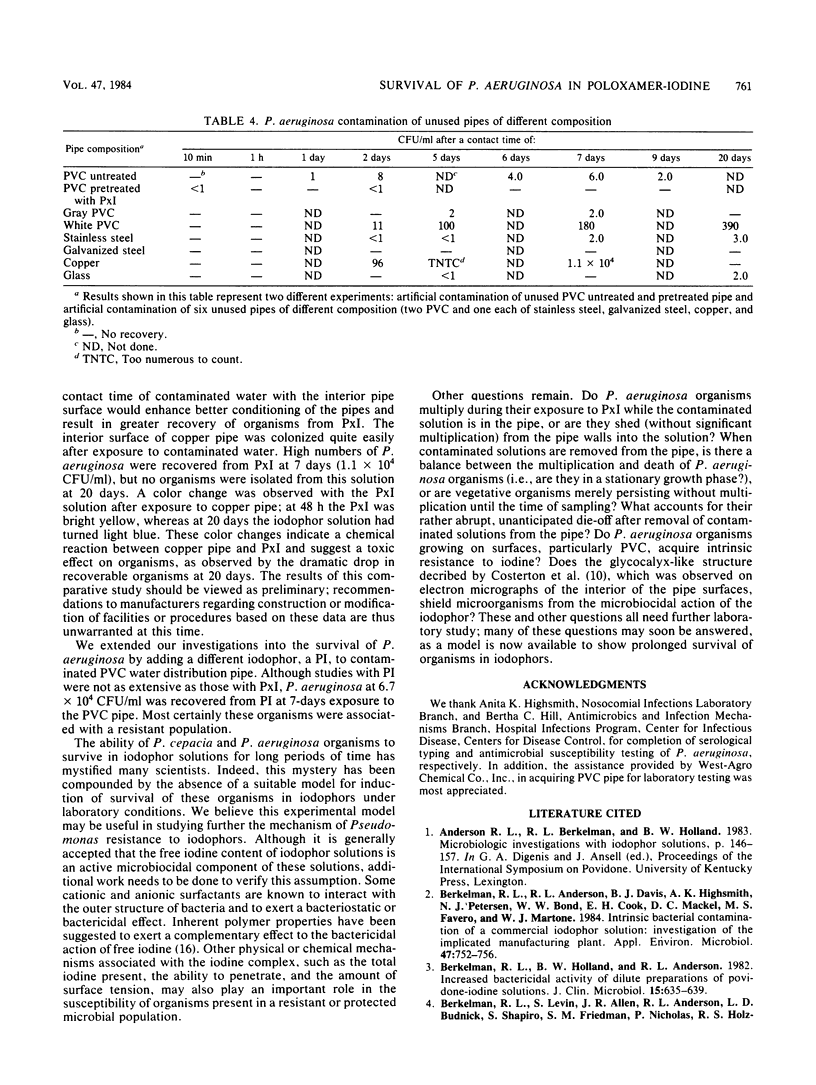
Laboratory investigations were conducted to study potential mechanisms for prolonged survival of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in poloxamer-iodine (PxI). P. aeruginosa organisms isolated from PxI and adapted for growth in distilled water or found as part of a mixed microbial population from water in a manufacturing plant did not survive more than 15 s after challenge in stock PxI solution. Batches of PxI were compounded in the laboratory to determine the survival and growth of P. aeruginosa during the various stages of preparation. No P. aeruginosa organisms were recovered from the finished product at 1 min after the addition of iodine-iodide. However, we found P. aeruginosa in PxI 48 h after adding sterile PxI to the inside of a naturally contaminated polyvinyl chloride water distribution pipe. These organisms (10(4) CFU/ml) survived for as long as 98 days in contaminated stock PxI after it was removed from the polyvinyl chloride pipe. Both decreasing the free iodine level through addition of potassium iodide and increasing the free iodine level through dilution of the product resulted in an increased length of survival of P. aeruginosa in contaminated PxI solution. Comparative survival studies with pipes of different composition revealed that other materials may exert an effect similar to polyvinyl chloride. We concluded that polyvinyl chloride and perhaps other materials may play an important role in the survival of P. aeruginosa in iodophors and may be one source of resistant microbial populations when used in manufacturing plants which produce these antimicrobial solutions.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berkelman R. L., Anderson R. L., Davis B. J., Highsmith A. K., Petersen N. J., Bond W. W., Cook E. H., Mackel D. C., Favero M. S., Martone W. J. Intrinsic bacterial contamination of a commercial iodophor solution: investigation of the implicated manufacturing plant. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Apr;47(4):752–756. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.4.752-756.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkelman R. L., Holland B. W., Anderson R. L. Increased bactericidal activity of dilute preparations of povidone-iodine solutions. J Clin Microbiol. 1982 Apr;15(4):635–639. doi: 10.1128/jcm.15.4.635-639.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkelman R. L., Lewin S., Allen J. R., Anderson R. L., Budnick L. D., Shapiro S., Friedman S. M., Nicholas P., Holzman R. S., Haley R. W. Pseudobacteremia attributed to contamination of povidone-iodine with Pseudomonas cepacia. Ann Intern Med. 1981 Jul;95(1):32–36. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-95-1-32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brokopp C. D., Gomez-Lus R., Farmer J. J., 3rd Serological typing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: use of commercial antisera and live antigens. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Jun;5(6):640–649. doi: 10.1128/jcm.5.6.640-649.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costerton J. W., Geesey G. G., Cheng K. J. How bacteria stick. Sci Am. 1978 Jan;238(1):86–95. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0178-86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craven D. E., Moody B., Connolly M. G., Kollisch N. R., Stottmeier K. D., McCabe W. R. Pseudobacteremia caused by povidone-iodine solution contaminated with Pseudomonas cepacia. N Engl J Med. 1981 Sep 10;305(11):621–623. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198109103051106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favero M. S. Iodine--champagne in a tin cup. Infect Control. 1982 Jan-Feb;3(1):30–32. doi: 10.1017/s0195941700057076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrott P. L., Terry P. M., Whitworth E. N., Frawley L. W., Coble R. S., Wachsmuth I. K., McGowan J. E., Jr Pseudomonas aeruginosa peritonitis associated with contaminated poloxamer-iodine solution. Lancet. 1982 Sep 25;2(8300):683–685. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90712-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



