Abstract
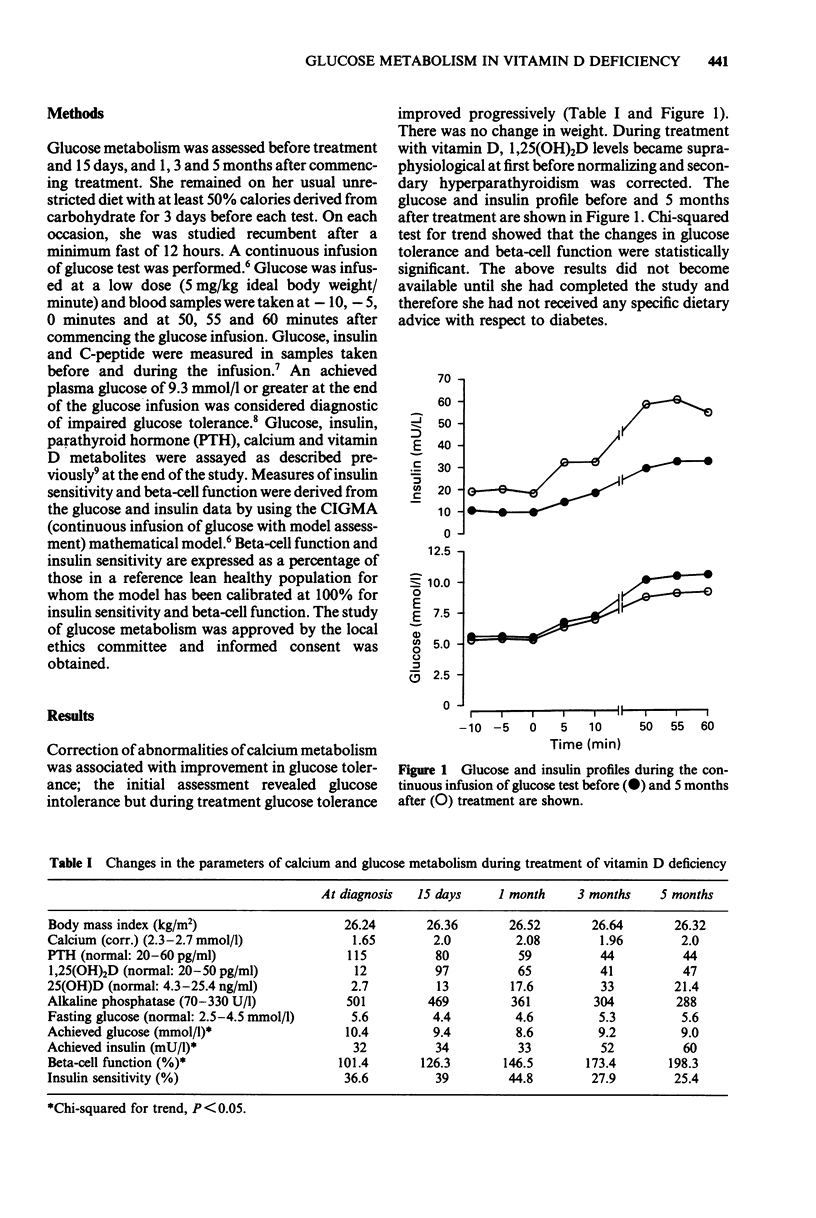
Glucose metabolism was studied in a patient with vitamin D deficiency during its treatment with small doses of vitamin D. A continuous infusion of glucose test was performed to assess glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity and beta-cell function were derived by mathematical modelling. Fasting glucose was 5.6 mmol/l and achieved glucose after the infusion was 10.4 mmol/l confirming diabetes. The test was repeated 0.5, 1, 3 and 5 months after starting treatment. Serum calcium increased glucose intolerance from 1.76 to 2.0, 2.08, 1.96 and 2.0 mmol/l, respectively; vitamin D reached supraphysiological levels initially and returned to normal levels, and parathyroid hormone levels were normalized. Her weight did not change during treatment. Glucose tolerance improved during treatment and achieved glucose was 9.4, 8.6, 9.2 and 9.0 mmol/l at 0.5, 1, 3 and 5 months, respectively; insulin sensitivity did not change. Beta-cell function improved from 101% at diagnosis to 126%, 147%, 173% and 198% at 0.5, 1, 3 and 5 months, respectively. Improvement in beta-cell function and consequently in glucose tolerance is likely to have been due to correction of hypocalcaemia, vitamin D deficiency and secondary hyperparathyroidism.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akmal M., Massry S. G., Goldstein D. A., Fanti P., Weisz A., DeFronzo R. A. Role of parathyroid hormone in the glucose intolerance of chronic renal failure. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):1037–1044. doi: 10.1172/JCI111765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaulieu C., Kestekian R., Havrankova J., Gascon-Barré M. Calcium is essential in normalizing intolerance to glucose that accompanies vitamin D depletion in vivo. Diabetes. 1993 Jan;42(1):35–43. doi: 10.2337/diab.42.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cade C., Norman A. W. Vitamin D3 improves impaired glucose tolerance and insulin secretion in the vitamin D-deficient rat in vivo. Endocrinology. 1986 Jul;119(1):84–90. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-1-84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gedik O., Akalin S. Effects of vitamin D deficiency and repletion on insulin and glucagon secretion in man. Diabetologia. 1986 Mar;29(3):142–145. doi: 10.1007/BF02427083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gylfe E., Grapengiesser E., Hellman B. Propagation of cytoplasmic Ca2+ oscillations in clusters of pancreatic beta-cells exposed to glucose. Cell Calcium. 1991 Feb-Mar;12(2-3):229–240. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(91)90023-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadowaki S., Norman A. W. Dietary vitamin D is essential for normal insulin secretion from the perfused rat pancreas. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):759–766. doi: 10.1172/JCI111269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kautzky-Willer A., Pacini G., Niederle B., Schernthaner G., Prager R. Insulin secretion, insulin sensitivity and hepatic insulin extraction in primary hyperparathyroidism before and after surgery. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1992 Aug;37(2):147–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1992.tb02299.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littledike E. T., Witzel D. A., Whipp S. C. Insulin: evidence for inhibition of release in spontaneous hypocalcemia. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Oct;129(1):135–139. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mak R. H., Wong J. H. The vitamin D/parathyroid hormone axis in the pathogenesis of hypertension and insulin resistance in uremia. Miner Electrolyte Metab. 1992;18(2-5):156–159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman A. W., Frankel J. B., Heldt A. M., Grodsky G. M. Vitamin D deficiency inhibits pancreatic secretion of insulin. Science. 1980 Aug 15;209(4458):823–825. doi: 10.1126/science.6250216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nyomba B. L., Bouillon R., De Moor P. Influence of vitamin D status on insulin secretion and glucose tolerance in the rabbit. Endocrinology. 1984 Jul;115(1):191–197. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-1-191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozono K., Seino Y., Yano H., Yamaoka K., Seino Y. 1,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 enhances the effect of refeeding on steady state preproinsulin messenger ribonucleic acid levels in rats. Endocrinology. 1990 Apr;126(4):2041–2045. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-4-2041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. F., Caterson I. D., Cooney G. J., Zilkens R. R., Turtle J. R. High affinity insulin binding and insulin receptor-effector coupling: modulation by Ca2+. Cell Calcium. 1990 Sep;11(8):547–556. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(90)90031-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



