Abstract
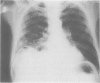
Diaphragmatic hernias of the Morgagni type are generally thought to be asymptomatic in adults. This traditional assumption led to a delay in diagnosing a Morgagni hernia as the cause of acute respiratory distress in a chronic schizophrenic man. While Morgagni hernias are usually considered to be long-standing, we present radiological evidence of an acutely expanding hernia. The patient's symptoms were relieved by surgical repair of the hernia. We advise caution before dismissing Morgagni hernias in adults as being long-standing and clinically insignificant.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ellyson J. H., Parks S. N. Hernia of Morgagni in a trauma patient. J Trauma. 1986 Jun;26(6):569–570. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198606000-00016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- París F., Tarazona V., Casillas M., Blasco E., Cantó A., Pastor J., Acosta A. Hernia of Morgagni. Thorax. 1973 Sep;28(5):631–636. doi: 10.1136/thx.28.5.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneidau A., Baron H. J., Rosin R. D. Morgagni revisited: a case of intermittent chest pain. Br J Radiol. 1982 Mar;55(651):238–240. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-55-651-238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valases C., Sills C. Anterior diaphragmatic hernia (hernia of Morgagni). N J Med. 1988 Jul;85(7):603–605. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolloch Y., Grunebaum M., Glanz I., Dintsman M. Symptomatic retrosternal (Morgagni) hernia. Am J Surg. 1974 May;127(5):601–605. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(74)90327-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]