Abstract
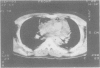
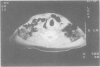
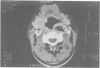
Descending necrotising mediastinitis is a rare but serious complication of oropharyngeal infections with high mortality. Diagnosis is frequently delayed, contributing to this high mortality, but awareness of such a complication and early diagnosis using computed tomographic scanning leads to prompt surgical drainage, proper antibiotic therapy, and survival.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertsen J., Thomsen E. M. Nonclostridial deep gas-producing infection in the neck. Arch Otolaryngol. 1970 Oct;92(4):383–385. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1970.04310040071013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander D. W., Leonard J. R., Trail M. L. Vascular complications of deep neck abscesses. A report of four cases. Laryngoscope. 1968 Mar;78(3):361–370. doi: 10.1288/00005537-196803000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen D., Loughnan T. E., Ord R. A. A re-evaluation of the role of tracheostomy in Ludwig's angina. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1985 Jun;43(6):436–439. doi: 10.1016/s0278-2391(85)80051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROOKS V. SUPPURATIVE SOFT TISSUE INFECTION OF THE HEAD AND NECK. West Indian Med J. 1963 Sep;12:200–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bounds G. A. Subphrenic and mediastinal abscess formation: a complication of Ludwig's angina. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1985 Oct;23(5):313–321. doi: 10.1016/0266-4356(85)90001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Weekly clinicopathological exercises. Case 15-1978. N Engl J Med. 1978 Apr 20;298(16):894–902. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197804202981607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow A. W., Roser S. M., Brady F. A. Orofacial odontogenic infections. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Mar;88(3):392–402. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-3-392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cogan I. C. Necrotizing mediastinitis secondary to descending cervical cellulitis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1973 Sep;36(3):307–320. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(73)90207-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Economopoulos G. C., Scherzer H. H., Gryboski W. A. Successful management of mediastinitis, pleural empyema, and aortopulmonary fistula from odontogenic infection. Ann Thorac Surg. 1983 Feb;35(2):184–187. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)61458-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist R. W., Blanck R. R., Butler R. H. Nontraumatic mediastinitis. JAMA. 1976 Aug 30;236(9):1048–1049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estrera A. S., Landay M. J., Grisham J. M., Sinn D. P., Platt M. R. Descending necrotizing mediastinitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1983 Dec;157(6):545–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garatea-Crelgo J., Gay-Escoda C. Mediastinitis from odontogenic infection. Report of three cases and review of the literature. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1991 Apr;20(2):65–68. doi: 10.1016/s0901-5027(05)80707-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkins D. B., Seltzer D. C., Barnett T. E., Stoneman G. B. Endotracheal tube perforation of the hypopharynx. West J Med. 1974 Apr;120(4):282–286. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendler B. H., Quinn P. D. Fatal mediastinitis secondary to odontogenic infection. J Oral Surg. 1978 Apr;36(4):308–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horowitz M. D., Sosa J. L., Lickstein D. A. Descending necrotizing mediastinitis. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990 Nov;50(5):859–860. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(90)90721-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howell H. S., Prinz R. A., Pickleman J. R. Anaerobic mediastinitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1976 Sep;143(3):353–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janecka I. P., Rankow R. M. Fatal mediastinitis following retropharyngeal abscess. Arch Otolaryngol. 1971 Jun;93(6):630–633. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1971.00770060932017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine T. M., Wurster C. F., Krespi Y. P. Mediastinitis occurring as a complication of odontogenic infections. Laryngoscope. 1986 Jul;96(7):747–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCurdy J. A., Jr, MacInnis E. L., Hays L. L. Fatal mediastinitis after a dental infection. J Oral Surg. 1977 Sep;35(9):726–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncada R., Warpeha R., Pickleman J., Spak M., Cardoso M., Berkow A., White H. Mediastinitis from odontogenic and deep cervical infection. Anatomic pathways of propagation. Chest. 1978 Apr;73(4):497–500. doi: 10.1378/chest.73.4.497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakajima H., Sega H., Yokota T., Kawashima T., Maruyama M., Sato M., Suzuki E., Wada K., Kioi S., Arakawa M. [Two cases of mediastinitis as a complication of odontogenic infection and tonsillitis]. Nihon Kyobu Shikkan Gakkai Zasshi. 1993 Jun;31(6):754–759. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North J., Emanuel B. Mediastinitis in a child caused by perforation of pharynx. Am J Dis Child. 1975 Aug;129(8):962–963. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1975.02120450068016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse H. E. MEDIASTINITIS FOLLOWING CERVICAL SUPPURATION. Ann Surg. 1938 Oct;108(4):588–611. doi: 10.1097/00000658-193810000-00009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. D., Fox G. L., Grover F. L., Cruz A. B., Jr Necrotizing fasciitis of the neck: A complication of dental extraction. Tex Med. 1975 May;71(5):69–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roser S. M., Chow A. W., Brady F. A. Necrotizing fasciitis. J Oral Surg. 1977 Sep;35(9):730–732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin M. M., Cozzi G. M. Fatal necrotizing mediastinitis as a complication of an odontogenic infection. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1987 Jun;45(6):529–533. doi: 10.1016/s0278-2391(87)80015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos G. H., Shapiro B. M., Komisar A. Role of transoral irrigation in mediastinitis due to hypopharyngeal perforation. Head Neck Surg. 1986 Nov-Dec;9(2):116–121. doi: 10.1002/hed.2890090208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow N., Lucas A. E., Grau M., Steiner M. Purulent mediastinal abscess secondary to Ludwig's angina. Arch Otolaryngol. 1983 Jan;109(1):53–55. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1983.00800150057011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spilka C. J. Pathways of dental infections. J Oral Surg. 1966 Mar;24(2):111–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss H. R., Tilghman D. M., Hankins J. Ludwig angina, empyema, pulmonary infiltration, and pericarditis secondary to extraction of a tooth. J Oral Surg. 1980 Mar;38(3):223–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheatley M. J., Stirling M. C., Kirsh M. M., Gago O., Orringer M. B. Descending necrotizing mediastinitis: transcervical drainage is not enough. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990 May;49(5):780–784. doi: 10.1016/0003-4975(90)90022-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wills P. I., Vernon R. P., Jr Complications of space infections of the head and neck. Laryngoscope. 1981 Jul;91(7):1129–1136. doi: 10.1288/00005537-198107000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff A. P., Kuhn F. A., Ogura J. H. Pharyngeal-esophageal perforations associated with rapid oral endotracheal intubation. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1972 Apr;81(2):258–261. doi: 10.1177/000348947208100213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. N., Samson P. C. Extrapleural empyema thoracis as a direct extension of Ludwig's angina. Case report. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1980 Jul;80(1):25–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zachariades N., Mezitis M., Stavrinidis P., Konsolaki-Agouridaki E. Mediastinitis, thoracic empyema, and pericarditis as complications of a dental abscess: report of a case. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1988 Jun;46(6):493–495. doi: 10.1016/0278-2391(88)90421-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]