Abstract
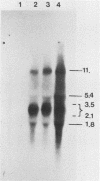
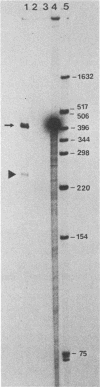
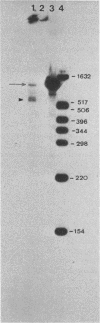
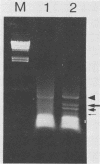
Mapping of transcripts of the human foamy virus genome was carried out in permissive human embryonic fibroblast cells by Northern blot hybridization and S1 nuclease analysis. Since several splice sites that are localized within a relatively narrow genomic region were detected, the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was employed, and cloning and sequencing of the splice site junctions of the corresponding viral cDNAs were subsequently performed. All spumavirus transcripts have a common but relatively short leader RNA. Genomic, singly spliced env mRNAs and several singly and multiply spliced subgenomic transcripts were identified. The multiply spliced viral mRNAs consist of various exons located in the central or 3' part of the viral genome. At least four novel gene products, termed Bet, Bes, Beo, and Bel3, are predicted to exist. The poly(A) addition site that defines the boundary of the R and U5 region in the 3' long terminal repeat was determined. The pattern of spumavirus splicing is more complex than that of oncoviruses and more similar to that of lentiviruses. One of the characteristic features of spumavirus transcription is the existence of singly spliced bel1 and bel2 mRNAs that alternatively are multiply spliced, thereby generating a complexity comparable to, but different from, that of lentiviruses and from that of other known retroviruses. The complex spumavirus transcriptional pattern of human spumavirus and the coding potential of the 10 exons identified are discussed.
Full text
PDF


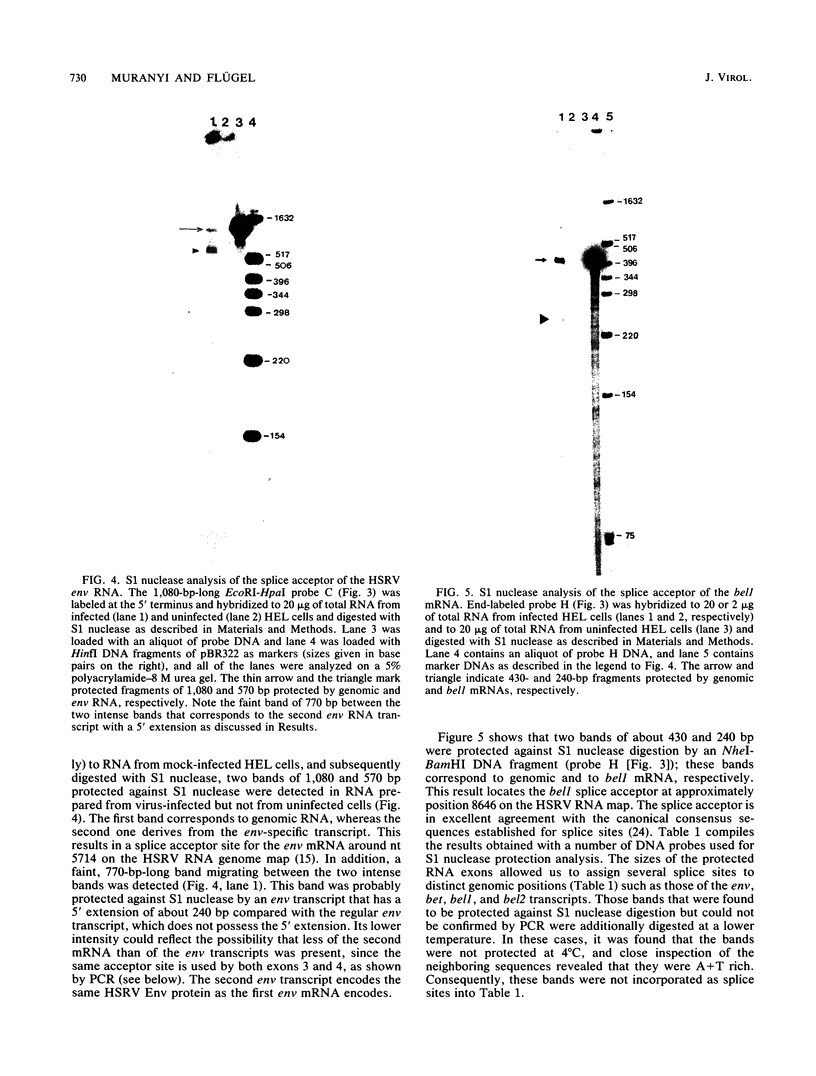
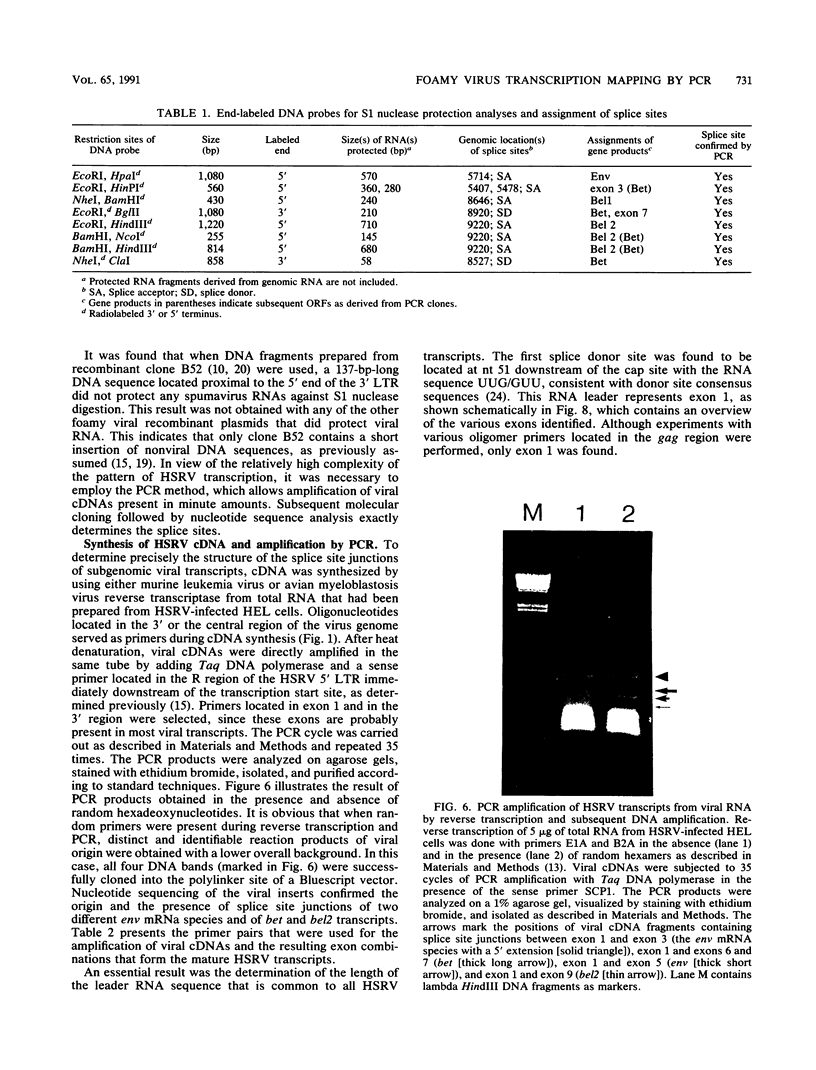




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Achong B. G., Mansell P. W., Epstein M. A., Clifford P. An unusual virus in cultures from a human nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1971 Feb;46(2):299–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arrigo S. J., Weitsman S., Zack J. A., Chen I. S. Characterization and expression of novel singly spliced RNA species of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4585–4588. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4585-4588.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J. Characterization of RNA molecules by S1 nuclease analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:334–347. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80110-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochrane A. W., Perkins A., Rosen C. A. Identification of sequences important in the nucleolar localization of human immunodeficiency virus Rev: relevance of nucleolar localization to function. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):881–885. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.881-885.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colombini S., Arya S. K., Reitz M. S., Jagodzinski L., Beaver B., Wong-Staal F. Structure of simian immunodeficiency virus regulatory genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4813–4817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. L., Molineaux S., Clements J. E. Visna virus exhibits a complex transcriptional pattern: one aspect of gene expression shared with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome retrovirus. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1325–1331. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1325-1331.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flügel R. M., Rethwilm A., Maurer B., Darai G. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the env gene and its flanking regions of the human spumaretrovirus reveals two novel genes. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2077–2084. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02473.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. P., Lobel L. I. Mutants of murine leukemia viruses and retroviral replication. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 8;907(2):93–123. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(87)90001-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guatelli J. C., Gingeras T. R., Richman D. D. Alternative splice acceptor utilization during human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection of cultured cells. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4093–4098. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4093-4098.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauber J., Perkins A., Heimer E. P., Cullen B. R. Trans-activation of human immunodeficiency virus gene expression is mediated by nuclear events. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(18):6364–6368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.18.6364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita T., Shimoyama M., Tobinai K., Ito M., Ito S., Ikeda S., Tajima K., Shimotohno K., Sugimura T. Detection of mRNA for the tax1/rex1 gene of human T-cell leukemia virus type I in fresh peripheral blood mononuclear cells of adult T-cell leukemia patients and viral carriers by using the polymerase chain reaction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5620–5624. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer B., Bannert H., Darai G., Flügel R. M. Analysis of the primary structure of the long terminal repeat and the gag and pol genes of the human spumaretrovirus. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1590–1597. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1590-1597.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer B., Flügel R. M. The 3'-orf protein of human immunodeficiency virus 2 shows sequence homology with the bel3 gene of the human spumaretrovirus. FEBS Lett. 1987 Oct 5;222(2):286–288. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80387-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergia A., Shaw K. E., Lackner J. E., Luciw P. A. Relationship of the env genes and the endonuclease domain of the pol genes of simian foamy virus type 1 and human foamy virus. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):406–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.406-410.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mergia A., Shaw K. E., Pratt-Lowe E., Barry P. A., Luciw P. A. Simian foamy virus type 1 is a retrovirus which encodes a transcriptional transactivator. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3598–3604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3598-3604.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rethwilm A., Baunach G., Netzer K. O., Maurer B., Borisch B., ter Meulen V. Infectious DNA of the human spumaretrovirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):733–738. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rethwilm A., Darai G., Rösen A., Maurer B., Flügel R. M. Molecular cloning of the genome of human spumaretrovirus. Gene. 1987;59(1):19–28. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90262-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruben S., Perkins A., Purcell R., Joung K., Sia R., Burghoff R., Haseltine W. A., Rosen C. A. Structural and functional characterization of human immunodeficiency virus tat protein. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.1-8.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz S., Felber B. K., Benko D. M., Fenyö E. M., Pavlakis G. N. Cloning and functional analysis of multiply spliced mRNA species of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2519–2529. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2519-2529.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. B., Senapathy P. RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7155–7174. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siomi H., Shida H., Nam S. H., Nosaka T., Maki M., Hatanaka M. Sequence requirements for nucleolar localization of human T cell leukemia virus type I pX protein, which regulates viral RNA processing. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):197–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90043-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J., Goh W. C., Rosen C., Dayton A., Terwilliger E., Haseltine W. A second post-transcriptional trans-activator gene required for HTLV-III replication. Nature. 1986 May 22;321(6068):412–417. doi: 10.1038/321412a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh L. K., Mohammed S., Chinnadurai G. Functional domains of the HIV-1 rev gene required for trans-regulation and subcellular localization. Virology. 1990 May;176(1):39–47. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90228-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viglianti G. A., Sharma P. L., Mullins J. I. Simian immunodeficiency virus displays complex patterns of RNA splicing. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4207–4216. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4207-4216.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Sigler P. B., McKnight S. L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):911–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2683088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]