Abstract
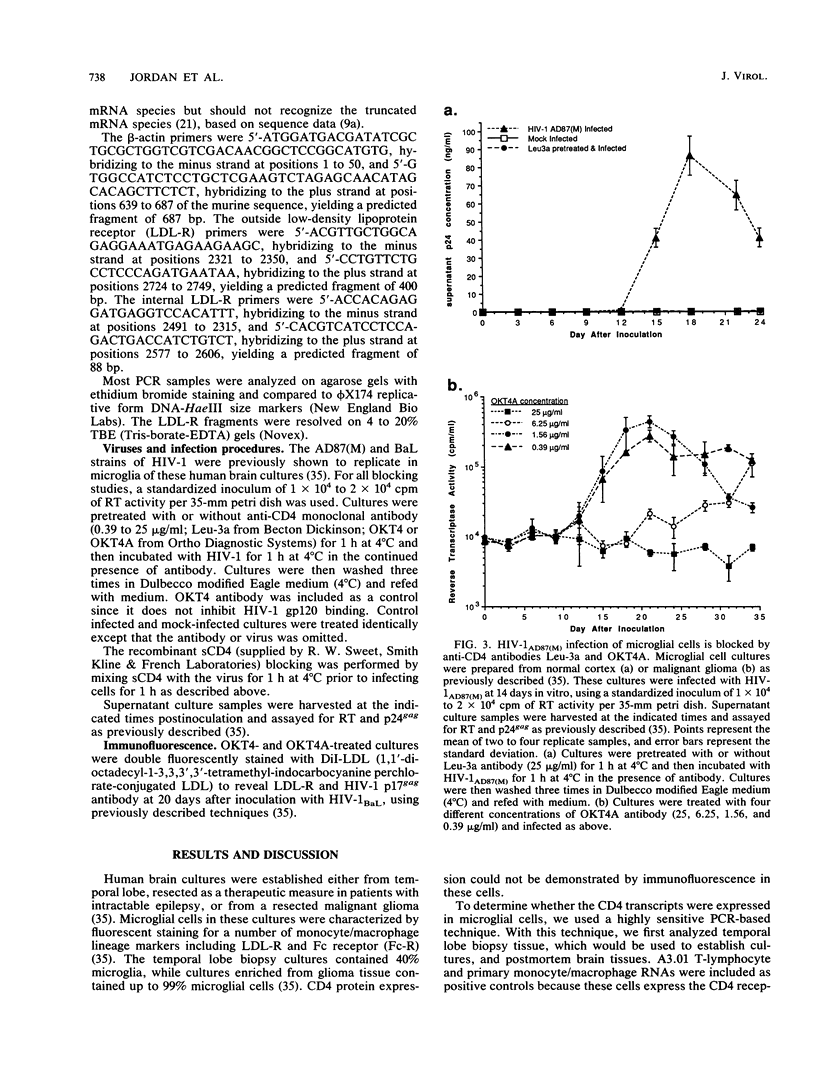
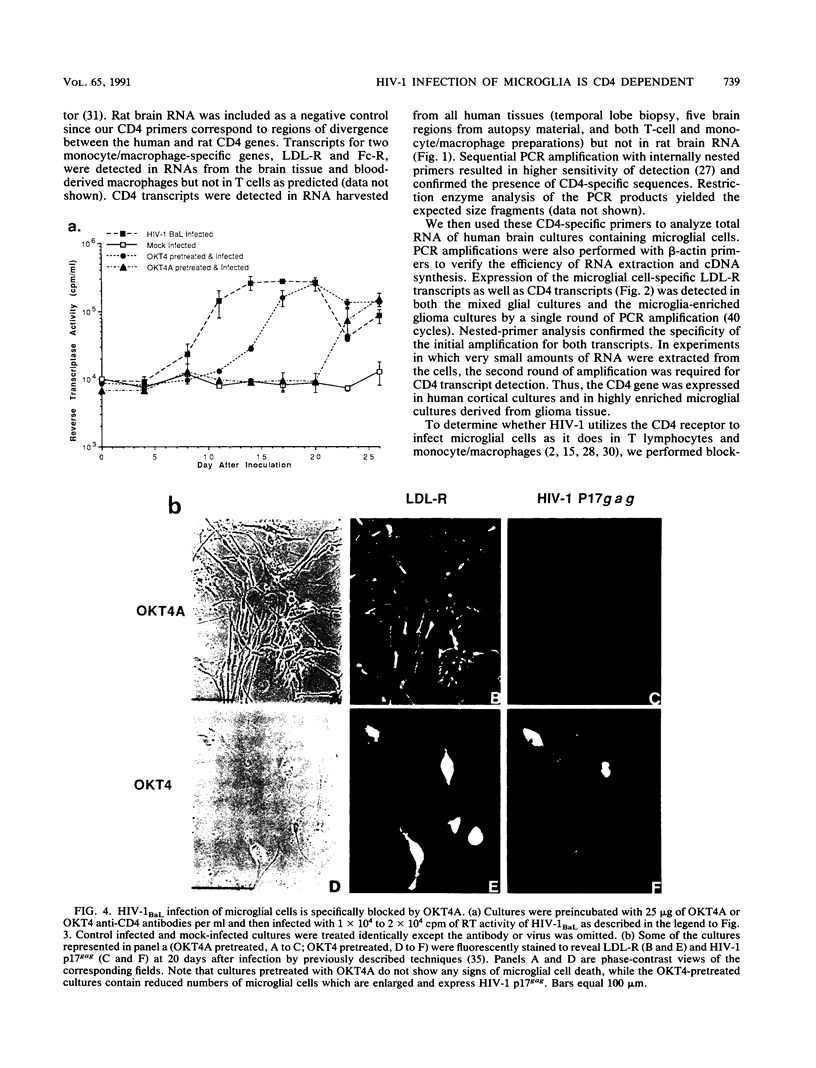
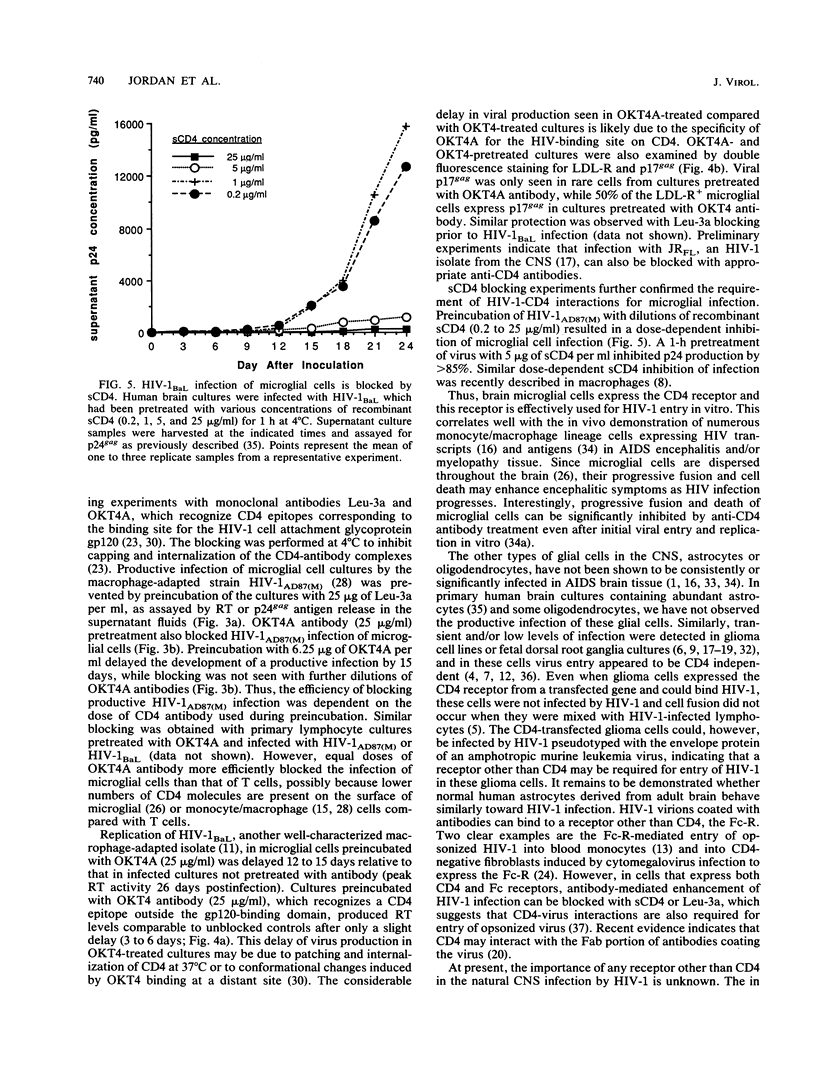
In the central nervous system of AIDS patients, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infects primarily microglia, a cell type of bone marrow origin. Moreover, microglial cells isolated from adult human brain support the replication of macrophage-adapted strains of HIV type 1 (HIV-1) (B.A. Watkins, H.H. Dorn, W.B. Kelly, R.C. Armstrong, B. Potts, F. Michaels, C.V. Kufta, and M. Dubois-Dalcq, Science 249:549-553, 1990). To determine whether the CD4 receptor, which is expressed in brain, mediates the entry of HIV-1 in microglial cells, we analyzed CD4 transcript expression in cultured microglia using highly sensitive polymerase chain reaction detection of cDNAs synthesized from RNA. With this method, CD4 transcripts could be detected in cultured microglia--as well as in various human brain regions and cultured macrophages used as positive controls--along with transcripts for the LDL and Fc receptors which are characteristic of cells of the macrophage lineage. We then attempted to block viral entry into microglial cells using anti-CD4 antibodies or soluble CD4 (sCD4), which recognize binding sites on CD4 and HIV-1 glycoprotein gp120, respectively. Cultures were pretreated with blocking antibodies (Leu-3a, OKT4A) or virus was preincubated with sCD4 prior to infection with HIV-1 strain AD87(M) or BaL. With either viral strain, these treatments resulted in the prevention of infection or significant and dose-dependent reduction in the number of infected cells and in the levels of reverse transcriptase or p24 antigen released in the medium. Thus, brain-derived microglial cells, which are the primary target of HIV-1 infection in the brain, express the CD4 receptor and this receptor is effectively used for viral entry in vitro.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Budka H. Multinucleated giant cells in brain: a hallmark of the acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Acta Neuropathol. 1986;69(3-4):253–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00688301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byrn R. A., Sekigawa I., Chamow S. M., Johnson J. S., Gregory T. J., Capon D. J., Groopman J. E. Characterization of in vitro inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus by purified recombinant CD4. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4370–4375. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4370-4375.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camerini D., Seed B. A CD4 domain important for HIV-mediated syncytium formation lies outside the virus binding site. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):747–754. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90089-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng-Mayer C., Rutka J. T., Rosenblum M. L., McHugh T., Stites D. P., Levy J. A. Human immunodeficiency virus can productively infect cultured human glial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3526–3530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Buller R., Portis J., Wehrly K. Failure of human immunodeficiency virus entry and infection in CD4-positive human brain and skin cells. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):215–221. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.215-221.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiodi F., Fuerstenberg S., Gidlund M., Asjö B., Fenyö E. M. Infection of brain-derived cells with the human immunodeficiency virus. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1244–1247. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1244-1247.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapham P. R., Weber J. N., Whitby D., McIntosh K., Dalgleish A. G., Maddon P. J., Deen K. C., Sweet R. W., Weiss R. A. Soluble CD4 blocks the infectivity of diverse strains of HIV and SIV for T cells and monocytes but not for brain and muscle cells. Nature. 1989 Jan 26;337(6205):368–370. doi: 10.1038/337368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collman R., Godfrey B., Cutilli J., Rhodes A., Hassan N. F., Sweet R., Douglas S. D., Friedman H., Nathanson N., Gonzalez-Scarano F. Macrophage-tropic strains of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 utilize the CD4 receptor. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4468–4476. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4468-4476.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhurst S., Bresser J., Stevenson M., Sakai K., Evinger-Hodges M. J., Volsky D. J. Susceptibility of human glial cells to infection with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). FEBS Lett. 1987 Mar 9;213(1):138–143. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)81479-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner S., Markovits P., Markovitz D. M., Betts R. F., Popovic M. Virus isolation from and identification of HTLV-III/LAV-producing cells in brain tissue from a patient with AIDS. JAMA. 1986 Nov 7;256(17):2365–2371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gartner S., Markovits P., Markovitz D. M., Kaplan M. H., Gallo R. C., Popovic M. The role of mononuclear phagocytes in HTLV-III/LAV infection. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):215–219. doi: 10.1126/science.3014648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harouse J. M., Kunsch C., Hartle H. T., Laughlin M. A., Hoxie J. A., Wigdahl B., Gonzalez-Scarano F. CD4-independent infection of human neural cells by human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2527–2533. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2527-2533.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homsy J., Meyer M., Tateno M., Clarkson S., Levy J. A. The Fc and not CD4 receptor mediates antibody enhancement of HIV infection in human cells. Science. 1989 Jun 16;244(4910):1357–1360. doi: 10.1126/science.2786647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazazi F., Mathijs J. M., Foley P., Cunningham A. L. Variations in CD4 expression by human monocytes and macrophages and their relationships to infection with the human immunodeficiency virus. J Gen Virol. 1989 Oct;70(Pt 10):2661–2672. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-10-2661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig S., Gendelman H. E., Orenstein J. M., Dal Canto M. C., Pezeshkpour G. H., Yungbluth M., Janotta F., Aksamit A., Martin M. A., Fauci A. S. Detection of AIDS virus in macrophages in brain tissue from AIDS patients with encephalopathy. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1089–1093. doi: 10.1126/science.3016903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyanagi Y., Miles S., Mitsuyasu R. T., Merrill J. E., Vinters H. V., Chen I. S. Dual infection of the central nervous system by AIDS viruses with distinct cellular tropisms. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):819–822. doi: 10.1126/science.3646751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunsch C., Hartle H. T., Wigdahl B. Infection of human fetal dorsal root ganglion glial cells with human immunodeficiency virus type 1 involves an entry mechanism independent of the CD4 T4A epitope. J Virol. 1989 Dec;63(12):5054–5061. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.12.5054-5061.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunsch C., Wigdahl B. Transient expression of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 genome results in a nonproductive infection in human fetal dorsal root ganglia glial cells. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):715–722. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90585-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenert P., Kroon D., Spiegelberg H., Golub E. S., Zanetti M. Human CD4 binds immunoglobulins. Science. 1990 Jun 29;248(4963):1639–1643. doi: 10.1126/science.2363051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddon P. J., Dalgleish A. G., McDougal J. S., Clapham P. R., Weiss R. A., Axel R. The T4 gene encodes the AIDS virus receptor and is expressed in the immune system and the brain. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90590-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Nicholson J. K., Cross G. D., Cort S. P., Kennedy M. S., Mawle A. C. Binding of the human retrovirus HTLV-III/LAV/ARV/HIV to the CD4 (T4) molecule: conformation dependence, epitope mapping, antibody inhibition, and potential for idiotypic mimicry. J Immunol. 1986 Nov 1;137(9):2937–2944. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeating J. A., Griffiths P. D., Weiss R. A. HIV susceptibility conferred to human fibroblasts by cytomegalovirus-induced Fc receptor. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):659–661. doi: 10.1038/343659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nara P. L., Hwang K. M., Rausch D. M., Lifson J. D., Eiden L. E. CD4 antigen-based antireceptor peptides inhibit infectivity of human immunodeficiency virus in vitro at multiple stages of the viral life cycle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7139–7143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry V. H., Gordon S. Macrophages and microglia in the nervous system. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Jun;11(6):273–277. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90110-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter-Jordan K., Rosenberg E. I., Keiser J. F., Gross J. D., Ross A. M., Nasim S., Garrett C. T. Nested polymerase chain reaction assay for the detection of cytomegalovirus overcomes false positives caused by contamination with fragmented DNA. J Med Virol. 1990 Feb;30(2):85–91. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890300202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts B. J., Maury W., Martin M. A. Replication of HIV-1 in primary monocyte cultures. Virology. 1990 Apr;175(2):465–476. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90431-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappolee D. A., Wang A., Mark D., Werb Z. Novel method for studying mRNA phenotypes in single or small numbers of cells. J Cell Biochem. 1989 Jan;39(1):1–11. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240390102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sattentau Q. J., Dalgleish A. G., Weiss R. A., Beverley P. C. Epitopes of the CD4 antigen and HIV infection. Science. 1986 Nov 28;234(4780):1120–1123. doi: 10.1126/science.2430333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan A., Dorsett D., York D., Bohan C., Anand R. Human immunodeficiency virus replication in human brain cells. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1988;99(1-2):135–141. doi: 10.1007/BF01311031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoler M. H., Eskin T. A., Benn S., Angerer R. C., Angerer L. M. Human T-cell lymphotropic virus type III infection of the central nervous system. A preliminary in situ analysis. JAMA. 1986 Nov 7;256(17):2360–2364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazeux R., Brousse N., Jarry A., Henin D., Marche C., Vedrenne C., Mikol J., Wolff M., Michon C., Rozenbaum W. AIDS subacute encephalitis. Identification of HIV-infected cells. Am J Pathol. 1987 Mar;126(3):403–410. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins B. A., Dorn H. H., Kelly W. B., Armstrong R. C., Potts B. J., Michaels F., Kufta C. V., Dubois-Dalcq M. Specific tropism of HIV-1 for microglial cells in primary human brain cultures. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):549–553. doi: 10.1126/science.2200125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J., Clapham P., McKeating J., Stratton M., Robey E., Weiss R. Infection of brain cells by diverse human immunodeficiency virus isolates: role of CD4 as receptor. J Gen Virol. 1989 Oct;70(Pt 10):2653–2660. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-10-2653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeira M., Byrn R. A., Groopman J. E. Inhibition of serum-enhanced HIV-1 infection of U937 monocytoid cells by recombinant soluble CD4 and anti-CD4 monoclonal antibody. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 1990 May;6(5):629–639. doi: 10.1089/aid.1990.6.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]