Abstract
Cell surface-associated viral glycoproteins are thought to play a major role as target antigens in cellular cytotoxicity and antiviral immunosurveillance. One such glycoprotein is the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-encoded glycoprotein 350 (gp350), which is expressed on both virion envelope and EBV producer cells and carries the virus attachment protein moiety. Although it is known that some antibodies to gp350 can neutralize the virus, the role of this glycoprotein in EBV-specific cellular cytotoxicity is not yet clear. We describe here a study in which we successfully used a new approach to demonstrate that gp350 is a target antigen for EBV-specific antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). Transfection of gp350-negative cells resistant to natural killer (NK) cell activity (i.e., Raji) with a recombinant vector (pZIP-MA) containing the gene encoding the EBV-gp350 and the neomycin resistance gene enabled us to isolate cell clones with a stable and strong expression of gp350 on their surface membranes. ADCC determined by using two clones clearly demonstrated that gp350 is the target of the EBV ADCC. Interestingly, this ADCC was comparable to that obtained against the EBV-superinfected (coated) Raji cell expressing the same percentage of gp350 positivity as the two clones. No cytotoxic activity was detected against either nontransfected (gp350-negative) Raji cells or cells transfected with the vector [pZIP-neo-SV(X)1] lacking the gp350 gene. In addition to demonstrating that gp350 is a target molecule for EBV-specific ADCC, our approach in using NK-resistant transfectants provides a lead for probing the role of cell surface-associated viral antigens in specific cellular killing and immunosurveillance.
Full text
PDF

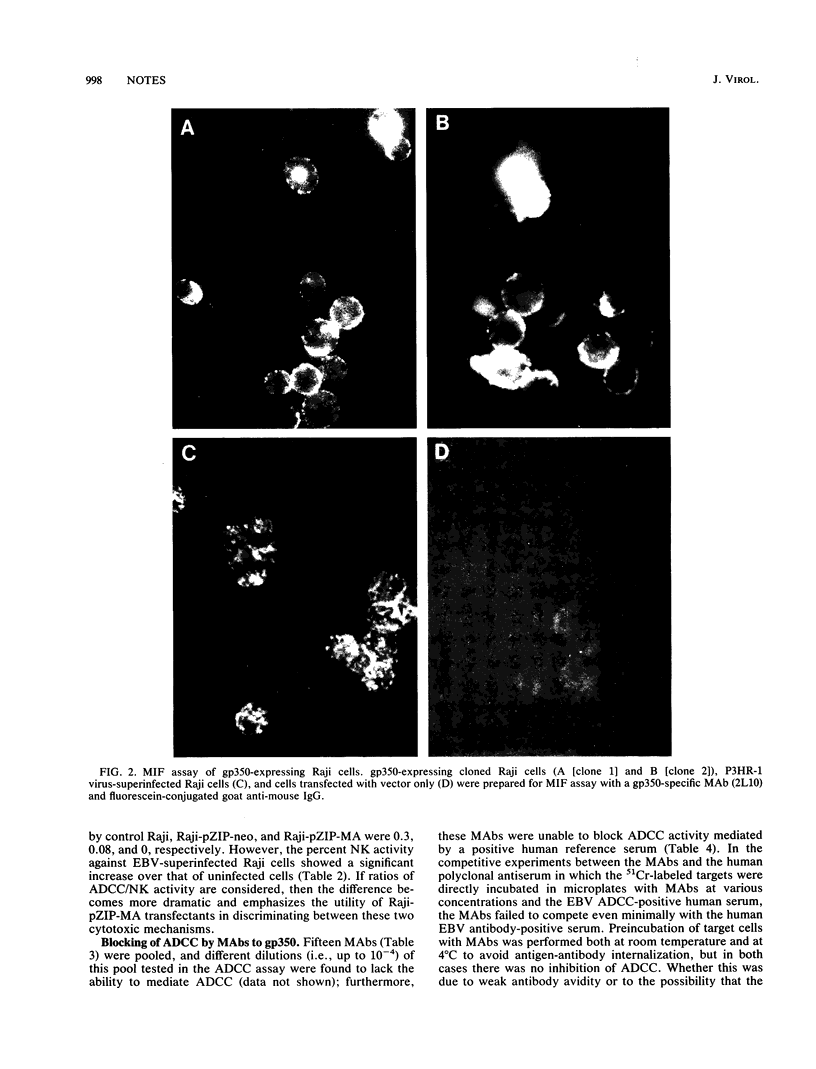
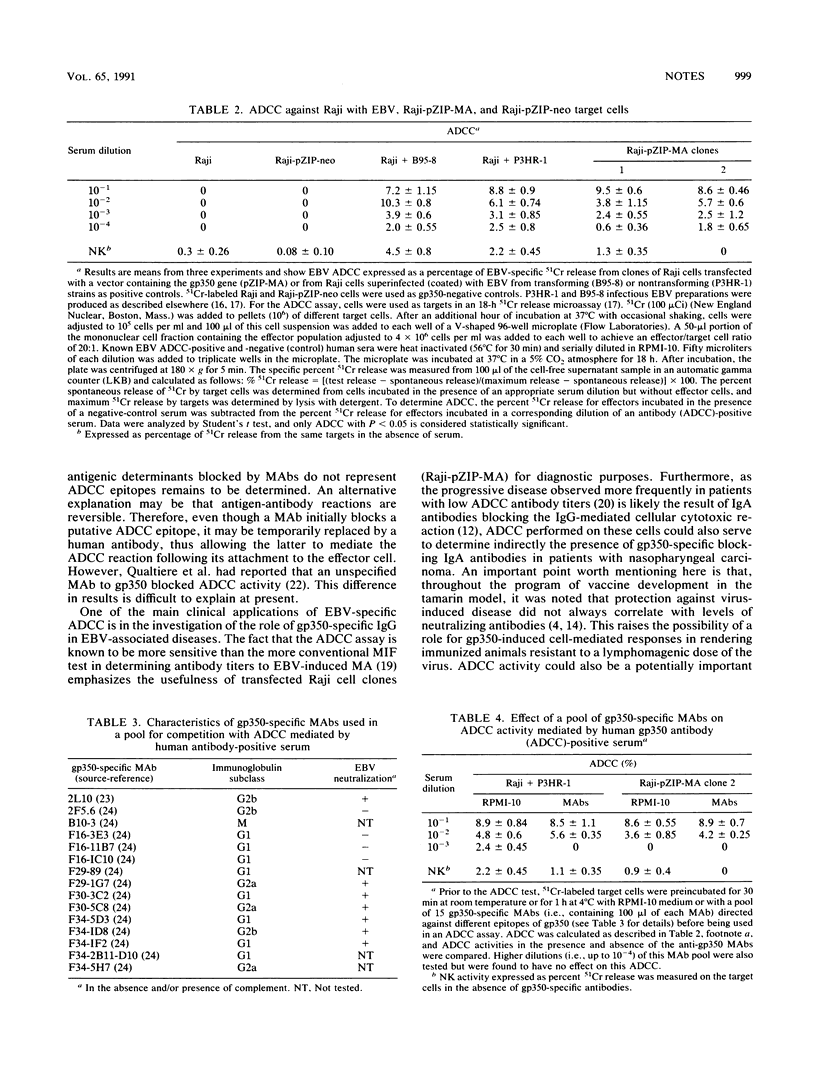


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Emini E. A., Schleif W. A., Armstrong M. E., Silberklang M., Schultz L. D., Lehman D., Maigetter R. Z., Qualtiere L. F., Pearson G. R., Ellis R. W. Antigenic analysis of the Epstein-Barr virus major membrane antigen (gp350/220) expressed in yeast and mammalian cells: implications for the development of a subunit vaccine. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):387–393. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90509-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M. A., Randle B. J., Finerty S., Kirkwood J. K. Not all potently neutralizing, vaccine-induced antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus ensure protection of susceptible experimental animals. Clin Exp Immunol. 1986 Mar;63(3):485–490. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle W., Henle G., Ho H. C., Burtin P., Cachin Y., Clifford P., de Schryver A., de-Thé G., Diehl V., Klein G. Antibodies to Epstein-Barr virus in nasopharyngeal carcinoma, other head and neck neoplasms, and control groups. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1970 Jan;44(1):225–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman G. J., Lazarowitz S. G., Hayward S. D. Monoclonal antibody against a 250,000-dalton glycoprotein of Epstein-Barr virus identifies a membrane antigen and a neutralizing antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2979–2983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hummel M., Thorley-Lawson D., Kieff E. An Epstein-Barr virus DNA fragment encodes messages for the two major envelope glycoproteins (gp350/300 and gp220/200). J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):413–417. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.413-417.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. F., Shurin S., Abramowsky C., Tubbs R. R., Sciotto C. G., Wahl R., Sands J., Gottman D., Katz B. Z., Sklar J. T-cell lymphomas containing Epstein-Barr viral DNA in patients with chronic Epstein-Barr virus infections. N Engl J Med. 1988 Mar 24;318(12):733–741. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198803243181203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurakata S., Ramos O. F., Klein G., Klein E. Lysis of P3HR-1 cells induced to enter the viral cycle by antibody-dependent and independent immunological mechanisms. Cell Immunol. 1989 Oct 1;123(1):134–147. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(89)90274-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe R. S., Keller P. M., Keech B. J., Davison A. J., Whang Y., Morgan A. J., Kieff E., Ellis R. W. Varicella-zoster virus as a live vector for the expression of foreign genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3896–3900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew G. D., Qualtiere L. F., Neel H. B., 3rd, Pearson G. R. IgA antibody, antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and prognosis in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1981 Feb 15;27(2):175–180. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910270208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mold C., Bradt B. M., Nemerow G. R., Cooper N. R. Activation of the alternative complement pathway by EBV and the viral envelope glycoprotein, gp350. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 1;140(11):3867–3874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A. J., Mackett M., Finerty S., Arrand J. R., Scullion F. T., Epstein M. A. Recombinant vaccinia virus expressing Epstein-Barr virus glycoprotein gp340 protects cottontop tamarins against EB virus-induced malignant lymphomas. J Med Virol. 1988 Jun;25(2):189–195. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890250209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson K., Klein G., Henle W., Henle G. The establishment of lymphoblastoid lines from adult and fetal human lymphoid tissue and its dependence on EBV. Int J Cancer. 1971 Nov 15;8(3):443–450. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910080312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULVERTAFT J. V. A STUDY OF MALIGNANT TUMOURS IN NIGERIA BY SHORT-TERM TISSUE CULTURE. J Clin Pathol. 1965 May;18:261–273. doi: 10.1136/jcp.18.3.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel P. C., Menezes J. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)--lymphoid cell interactions. II. The influence of the EBV replication cycle on natural killing and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity against EBV-infected cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1982 Jun;48(3):589–601. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel P., Menezes J. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-lymphoid cell interactions. I. Quantification of EBV particles required for the membrane immunofluorescence assay and the comparative expression of EBV receptors on different human B, T and null cell lines. J Gen Virol. 1981 Mar;53(Pt 1):1–11. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-53-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. R., Orr T. W. Antibody-dependent lymphocyte cytotoxicity against cells expressing Epstein-Barr virus antigens. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1976 Mar;56(3):485–488. doi: 10.1093/jnci/56.3.485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson G. R., Qualtiere L. F. Papain solubilization of the Epstein-Barr virus-induced membrane antigen. J Virol. 1978 Oct;28(1):344–351. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.1.344-351.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qualtiere L. F., Chase R., Pearson G. R. Purification and biologic characterization of a major Epstein Barr virus-induced membrane glycoprotein. J Immunol. 1982 Aug;129(2):814–818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qualtiere L. F., Chase R., Vroman B., Pearson G. R. Identification of Epstein-Barr virus strain differences with monoclonal antibody to a membrane glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):616–620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qualtiere L. F., Decoteau J. F., Hassan Nasr-el-Din M. Epitope mapping of the major Epstein-Barr virus outer envelope glycoprotein gp350/220. J Gen Virol. 1987 Feb;68(Pt 2):535–543. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-2-535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saemundsen A. K., Albeck H., Hansen J. P., Nielsen N. H., Anvret M., Henle W., Henle G., Thomsen K. A., Kristensen H. K., Klein G. Epstein-Barr virus in nasopharyngeal and salivary gland carcinomas of Greenland Eskimoes. Br J Cancer. 1982 Nov;46(5):721–728. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1982.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanner J., Weis J., Fearon D., Whang Y., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus gp350/220 binding to the B lymphocyte C3d receptor mediates adsorption, capping, and endocytosis. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):203–213. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90216-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson D. A., Geilinger K. Monoclonal antibodies against the major glycoprotein (gp350/220) of Epstein-Barr virus neutralize infectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5307–5311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toneguzzo F., Hayday A. C., Keating A. Electric field-mediated DNA transfer: transient and stable gene expression in human and mouse lymphoid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):703–706. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whang Y., Silberklang M., Morgan A., Munshi S., Lenny A. B., Ellis R. W., Kieff E. Expression of the Epstein-Barr virus gp350/220 gene in rodent and primate cells. J Virol. 1987 Jun;61(6):1796–1807. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.6.1796-1807.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]