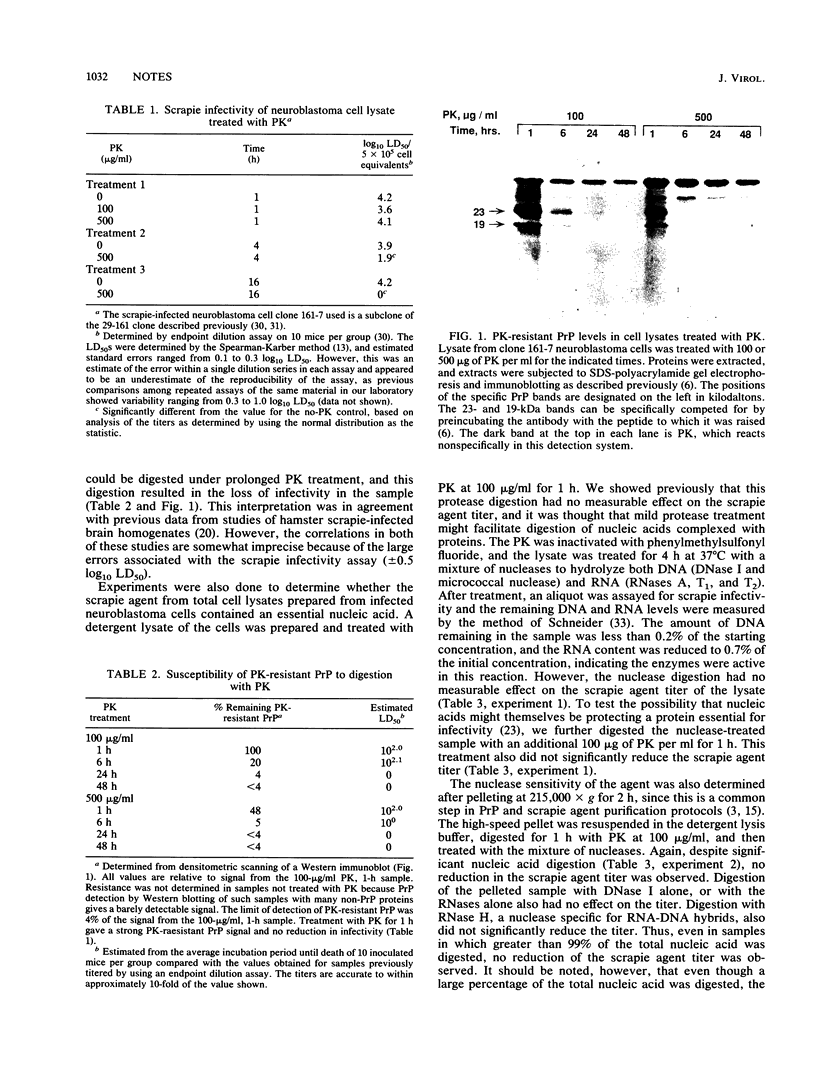
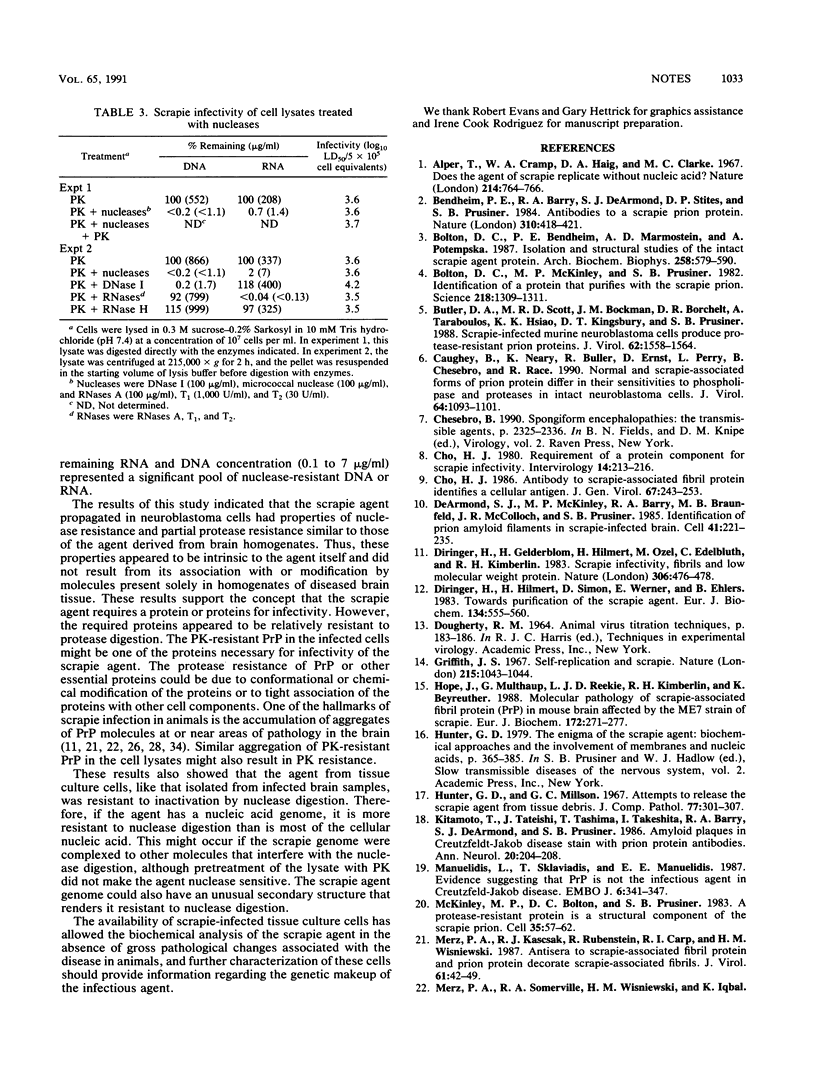
Abstract
The scrapie agent has been propagated in vitro in mouse neuroblastoma cells. To further characterize the tissue culture-derived scrapie agent, we studied the effects of protease and nuclease digestion on the agent derived from these cells. The scrapie agent in these cells was found to be resistant to protease digestions for short times but was inactivated by prolonged digestion at high protease concentrations. In contrast, digestion with a variety of nucleases did not alter the agent titer. These results demonstrate that the agent requires an essential protein or proteins for infectivity. If the agent also contains a nucleic acid genome, it must be more nuclease resistant than the majority of cellular DNA and RNA. These properties of the tissue culture-derived scrapie agent were identical to those of brain-derived scrapie agent and thus cannot be attributed to secondary effects of tissue pathology, since the infected cell cultures show no cytopathic effects as a result of infection.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper T., Cramp W. A., Haig D. A., Clarke M. C. Does the agent of scrapie replicate without nucleic acid? Nature. 1967 May 20;214(5090):764–766. doi: 10.1038/214764a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendheim P. E., Barry R. A., DeArmond S. J., Stites D. P., Prusiner S. B. Antibodies to a scrapie prion protein. Nature. 1984 Aug 2;310(5976):418–421. doi: 10.1038/310418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., Bendheim P. E., Marmorstein A. D., Potempska A. Isolation and structural studies of the intact scrapie agent protein. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Nov 1;258(2):579–590. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90380-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B. Identification of a protein that purifies with the scrapie prion. Science. 1982 Dec 24;218(4579):1309–1311. doi: 10.1126/science.6815801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler D. A., Scott M. R., Bockman J. M., Borchelt D. R., Taraboulos A., Hsiao K. K., Kingsbury D. T., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie-infected murine neuroblastoma cells produce protease-resistant prion proteins. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1558–1564. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1558-1564.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caughey B., Neary K., Buller R., Ernst D., Perry L. L., Chesebro B., Race R. E. Normal and scrapie-associated forms of prion protein differ in their sensitivities to phospholipase and proteases in intact neuroblastoma cells. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1093–1101. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1093-1101.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho H. J. Antibody to scrapie-associated fibril protein identifies a cellular antigen. J Gen Virol. 1986 Feb;67(Pt 2):243–253. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-2-243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho H. J. Requirement of a protein component for scrapie infectivity. Intervirology. 1980;14(3-4):213–216. doi: 10.1159/000149185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeArmond S. J., McKinley M. P., Barry R. A., Braunfeld M. B., McColloch J. R., Prusiner S. B. Identification of prion amyloid filaments in scrapie-infected brain. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):221–235. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90076-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diringer H., Gelderblom H., Hilmert H., Ozel M., Edelbluth C., Kimberlin R. H. Scrapie infectivity, fibrils and low molecular weight protein. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):476–478. doi: 10.1038/306476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diringer H., Hilmert H., Simon D., Werner E., Ehlers B. Towards purification of the scrapie agent. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Aug 15;134(3):555–560. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07602.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. S. Self-replication and scrapie. Nature. 1967 Sep 2;215(5105):1043–1044. doi: 10.1038/2151043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope J., Multhaup G., Reekie L. J., Kimberlin R. H., Beyreuther K. Molecular pathology of scrapie-associated fibril protein (PrP) in mouse brain affected by the ME7 strain of scrapie. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Mar 1;172(2):271–277. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13883.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter G. D., Millson G. C. Attempts to release the scrapie agent from tissue debris. J Comp Pathol. 1967 Jul;77(3):301–307. doi: 10.1016/0021-9975(67)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamoto T., Tateishi J., Tashima T., Takeshita I., Barry R. A., DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B. Amyloid plaques in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease stain with prion protein antibodies. Ann Neurol. 1986 Aug;20(2):204–208. doi: 10.1002/ana.410200205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Sklaviadis T., Manuelidis E. E. Evidence suggesting that PrP is not the infectious agent in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):341–347. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04760.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinley M. P., Bolton D. C., Prusiner S. B. A protease-resistant protein is a structural component of the scrapie prion. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90207-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz P. A., Kascsak R. J., Rubenstein R., Carp R. I., Wisniewski H. M. Antisera to scrapie-associated fibril protein and prion protein decorate scrapie-associated fibrils. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):42–49. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.42-49.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narang H. K., Asher D. M., Gajdusek D. C. Evidence that DNA is present in abnormal tubulofilamentous structures found in scrapie. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3575–3579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattison I. H., Jones K. M. The possible nature of the transmissible agent of scrapie. Vet Rec. 1967 Jan 7;80(1):2–9. doi: 10.1136/vr.80.1.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Bolton D. C., Groth D. F., Bowman K. A., Cochran S. P., McKinley M. P. Further purification and characterization of scrapie prions. Biochemistry. 1982 Dec 21;21(26):6942–6950. doi: 10.1021/bi00269a050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Groth D. F., Cochran S. P., McKinley M. P., Masiarz F. R. Gel electrophoresis and glass permeation chromatography of the hamster scrapie agent after enzymatic digestion and detergent extraction. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 14;19(21):4892–4898. doi: 10.1021/bi00562a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., McKinley M. P., Bowman K. A., Bolton D. C., Bendheim P. E., Groth D. F., Glenner G. G. Scrapie prions aggregate to form amyloid-like birefringent rods. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., McKinley M. P., Groth D. F., Bowman K. A., Mock N. I., Cochran S. P., Masiarz F. R. Scrapie agent contains a hydrophobic protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6675–6679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Novel proteinaceous infectious particles cause scrapie. Science. 1982 Apr 9;216(4542):136–144. doi: 10.1126/science.6801762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Race R. E., Caughey B., Graham K., Ernst D., Chesebro B. Analyses of frequency of infection, specific infectivity, and prion protein biosynthesis in scrapie-infected neuroblastoma cell clones. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2845–2849. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2845-2849.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Race R. E., Fadness L. H., Chesebro B. Characterization of scrapie infection in mouse neuroblastoma cells. J Gen Virol. 1987 May;68(Pt 5):1391–1399. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-5-1391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. W., Lofthouse R., Brown R., Crow T. J., Barry R. A., Prusiner S. B. Prion-protein immunoreactivity in human transmissible dementias. N Engl J Med. 1986 Nov 6;315(19):1231–1233. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198611063151919. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley C. A., Burrola P. G., Buchmeier M. J., Wooddell M. K., Barry R. A., Prusiner S. B., Lampert P. W. Immuno-gold localization of prion filaments in scrapie-infected hamster brains. Lab Invest. 1987 Dec;57(6):646–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]