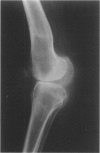
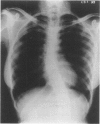
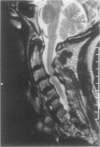
Abstract
1996 is polio awareness year. This paper reviews the clinical syndrome of acute paralytic poliomyelitis and its sequelae. We discuss epidemiological studies of the syndrome of late functional deterioration many years after the acute infection and the current hypotheses of the pathophysiology of such disorders. Recent evidence has suggested that potentially treatable factors may be implicated in the majority of such patients and it is therefore important to exclude such disorders before attributing late functional deterioration to progressive post-polio muscular atrophy.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON G. W., RONDEAU J. L. Absence of tonsils as a factor in the development of bulbar poliomyelitis. J Am Med Assoc. 1954 Jul 24;155(13):1123–1130. doi: 10.1001/jama.1954.03690310001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arlazoroff A., Bleicher Z., Klein C., Vure E., Lahat E., Gross B., Handsher R. Vaccine-associated contact paralytic poliomyelitis with atypical neurological presentation. Acta Neurol Scand. 1987 Sep;76(3):210–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1987.tb03569.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armon C., Daube J. R., Windebank A. J., Kurland L. T. How frequently does classic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis develop in survivors of poliomyelitis? Neurology. 1990 Jan;40(1):172–174. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.1.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BODIAN D. Histopathologic basis of clinical findings in poliomyelitis. Am J Med. 1949 May;6(5):563–578. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(49)90130-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley W. G. Recent views on amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with emphasis on electrophysiological studies. Muscle Nerve. 1987 Jul-Aug;10(6):490–502. doi: 10.1002/mus.880100603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashman N. R., Maselli R., Wollmann R. L., Roos R., Simon R., Antel J. P. Late denervation in patients with antecedent paralytic poliomyelitis. N Engl J Med. 1987 Jul 2;317(1):7–12. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198707023170102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chroni E., Howard R. S., Panayiotopoulos C. P., Spencer G. T. Multiple sclerosis presenting as late functional deterioration after poliomyelitis. Postgrad Med J. 1995 Jan;71(831):52–54. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.71.831.52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chumakov M., Voroshilova M., Shindarov L., Lavrova I., Gracheva L., Koroleva G., Vasilenko S., Brodvarova I., Nikolova M., Gyurova S. Enterovirus 71 isolated from cases of epidemic poliomyelitis-like disease in Bulgaria. Arch Virol. 1979;60(3-4):329–340. doi: 10.1007/BF01317504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalakas M. C., Elder G., Hallett M., Ravits J., Baker M., Papadopoulos N., Albrecht P., Sever J. A long-term follow-up study of patients with post-poliomyelitis neuromuscular symptoms. N Engl J Med. 1986 Apr 10;314(15):959–963. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198604103141505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalakas M. C. Morphologic changes in the muscles of patients with postpoliomyelitis neuromuscular symptoms. Neurology. 1988 Jan;38(1):99–104. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.1.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drachman D. B., Murphy S. R., Nigam M. P., Hills J. R. "Myopathic" changes in chronically denervated muscle. Arch Neurol. 1967 Jan;16(1):14–24. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470190018002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gear J. H. Nonpolio causes of polio-like paralytic syndromes. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 May-Jun;6 (Suppl 2):S379–S384. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.supplement_2.s379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall A. J. Polio eradication as 2000 approaches. BMJ. 1992 Jul 11;305(6845):69–70. doi: 10.1136/bmj.305.6845.69. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard R. S., Wiles C. M., Spencer G. T. The late sequelae of poliomyelitis. Q J Med. 1988 Mar;66(251):219–232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hull H. F., Ward N. A., Hull B. P., Milstien J. B., de Quadros C. Paralytic poliomyelitis: seasoned strategies, disappearing disease. Lancet. 1994 May 28;343(8909):1331–1337. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(94)92472-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON E. W., GUYTON J. D., OLSEN K. J. Motor nerve conduction velocity studies in poliomyelitis. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1960 May;41:185–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joce R., Wood D., Brown D., Begg N. Paralytic poliomyelitis in England and Wales, 1985-91. BMJ. 1992 Jul 11;305(6845):79–82. doi: 10.1136/bmj.305.6845.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katiyar B. C., Misra S., Singh R. B., Singh A. K., Gupta S., Gulati A. K., Christopher S., John T. J. Adult polio-like syndrome following Enterovirus 70 conjunctivitis (natural history of the disease). Acta Neurol Scand. 1983 May;67(5):263–274. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1983.tb04575.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. J., Hazleman B., Nichols P. J. Late onset respiratory failure in patients with previous poliomyelitis. Q J Med. 1974 Oct;43(172):551–568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchers W., de Visser M., Jongen P., van Loon A., Nibbeling R., Oostvogel P., Willemse D., Galama J. The postpolio syndrome: no evidence for poliovirus persistence. Ann Neurol. 1992 Dec;32(6):728–732. doi: 10.1002/ana.410320605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Men H. X., Bian C. H., Yang C. D., Zhang Z. L., Wu C. C., Pang B. Y. Surgical treatment of the flail knee after poliomyelitis. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1991 Mar;73(2):195–199. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.73B2.2005137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miranda-Pfeilsticker B., Figarella-Branger D., Pellissier J. F., Serratrice G. Le syndrome post-poliomyélitique: 29 cas. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1992;148(5):355–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muir P., Nicholson F., Jhetam M., Neogi S., Banatvala J. E. Rapid diagnosis of enterovirus infection by magnetic bead extraction and polymerase chain reaction detection of enterovirus RNA in clinical specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1993 Jan;31(1):31–38. doi: 10.1128/jcm.31.1.31-38.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nichols P. J., Lane D. J., Hamilton E. A., Hazleman B. L. Late onset of respiratory failure after poliomyelitis. Lancet. 1972 Dec 16;2(7790):1320–1320. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(72)92700-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezeshkpour G. H., Dalakas M. C. Long-term changes in the spinal cords of patients with old poliomyelitis. Signs of continuous disease activity. Arch Neurol. 1988 May;45(5):505–508. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1988.00520290033010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Querfurth H., Swanson P. D. Vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis. Regional case series and review. Arch Neurol. 1990 May;47(5):541–544. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1990.00530050061013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSSELL W. R. Paralytic poliomyelitis; the early symptoms and the effect of physical activity on the course of the disease. Br Med J. 1949 Mar 19;1(4602):465–471. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.4602.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravits J., Hallett M., Baker M., Nilsson J., Dalakas M. Clinical and electromyographic studies of postpoliomyelitis muscular atrophy. Muscle Nerve. 1990 Aug;13(8):667–674. doi: 10.1002/mus.880130802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roivainen M., Kinnunen E., Hovi T. Twenty-one patients with strictly defined postpoliomyelitis syndrome: no poliovirus-specific IgM antibodies in the cerebrospinal fluid. Ann Neurol. 1994 Jul;36(1):115–116. doi: 10.1002/ana.410360125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharief M. K., Hentges R., Ciardi M. Intrathecal immune response in patients with the post-polio syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1991 Sep 12;325(11):749–755. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199109123251101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- So Y. T., Olney R. K. AAEM case report #23: acute paralytic poliomyelitis. Muscle Nerve. 1991 Dec;14(12):1159–1164. doi: 10.1002/mus.880141203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swingler R. J., Fraser H., Warlow C. P. Motor neuron disease and polio in Scotland. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1992 Dec;55(12):1116–1120. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.55.12.1116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson B. E., Irving D. The numbers of limb motor neurons in the human lumbosacral cord throughout life. J Neurol Sci. 1977 Nov;34(2):213–219. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(77)90069-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiechers D. O., Hubbell S. L. Late changes in the motor unit after acute poliomyelitis. Muscle Nerve. 1981 Nov-Dec;4(6):524–528. doi: 10.1002/mus.880040610. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Windebank A. J., Litchy W. J., Daube J. R., Kurland L. T., Codd M. B., Iverson R. Late effects of paralytic poliomyelitis in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Neurology. 1991 Apr;41(4):501–507. doi: 10.1212/wnl.41.4.501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZILKHA K. J. Discussion on motor neurone disease. Proc R Soc Med. 1962 Dec;55:1028–1029. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoll G. J., Melchers W. J., Kopecka H., Jambroes G., van der Poel H. J., Galama J. M. General primer-mediated polymerase chain reaction for detection of enteroviruses: application for diagnostic routine and persistent infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1992 Jan;30(1):160–165. doi: 10.1128/jcm.30.1.160-165.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]