Abstract
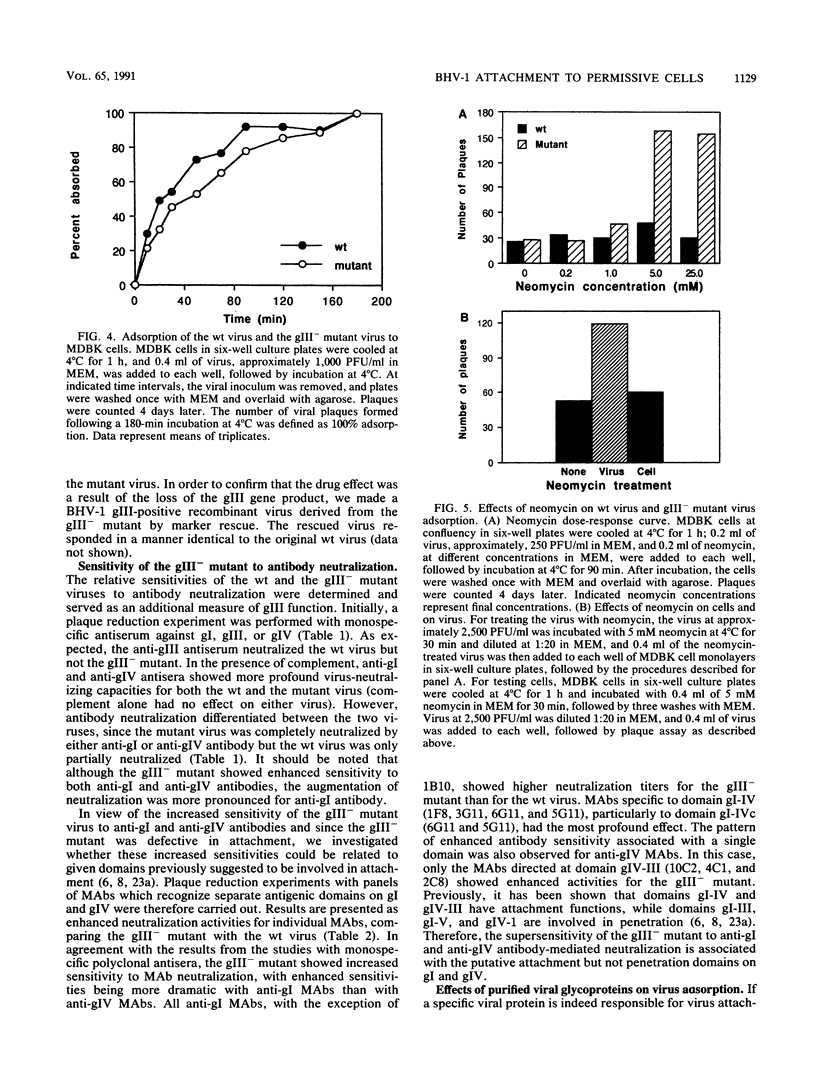
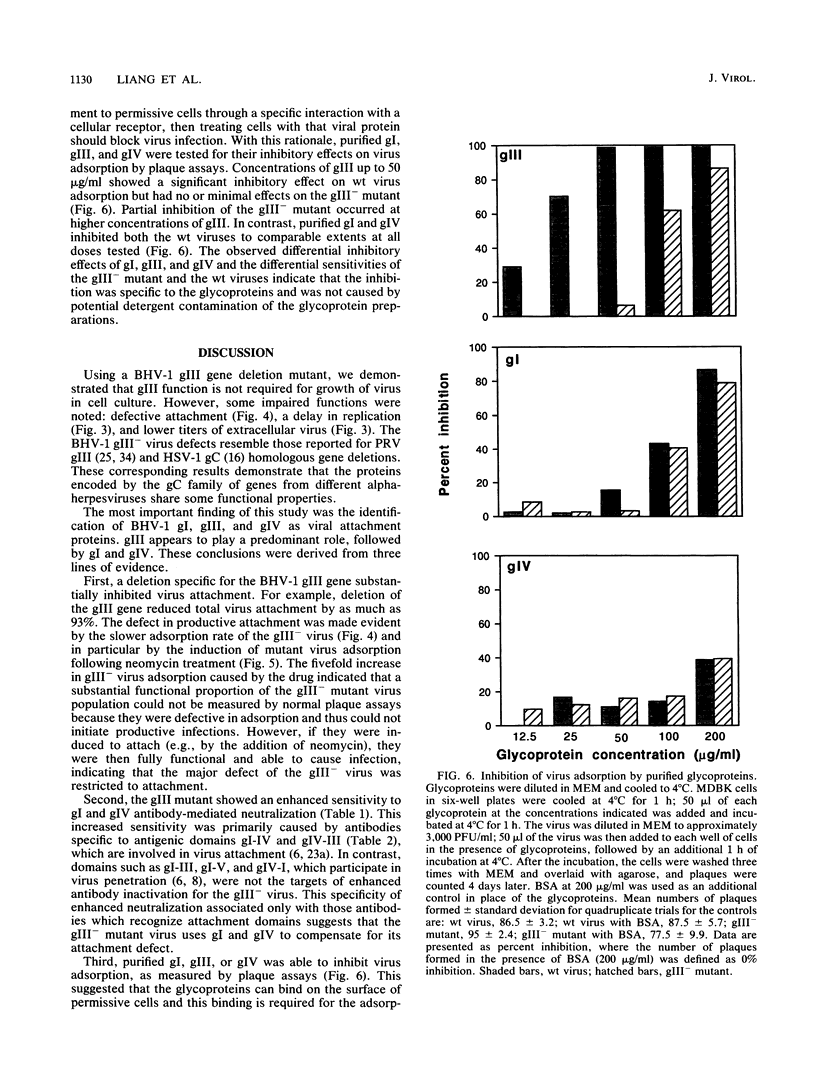
A bovine herpesvirus 1 (BHV-1) gIII deletion mutant (gIII-) was produced by means of recombinant DNA that retained the ability to replicate in cell culture. However, the gIII- mutant was functionally defective, showing impaired attachment to permissive cells, a delay in virus replication, and reduced extracellular virus production. The attachment defect exhibited by the gIII- mutant is an indication of the role played by gIII in the normal infection process. This was shown by dramatically decreased binding of radiolabelled gIII- virus to permissive cells and a slower adsorption rate, as measured by plaque formation, than the wild-type (wt) virus. Furthermore, treatment of the gIII- virus with neomycin increased virus adsorption and plaque formation by severalfold, whereas neomycin treatment had no effect on the wt virus. This observation showed that the gIII- mutant was strictly defective in adsorption but fully competent to produce productive infections once induced to attach. The gIII- mutant showed greater sensitivities than did the wt virus to anti-gI and anti-gIV antibody-mediated neutralization. Analyses with panels of monoclonal antibodies to gI and gIV revealed that the epitopes gI-IV and gIV-III were the main targets for enhanced neutralization. This provided evidence that gI and gIV may also participate in virus attachment. Finally, when affinity-purified gI, gIII, and gIV were tested for their ability to inhibit virus adsorption, gIII had the most pronounced inhibitory effect, followed by gI and then gIV. gIII was able to completely inhibit wt virus adsorption, and at a high concentration, it also partially inhibited the gIII- mutant. gI and gIV inhibited wt and gIII- mutant adsorption to a comparable extent. Our results collectively indicate that gIII plays a predominant role in virus attachment, but gI and gIV also contribute to this process. In addition, a potential cooperative mechanism for virus attachment with these three proteins is presented.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Babiuk L. A., L'Italien J., van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., Zamb T., Lawman J. P., Hughes G., Gifford G. A. Protection of cattle from bovine herpesvirus type I (BHV-1) infection by immunization with individual viral glycoproteins. Virology. 1987 Jul;159(1):57–66. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90347-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiuk L. A., Wardley R. C., Rouse B. T. Defense mechanisms against bovine herpesvirus: relationship of virus-host cell events to susceptibility to antibody-complement cell lysis. Infect Immun. 1975 Nov;12(5):958–963. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.5.958-963.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Hayakawa H., Berg P. Electroporation for the efficient transfection of mammalian cells with DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 11;15(3):1311–1326. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick D. R., Babiuk L. A., Zamb T. J. Nucleotide sequence of bovine herpesvirus type 1 glycoprotein gIII, a structural model for gIII as a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, and implications for the homologous glycoproteins of other herpesviruses. Virology. 1989 Nov;173(1):46–57. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90220-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzpatrick D. R., Redmond M. J., Attah-Poku S. K., van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., Babiuk L. A., Zamb T. J. Mapping of 10 epitopes on bovine herpesvirus type 1 glycoproteins gI and gIII. Virology. 1990 May;176(1):145–157. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90239-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuller A. O., Spear P. G. Specificities of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies that inhibit adsorption of herpes simplex virus to cells and lack of inhibition by potent neutralizing antibodies. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):475–482. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.475-482.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes G., Babiuk L. A., van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S. Functional and topographical analyses of epitopes on bovine herpesvirus type 1 glycoprotein IV. Arch Virol. 1988;103(1-2):47–60. doi: 10.1007/BF01319808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Burke R. L., Gregory T. Soluble forms of herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D bind to a limited number of cell surface receptors and inhibit virus entry into cells. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2569–2576. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2569-2576.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Ligas M. W. Herpes simplex viruses lacking glycoprotein D are unable to inhibit virus penetration: quantitative evidence for virus-specific cell surface receptors. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4605–4612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4605-4612.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., McDermott M. R., Chrisp C., Glorioso J. C. Pathogenicity in mice of herpes simplex virus type 2 mutants unable to express glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1986 Apr;58(1):36–42. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.1.36-42.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Wittels M., Spear P. G. Binding to cells of virosomes containing herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins and evidence for fusion. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):238–247. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.238-247.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn J. E., Kramer M. D., Willenbacher W., Wieland U., Lorentzen E. U., Braun R. W. Identification of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins interacting with the cell surface. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2491–2497. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2491-2497.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langeland N., Holmsen H., Lillehaug J. R., Haarr L. Evidence that neomycin inhibits binding of herpes simplex virus type 1 to the cellular receptor. J Virol. 1987 Nov;61(11):3388–3393. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.11.3388-3393.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langeland N., Moore L. J., Holmsen H., Haarr L. Interaction of polylysine with the cellular receptor for herpes simplex virus type 1. J Gen Virol. 1988 Jun;69(Pt 6):1137–1145. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-6-1137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langeland N., Oyan A. M., Marsden H. S., Cross A., Glorioso J. C., Moore L. J., Haarr L. Localization on the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome of a region encoding proteins involved in adsorption to the cellular receptor. J Virol. 1990 Mar;64(3):1271–1277. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.3.1271-1277.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lentz T. L. The recognition event between virus and host cell receptor: a target for antiviral agents. J Gen Virol. 1990 Apr;71(Pt 4):751–766. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-4-751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall R. L., Rodriguez L. L., Letchworth G. J., 3rd Characterization of envelope proteins of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus (bovine herpesvirus 1) by biochemical and immunological methods. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):745–753. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.745-753.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayfield J. E., Good P. J., VanOort H. J., Campbell A. R., Reed D. E. Cloning and cleavage site mapping of DNA from bovine herpesvirus 1 (Cooper strain). J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):259–264. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.259-264.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra V., Blumenthal R. M., Babiuk L. A. Proteins Specified by bovine herpesvirus 1 (infectious bovine rhinotracheitis virus). J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):367–378. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.367-378.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra V., Nelson R., Smith M. Sequence of a bovine herpesvirus type-1 glycoprotein gene that is homologous to the herpes simplex gene for the glycoprotein gB. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):542–549. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90525-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerow G. R., Jensen F. C., Cooper N. R. Neutralization of Epstein-Barr virus by nonimmune human serum. Role of cross-reacting antibody to herpes simplex virus and complement. J Clin Invest. 1982 Nov;70(5):1081–1091. doi: 10.1172/JCI110696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreurs C., Mettenleiter T. C., Zuckermann F., Sugg N., Ben-Porat T. Glycoprotein gIII of pseudorabies virus is multifunctional. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2251–2257. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2251-2257.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stannard L. M., Fuller A. O., Spear P. G. Herpes simplex virus glycoproteins associated with different morphological entities projecting from the virion envelope. J Gen Virol. 1987 Mar;68(Pt 3):715–725. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-3-715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WuDunn D., Spear P. G. Initial interaction of herpes simplex virus with cells is binding to heparan sulfate. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):52–58. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.52-58.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuckermann F., Zsak L., Reilly L., Sugg N., Ben-Porat T. Early interactions of pseudorabies virus with host cells: functions of glycoprotein gIII. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3323–3329. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3323-3329.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., Babiuk L. A. Antigenic and immunogenic characteristics of bovine herpesvirus type-1 glycoproteins GVP 3/9 and GVP 6/11a/16, purified by immunoadsorbent chromatography. Virology. 1985 Jul 15;144(1):204–215. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90318-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., Babiuk L. A. Synthesis and processing of bovine herpesvirus 1 glycoproteins. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):401–410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.401-410.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., Zamb T., Babiuk L. A. Synthesis, cellular location, and immunogenicity of bovine herpesvirus 1 glycoproteins gI and gIII expressed by recombinant vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1989 May;63(5):2159–2168. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.5.2159-2168.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Drunen Littel-van den Hurk S., van den Hurk J. V., Gilchrist J. E., Misra V., Babiuk L. A. Interactions of monoclonal antibodies and bovine herpesvirus type 1 (BHV-1) glycoproteins: characterization of their biochemical and immunological properties. Virology. 1984 Jun;135(2):466–479. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90201-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]