Abstract
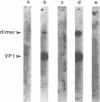
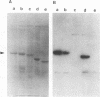
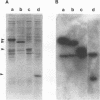
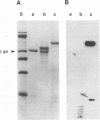
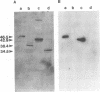
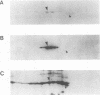
The major capsid protein of polyomavirus, VP1, has been expression cloned in Escherichia coli, and the recombinant VP1 protein has been purified to near homogeneity (A. D. Leavitt, T. M. Roberts, and R. L. Garcea, J. Biol. Chem. 260:12803-12809, 1985). With this recombinant protein, a nitrocellulose filter transfer assay was developed for detecting DNA binding to VP1 (Southwestern assay). In optimizing conditions for this assay, dithiothreitol was found to inhibit DNA binding significantly. With recombinant VP1 proteins deleted at the carboxy and amino termini, a region of the protein affecting DNA binding was identified within the first 7 amino acids (MAPKRKS) of the VP1 amino terminus. Southwestern analysis of virion proteins separated by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis demonstrated equivalent DNA binding among the different VP1 isoelectric focusing subspecies, suggesting that VP1 phosphorylation does not modulate this function. By means of partial proteolysis of purified recombinant VP1 capsomeres for assessing structural features of the protein domain affecting DNA binding, a trypsin-sensitive site at lysine 28 was found to eliminate VP1 binding to DNA. The binding constant of recombinant VP1 to polyomavirus DNA was determined by an immunoprecipitation assay (R. D. G. McKay, J. Mol. Biol. 145:471-488, 1981) to be 1 x 10(-11) to 2 x 10(-11) M, which was not significantly different from its affinity for plasmid DNA. McKay analysis of deleted VP1 proteins and VP1-beta-galactosidase fusion proteins indicated that the amino terminus was both necessary and sufficient for DNA binding. As shown by electron microscopy, DNA inhibited in vitro capsomere self-assembly into capsidlike structures (D. M. Salunke, D. L. D. Caspar, and R. L. Garcea, Cell 46:895-904, 1986). Thus, VP1 is a high-affinity, non-sequence-specific DNA-binding protein with the binding function localized near its trypsin-accessible amino terminus. The inhibitory effects of disulfide reagents on DNA binding and of DNA on capsid assembly suggest possible intermediate steps in virion assembly.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amann E., Brosius J. "ATG vectors' for regulated high-level expression of cloned genes in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1985;40(2-3):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amann E., Brosius J., Ptashne M. Vectors bearing a hybrid trp-lac promoter useful for regulated expression of cloned genes in Escherichia coli. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):167–178. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90222-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bina M., Ng S. C., Blasquez V. Simian virus 40 chromatin interaction with the capsid proteins. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 1983 Dec;1(3):689–704. doi: 10.1080/07391102.1983.10507475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasquez V., Beecher S., Bina M. Simian virus 40 morphogenetic pathway. An analysis of assembly-defective tsB201 DNA protein complexes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):8477–8484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasquez V., Stein A., Ambrose C., Bina M. Simian virus 40 protein VP1 is involved in spacing nucleosomes in minichromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 5;191(1):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90425-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg B. M., Giorgi C., Kolakofsky D. N protein of vesicular stomatitis virus selectively encapsidates leader RNA in vitro. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):559–567. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90475-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J. N., Winston V. D., Consigli R. A. Dissociation of polyoma virus by the chelation of calcium ions found associated with purified virions. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):717–724. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.717-724.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christiansen G., Landers T., Griffith J., Berg P. Characterization of components released by alkali disruption of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1079–1084. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1079-1084.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coca-Prados M., Hsu M. T. Intracellular forms of simian virus 40 nucleoprotein complexes. II. Biochemical and electron microscopic analysis of simian virus 40 virion assembly. J Virol. 1979 Jul;31(1):199–208. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.1.199-208.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desplan C., Theis J., O'Farrell P. H. The Drosophila developmental gene, engrailed, encodes a sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):630–635. doi: 10.1038/318630a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingwall C., Sharnick S. V., Laskey R. A. A polypeptide domain that specifies migration of nucleoplasmin into the nucleus. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):449–458. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Walter G. Subunit interactions in polyoma virus structure. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):783–796. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90499-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez-Munoz R., Coca-Prados M., Hsu M. T. Intracellular forms of simian virus 40 nucleoprotein complexes. I. Methods of isolation and characterization in CV-1 cells. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):612–623. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.612-623.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann T., David D. Structural roles of polyoma virus proteins. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):776–782. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.776-782.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann T. In vitro reassembly of shell-like particles from disrupted polyoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2574–2578. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Seidman M. M., Levine A. J. Intracellular SV40 nucleoprotein complexes: synthesis to encapsidation. Virology. 1980 Dec;107(2):389–401. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90306-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcea R. L., Benjamin T. L. Host range transforming gene of polyoma virus plays a role in virus assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3613–3617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcea R. L., Benjamin T. L. Isolation and characterization of polyoma nucleoprotein complexes. Virology. 1983 Oct 15;130(1):65–75. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90118-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcea R. L., Salunke D. M., Caspar D. L. Site-directed mutation affecting polyomavirus capsid self-assembly in vitro. Nature. 1987 Sep 3;329(6134):86–87. doi: 10.1038/329086a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. A., Goldberg A. L. Production of abnormal proteins in E. coli stimulates transcription of lon and other heat shock genes. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):587–595. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. GCN4 protein, synthesized in vitro, binds HIS3 regulatory sequences: implications for general control of amino acid biosynthetic genes in yeast. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunkapiller M. W., Hewick R. M., Dreyer W. J., Hood L. E. High-sensitivity sequencing with a gas-phase sequenator. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:399–413. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jakobovits E. B., Aloni Y. Isolation and characterization of various forms of simian virus 40 DNA-protein complexes. Virology. 1980 Apr 15;102(1):107–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Bella F., Vesco C. Late modifications of simian virus 40 chromatin during the lytic cycle occur in an immature form of virion. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1138–1150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1138-1150.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavitt A. D., Roberts T. M., Garcea R. L. Polyoma virus major capsid protein, VP1. Purification after high level expression in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12803–12809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattern C. F., Takemoto K. K., Daniel W. A. Replication of polyoma virus in mouse embryo cells: electron microscopic observations. Virology. 1966 Oct;30(2):242–256. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90099-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay R. D. Binding of a simian virus 40 T antigen-related protein to DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 25;145(3):471–488. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90540-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng S. C., Bina M. Temperature-sensitive BC mutants of simian virus 40: block in virion assembly and accumulation of capsid-chromatin complexes. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):471–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.471-477.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Baker T. S., Caspar D. L., Murakami W. T. Polyoma virus capsid structure at 22.5 A resolution. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):110–115. doi: 10.1038/295110a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. J., Tanese N., Goff S. P. Gene product of Moloney murine leukemia virus required for proviral integration is a DNA-binding protein. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 5;203(1):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90097-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Müller-Hill B. Easy identification of cDNA clones. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1791–1794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salunke D. M., Caspar D. L., Garcea R. L. Polymorphism in the assembly of polyomavirus capsid protein VP1. Biophys J. 1989 Nov;56(5):887–900. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(89)82735-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salunke D. M., Caspar D. L., Garcea R. L. Self-assembly of purified polyomavirus capsid protein VP1. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):895–904. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90071-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saragosti S., Cereghini S., Yaniv M. Fine structure of the regulatory region of simian virus 40 minichromosomes revealed by DNAase I digestion. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep 15;160(2):133–146. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90171-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith A. E., Kalderon D., Roberts B. L., Colledge W. H., Edge M., Gillett P., Markham A., Paucha E., Richardson W. D. The nuclear location signal. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Oct 22;226(1242):43–58. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeda E., Arrand J. R., Smolar N., Walsh J. E., Griffin B. E. Coding potential and regulatory signals of the polyoma virus genome. Nature. 1980 Jan 31;283(5746):445–453. doi: 10.1038/283445a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soussi T. DNA-binding properties of the major structural protein of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):740–742. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.740-742.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]