Abstract
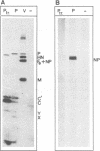
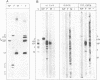
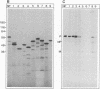
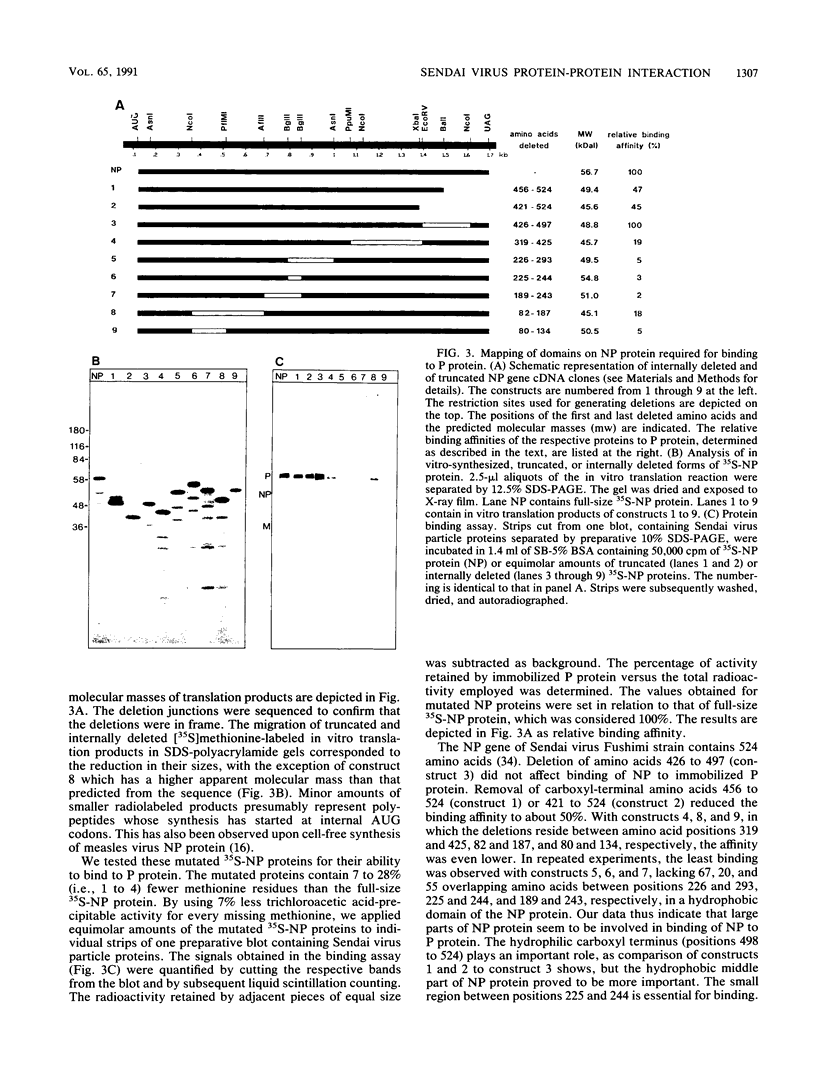
Proteins from Sendai virus particles and from infected cells were analyzed in a protein-blotting protein-overlay assay for their interaction with in vitro-synthesized, [35S]methionine-labeled viral proteins NP, P, and M. After separation by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, transfer onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes, and renaturation, the immobilized proteins were found to interact specifically with radiolabeled proteins. NP proteins from virus particles and from infected cells retained 35S-P protein equally well. Conversely, P protein from virus particles and from infected cells retained 35S-NP protein. 35S-M protein was retained mainly by NP protein but also by several cellular proteins. To determine the domains on NP protein required for binding to immobilized P protein, a series of truncated and internally deleted 35S-NP proteins was constructed. The only deletion that did not affect binding resides between residues 426 and 497. The carboxyl-terminal 27 residues (positions 498 to 524) contribute significantly to the binding affinity. Removal of 20 residues (positions 225 to 244) in the hydrophobic middle part of NP protein completely abolished its binding to P protein.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerjee A. K. Transcription and replication of rhabdoviruses. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Mar;51(1):66–87. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.1.66-87.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen B., Steinberg J., Laemmli U. K., Weintraub H. The detection of DNA-binding proteins by protein blotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):1–20. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle J. F., Holmes K. V. RNA-binding proteins of bovine rotavirus. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):561–568. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.561-568.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran J., Kolakofsky D. Scanning independent ribosomal initiation of the Sendai virus Y proteins in vitro and in vivo. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):521–526. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03406.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defer C., Belin M. T., Caillet-Boudin M. L., Boulanger P. Human adenovirus-host cell interactions: comparative study with members of subgroups B and C. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3661–3673. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3661-3673.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande K. L., Portner A. Monoclonal antibodies to the P protein of Sendai virus define its structure and role in transcription. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90451-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande K. L., Portner A. Structural and functional analysis of Sendai virus nucleocapsid protein NP with monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1984 Nov;139(1):32–42. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90327-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einberger H., Mertz R., Hofschneider P. H., Neubert W. J. Purification, renaturation, and reconstituted protein kinase activity of the Sendai virus large (L) protein: L protein phosphorylates the NP and P proteins in vitro. J Virol. 1990 Sep;64(9):4274–4280. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.9.4274-4280.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill D. S., Takai S., Portner A., Kingsbury D. W. Mapping of antigenic domains of Sendai virus nucleocapsid protein expressed in Escherichia coli. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4805–4808. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4805-4808.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi C., Blumberg B. M., Kolakofsky D. Sendai virus contains overlapping genes expressed from a single mRNA. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):829–836. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh H., Shioda T., Sakai Y., Mizumoto K., Shibuta H. Rescue of Sendai virus from viral ribonucleoprotein-transfected cells by infection with recombinant vaccinia viruses carrying Sendai virus L and P/C genes. Virology. 1989 Aug;171(2):434–443. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90612-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görlach M., Hermann M., Schwemmle M., Hilse K. Binding of globin mRNA, beta-globin mRNA segments and RNA homopolymers by immobilized protein of polysomal globin messenger ribonucleoprotein. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Oct 1;184(3):589–596. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15054.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Elution of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gels, removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate, and renaturation of enzymatic activity: results with sigma subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase, wheat germ DNA topoisomerase, and other enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):76–86. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamaguchi M., Yoshida T., Nishikawa K., Naruse H., Nagai Y. Transcriptive complex of Newcastle disease virus. I. Both L and P proteins are required to constitute an active complex. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):105–117. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90322-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasel K. W., Day S., Millward S., Richardson C. D., Bellini W. J., Greer P. A. Characterization of cloned measles virus mRNAs by in vitro transcription, translation, and immunoprecipitation. Intervirology. 1987;28(1):26–39. doi: 10.1159/000149994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heggeness M. H., Scheid A., Choppin P. W. the relationship of conformational changes in the Sendai virus nucleocapsid to proteolytic cleavage of the NP polypeptide. Virology. 1981 Oct 30;114(2):555–562. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90235-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka Y., Kanda T., Iwasaki K., Nomoto A., Shioda T., Shibuta H. Nucleotide sequence of a Sendai virus genome region covering the entire M gene and the 3' proximal 1013 nucleotides of the F gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 12;12(21):7965–7973. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.21.7965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill V. M., Summers D. F. A minor microtubule-associated protein is responsible for the stimulation of vesicular stomatitis virus transcription in vitro. J Gen Virol. 1990 Feb;71(Pt 2):289–298. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-2-289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homann H. E., Hofschneider P. H., Neubert W. J. Sendai virus gene expression in lytically and persistently infected cells. Virology. 1990 Jul;177(1):131–140. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90467-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hübscher U. Double replica southwestern. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5486–5486. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacks S. A., Springhorn S. S. Renaturation of enzymes after polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7467–7473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb R. A., Choppin P. W. The synthesis of Sendai virus polypeptides in infected cells. III. Phosphorylation of polypeptides. Virology. 1977 Sep;81(2):382–397. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90154-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesot H., Kühl U., Mark K. Isolation of a laminin-binding protein from muscle cell membranes. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):861–865. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01514.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Fox C. F. Protein-protein interactions within paramyxoviruses identified by native disulfide bonding or reversible chemical cross-linking. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):152–166. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.152-166.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mischak H., Neubauer C., Berger B., Kuechler E., Blaas D. Detection of the human rhinovirus minor group receptor on renaturing Western blots. J Gen Virol. 1988 Oct;69(Pt 10):2653–2656. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-69-10-2653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moyer S. A., Baker S. C., Lessard J. L. Tubulin: a factor necessary for the synthesis of both Sendai virus and vesicular stomatitis virus RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5405–5409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Takio K., Eto Y., Shibai H., Titani K., Sugino H. Activin-binding protein from rat ovary is follistatin. Science. 1990 Feb 16;247(4944):836–838. doi: 10.1126/science.2106159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubert W. J. Cloning and sequencing of the polymerase gene (P) of Sendai virus (strain Fushimi). Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):10101–10101. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.10101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donald P. Measuring the change of population fitness by natural selection. Nature. 1970 Jul 18;227(5255):307–308. doi: 10.1038/227307a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raghow R., Kingsbury D. W. Protein-RNA contacts in Sendai virus nucleocapsids revealed by photo-crosslinking. Virology. 1979 Oct 15;98(1):267–271. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90546-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy P., Adachi A., Urakawa T., Booth T. F., Thomas C. P. Identification of bluetongue virus VP6 protein as a nucleic acid-binding protein and the localization of VP6 in virus-infected vertebrate cells. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.1-8.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan K. W., Kingsbury D. W. Carboxyl-terminal region of Sendai virus P protein is required for binding to viral nucleocapsids. Virology. 1988 Nov;167(1):106–112. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan K. W., Portner A. Separate domains of Sendai virus P protein are required for binding to viral nucleocapsids. Virology. 1990 Feb;174(2):515–521. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90105-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schenkel J., Sekeris C. E., Alonso A., Bautz E. K. RNA-binding properties of hnRNP proteins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Feb 1;171(3):565–569. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13825.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioda T., Hidaka Y., Kanda T., Shibuta H., Nomoto A., Iwasaki K. Sequence of 3,687 nucleotides from the 3' end of Sendai virus genome RNA and the predicted amino acid sequences of viral NP, P and C proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Nov 11;11(21):7317–7330. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.21.7317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shioda T., Iwasaki K., Shibuta H. Determination of the complete nucleotide sequence of the Sendai virus genome RNA and the predicted amino acid sequences of the F, HN and L proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1545–1563. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szewczyk B., Laver W. G., Summers D. F. Purification, thioredoxin renaturation, and reconstituted activity of the three subunits of the influenza A virus RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7907–7911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidal S., Curran J., Orvell C., Kolakofsky D. Mapping of monoclonal antibodies to the Sendai virus P protein and the location of its phosphates. J Virol. 1988 Jun;62(6):2200–2203. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.6.2200-2203.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Kuter D. J. Reversible denaturation of enzymes by sodium dodecyl sulfate. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 25;246(14):4504–4509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willenbrink W., Neubert W. J. Cloning and sequencing of the matrix protein gene (M) of Sendai virus (strain Fushimi). Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3993–3993. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]