Abstract
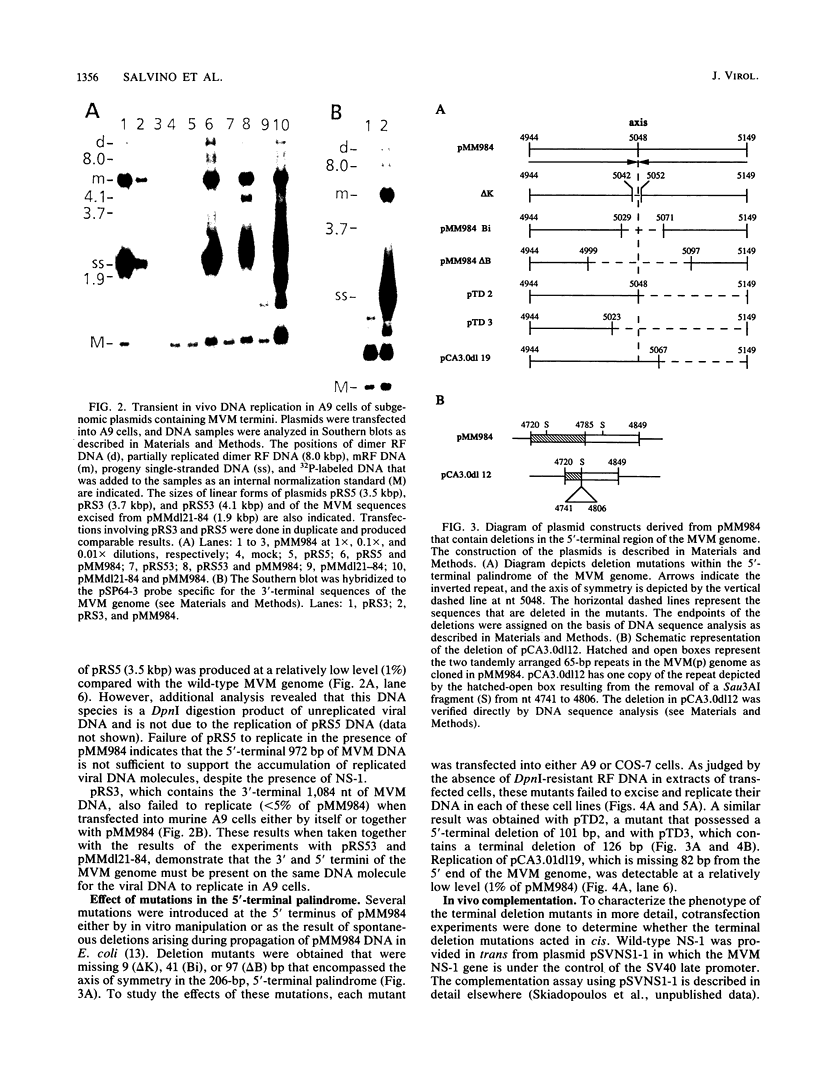
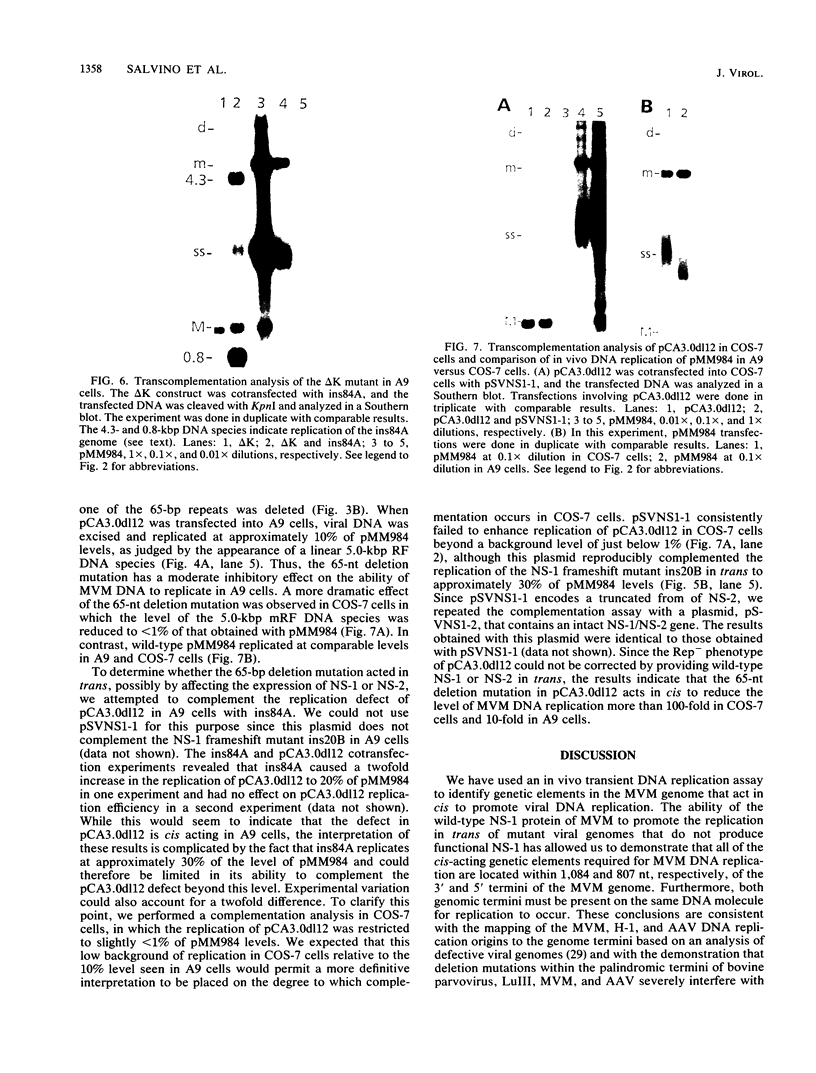
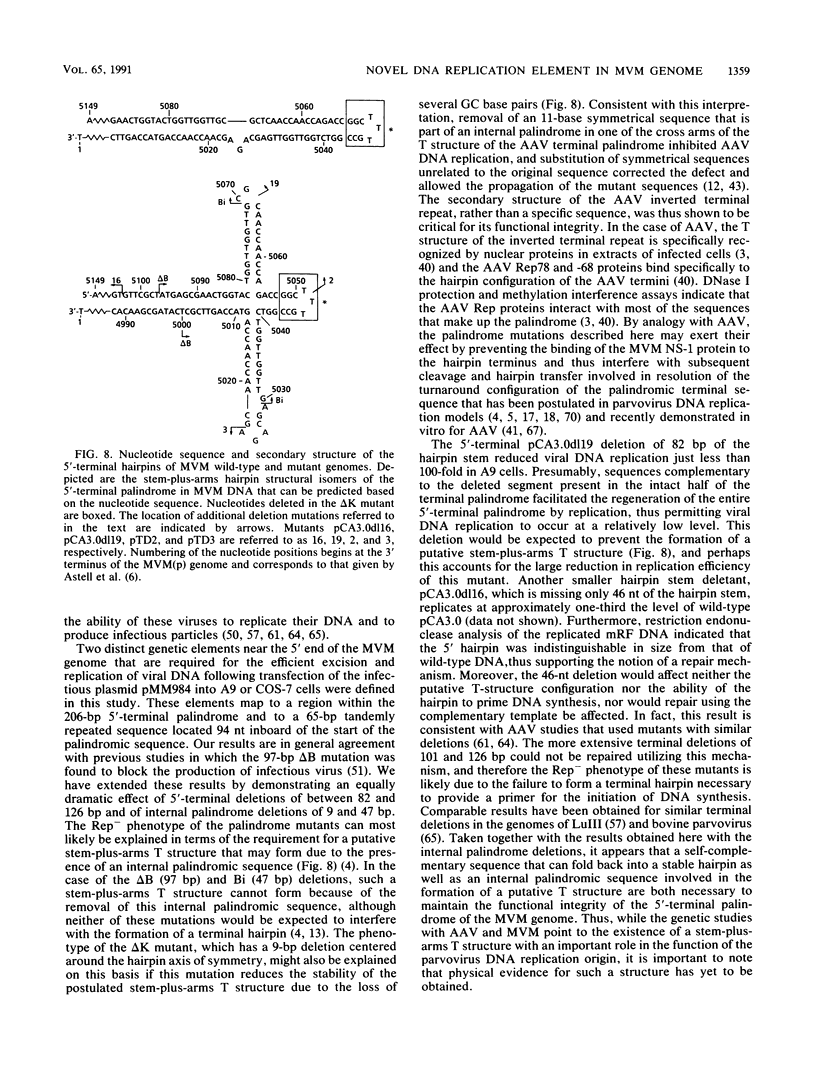
Mutations were introduced into plasmid pMM984, a full-length infectious clone of the fibrotropic strain of minute virus of mice, to identify cis-acting genetic elements required for the excision and replication of the viral genome. The replicative capacity of these mutants was measured directly, using an in vivo transient DNA replication assay following transfection of plasmids into murine A9 cells and primate COS-7 cells. Experiments with subgenomic constructs indicated that both viral termini must be present on the same DNA molecule for replication to occur and that the viral nonstructural protein NS-1 must be provided in trans. The necessary sequences were located within 1,084 and 807 nucleotides of the 3' and 5' ends of the minute virus of mice genome, respectively. The inhibitory effect of deletions within the 206-bp 5'-terminal palindrome demonstrated that these sequences comprise a cis-acting genetic element that is absolutely essential for the excision and replication of viral DNA. The results further indicated a requirement for a stem-plus-arms T structure as well as for the formation of a simple hairpin. In addition, the removal of one copy of a tandemly arranged 65-bp repeat found 94 nucleotides inboard of the 5'-terminal palindrome inhibited viral DNA replication in cis by 10- and just greater than 100-fold in A9 and COS-7 cells, respectively. The latter results define a novel genetic element within the 65-bp repeated sequence, distinct from the terminal palindrome, that is capable of regulating minute virus of mice DNA replication in a species-specific manner.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anton I. A., Lane D. P. Non-structural protein 1 of parvoviruses: homology to purine nucleotide using proteins and early proteins of papovaviruses. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 10;14(19):7813–7813. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.19.7813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonietti J. P., Sahli R., Beard P., Hirt B. Characterization of the cell type-specific determinant in the genome of minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):552–557. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.552-557.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashktorab H., Srivastava A. Identification of nuclear proteins that specifically interact with adeno-associated virus type 2 inverted terminal repeat hairpin DNA. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3034–3039. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3034-3039.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astell C. R., Chow M. B., Ward D. C. Sequence analysis of the termini of virion and replicative forms of minute virus of mice DNA suggests a modified rolling hairpin model for autonomous parvovirus DNA replication. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):171–177. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.171-177.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astell C. R., Gardiner E. M., Tattersall P. DNA sequence of the lymphotropic variant of minute virus of mice, MVM(i), and comparison with the DNA sequence of the fibrotropic prototype strain. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):656–669. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.656-669.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astell C. R., Mol C. D., Anderson W. F. Structural and functional homology of parvovirus and papovavirus polypeptides. J Gen Virol. 1987 Mar;68(Pt 3):885–893. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-3-885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astell C. R., Thomson M., Chow M. B., Ward D. C. Structure and replication of minute virus of mice DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):751–762. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns K. I., Bohenzky R. A. Adeno-associated viruses: an update. Adv Virus Res. 1987;32:243–306. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60479-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom M. E., Alexandersen S., Garon C. F., Mori S., Wei W., Perryman S., Wolfinbarger J. B. Nucleotide sequence of the 5'-terminal palindrome of Aleutian mink disease parvovirus and construction of an infectious molecular clone. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3551–3556. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3551-3556.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohenzky R. A., LeFebvre R. B., Berns K. I. Sequence and symmetry requirements within the internal palindromic sequences of the adeno-associated virus terminal repeat. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):316–327. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90502-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boissy R., Astell C. R. An Escherichia coli recBCsbcBrecF host permits the deletion-resistant propagation of plasmid clones containing the 5'-terminal palindrome of minute virus of mice. Gene. 1985;35(1-2):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90170-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broach J. R., Li Y. Y., Feldman J., Jayaram M., Abraham J., Nasmyth K. A., Hicks J. B. Localization and sequence analysis of yeast origins of DNA replication. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 2):1165–1173. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
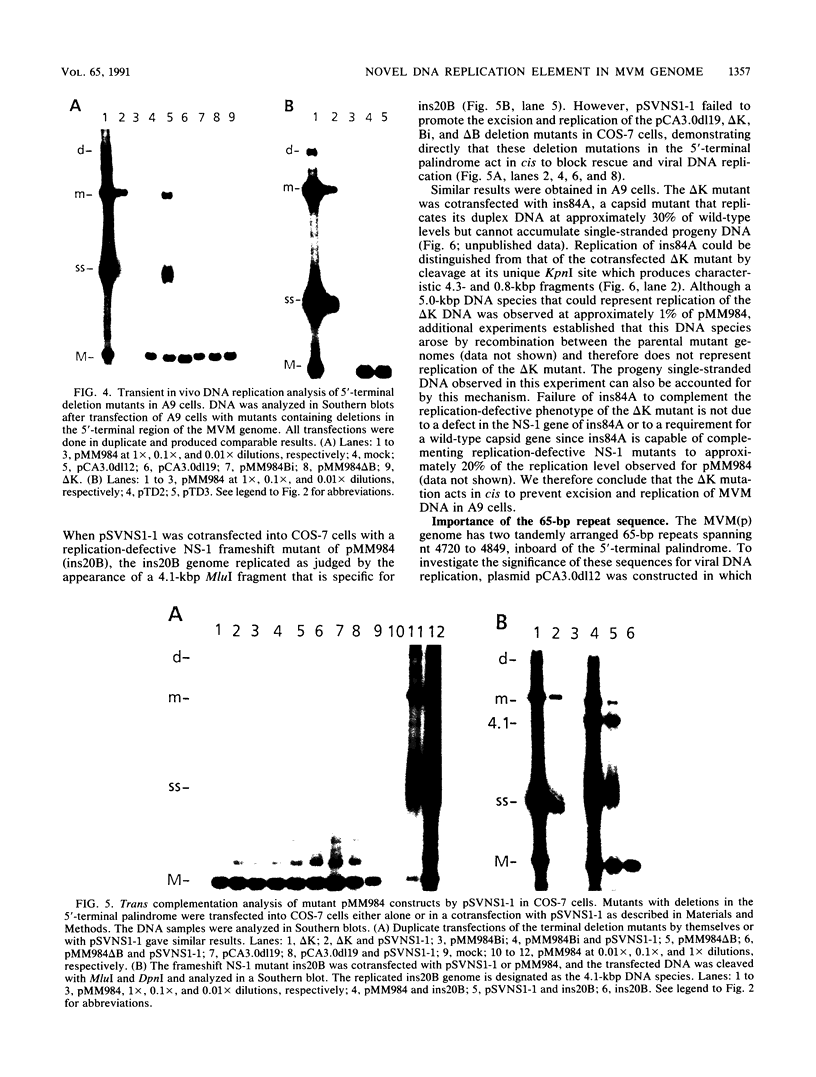
- Chejanovsky N., Carter B. J. Mutation of a consensus purine nucleotide binding site in the adeno-associated virus rep gene generates a dominant negative phenotype for DNA replication. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1764–1770. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1764-1770.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen K. C., Tyson J. J., Lederman M., Stout E. R., Bates R. C. A kinetic hairpin transfer model for parvoviral DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1989 Jul 20;208(2):283–296. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90389-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow M., Bodnar J. W., Polvino-Bodnar M., Ward D. C. Identification and characterization of a protein covalently bound to DNA of minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1094–1104. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1094-1104.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens K. E., Pintel D. Minute virus of mice (MVM) mRNAs predominantly polyadenylate at a single site. Virology. 1987 Oct;160(2):511–514. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Gunther M., Tattersall P. Evidence for a ligation step in the DNA replication of the autonomous parvovirus minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):1002–1006. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.1002-1006.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotmore S. F., Tattersall P. The NS-1 polypeptide of minute virus of mice is covalently attached to the 5' termini of duplex replicative-form DNA and progeny single strands. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):851–860. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.851-860.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey S. K., Faust E. A. Murine DNA polymerase.alpha-primase initiates RNA-primed DNA synthesis preferentially upstream of a 3'-CC(C/A)-5' motif. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3611–3614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLucia A. L., Deb S., Partin K., Tegtmeyer P. Functional interactions of the simian virus 40 core origin of replication with flanking regulatory sequences. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):138–144. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.138-144.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deb S., DeLucia A. L., Koff A., Tsui S., Tegtmeyer P. The adenine-thymine domain of the simian virus 40 core origin directs DNA bending and coordinately regulates DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4578–4584. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deiss V., Tratschin J. D., Weitz M., Siegl G. Cloning of the human parvovirus B19 genome and structural analysis of its palindromic termini. Virology. 1990 Mar;175(1):247–254. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90205-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust E. A., Gloor G. Characterization of a metastable, partially replicated dimeric intermediate of minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):621–625. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.621-625.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faust E. A., Nagy R., Davey S. K. Mouse DNA polymerase alpha-primase terminates and reinitiates DNA synthesis 2-14 nucleotides upstream of C2A1-2(C2-3/T2) sequences on a minute virus of mice DNA template. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4023–4027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner E. M., Tattersall P. Mapping of the fibrotropic and lymphotropic host range determinants of the parvovirus minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2605–2613. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2605-2613.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Abrahams P. J., Mulder C., Heijneker H. L., Warnaar S. O., De Vries F. A., Fiers W., Van Der Eb A. J. Studies on in vitro transformation by DNA and DNA fragments of human adenoviruses and simian virus 40. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):637–650. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermonat P. L., Labow M. A., Wright R., Berns K. I., Muzyczka N. Genetics of adeno-associated virus: isolation and preliminary characterization of adeno-associated virus type 2 mutants. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):329–339. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.329-339.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertz G. Z., Young M. R., Mertz J. E. The A+T-rich sequence of the simian virus 40 origin is essential for replication and is involved in bending of the viral DNA. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2322–2325. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2322-2325.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho T. F., Gupta J. S., Faust E. A. A novel primase-free form of murine DNA polymerase alpha induced by infection with minute virus of mice. Biochemistry. 1989 May 30;28(11):4622–4628. doi: 10.1021/bi00437a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Im D. S., Muzyczka N. Factors that bind to adeno-associated virus terminal repeats. J Virol. 1989 Jul;63(7):3095–3104. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.7.3095-3104.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Im D. S., Muzyczka N. The AAV origin binding protein Rep68 is an ATP-dependent site-specific endonuclease with DNA helicase activity. Cell. 1990 May 4;61(3):447–457. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90526-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly T. J., Jr, Nathans D. The genome of simian virus 40. Adv Virus Res. 1977;21:85–173. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60762-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. THREE DEGREES OF GUANYLIC ACID--INOSINIC ACID PYROPHOSPHORYLASE DEFICIENCY IN MOUSE FIBROBLASTS. Nature. 1964 Sep 12;203:1142–1144. doi: 10.1038/2031142a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefebvre R. B., Riva S., Berns K. I. Conformation takes precedence over sequence in adeno-associated virus DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1416–1419. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. J., Peden K. W., Dixon R. A., Kelly T. Functional organization of the simian virus 40 origin of DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;6(4):1117–1128. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.4.1117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund E., Griffin B. E., Fried M. Polyoma virus defective DNAs. II. Physical map of a molecule with rearranged and reiterated sequences (D74). J Mol Biol. 1977 Dec 5;117(2):497–513. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90139-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lusky M., Botchan M. Inhibition of SV40 replication in simian cells by specific pBR322 DNA sequences. Nature. 1981 Sep 3;293(5827):79–81. doi: 10.1038/293079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchlinsky M. J., Tattersall P. J., Leary J. J., Cotmore S. F., Gardiner E. M., Ward D. C. Construction of an infectious molecular clone of the autonomous parvovirus minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):227–232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.227-232.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. J., Dufort D., Hassell J. A. Multiple subelements within the polyomavirus enhancer function synergistically to activate DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):5000–5015. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.5000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller W. J., Mueller C. R., Mes A. M., Hassell J. A. Polyomavirus origin for DNA replication comprises multiple genetic elements. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):586–599. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.586-599.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W., Pipas J. M., Pearson-White S., Nathans D. Isolation of mutants of an animal virus in bacteria. Science. 1980 Sep 19;209(4463):1392–1396. doi: 10.1126/science.6251547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ranz A. I., Manclús J. J., Díaz-Aroca E., Casal J. I. Porcine parvovirus: DNA sequence and genome organization. J Gen Virol. 1989 Oct;70(Pt 10):2541–2553. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-10-2541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed A. P., Jones E. V., Miller T. J. Nucleotide sequence and genome organization of canine parvovirus. J Virol. 1988 Jan;62(1):266–276. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.1.266-276.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd Both excision and replication of cloned autonomous parvovirus DNA require the NS1 (rep) protein. J Virol. 1989 Oct;63(10):4249–4256. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.10.4249-4256.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd, Klaassen B. DNA sequence of the 5' terminus containing the replication origin of parvovirus replicative form DNA. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):990–999. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.990-999.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode S. L., 3rd trans-Activation of parvovirus P38 promoter by the 76K noncapsid protein. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):886–889. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.886-889.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahli R., McMaster G. K., Hirt B. DNA sequence comparison between two tissue-specific variants of the autonomous parvovirus, minute virus of mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 May 24;13(10):3617–3633. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.10.3617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samulski R. J., Srivastava A., Berns K. I., Muzyczka N. Rescue of adeno-associated virus from recombinant plasmids: gene correction within the terminal repeats of AAV. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90342-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarver N., Byrne J. C., Howley P. M. Transformation and replication in mouse cells of a bovine papillomavirus--pML2 plasmid vector that can be rescued in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7147–7151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Senapathy P., Tratschin J. D., Carter B. J. Replication of adeno-associated virus DNA. Complementation of naturally occurring rep- mutants by a wild-type genome or an ori- mutant and correction of terminal palindrome deletions. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 15;179(1):1–20. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90303-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull B. C., Chen K. C., Lederman M., Stout E. R., Bates R. C. Genomic clones of bovine parvovirus: construction and effect of deletions and terminal sequence inversions on infectivity. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):417–426. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.417-426.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder R. O., Samulski R. J., Muzyczka N. In vitro resolution of covalently joined AAV chromosome ends. Cell. 1990 Jan 12;60(1):105–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90720-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P., Bratton J. Reciprocal productive and restrictive virus-cell interactions of immunosuppressive and prototype strains of minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):944–955. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.944-955.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tratschin J. D., Miller I. L., Carter B. J. Genetic analysis of adeno-associated virus: properties of deletion mutants constructed in vitro and evidence for an adeno-associated virus replication function. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):611–619. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.611-619.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullis G. E., Labieniec-Pintel L., Clemens K. E., Pintel D. Generation and characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutation in the NS-1 gene of the autonomous parvovirus minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1988 Aug;62(8):2736–2744. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.8.2736-2744.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twigg A. J., Sherratt D. Trans-complementable copy-number mutants of plasmid ColE1. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):216–218. doi: 10.1038/283216a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Houten J. V., Newlon C. S. Mutational analysis of the consensus sequence of a replication origin from yeast chromosome III. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):3917–3925. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.3917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasudevacharya J., Basak S., Srinivas R. V., Compans R. W. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the capsid genes and the right-hand terminal palindrome of porcine parvovirus, strain NADL-2. Virology. 1989 Dec;173(2):368–377. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90549-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]