Abstract
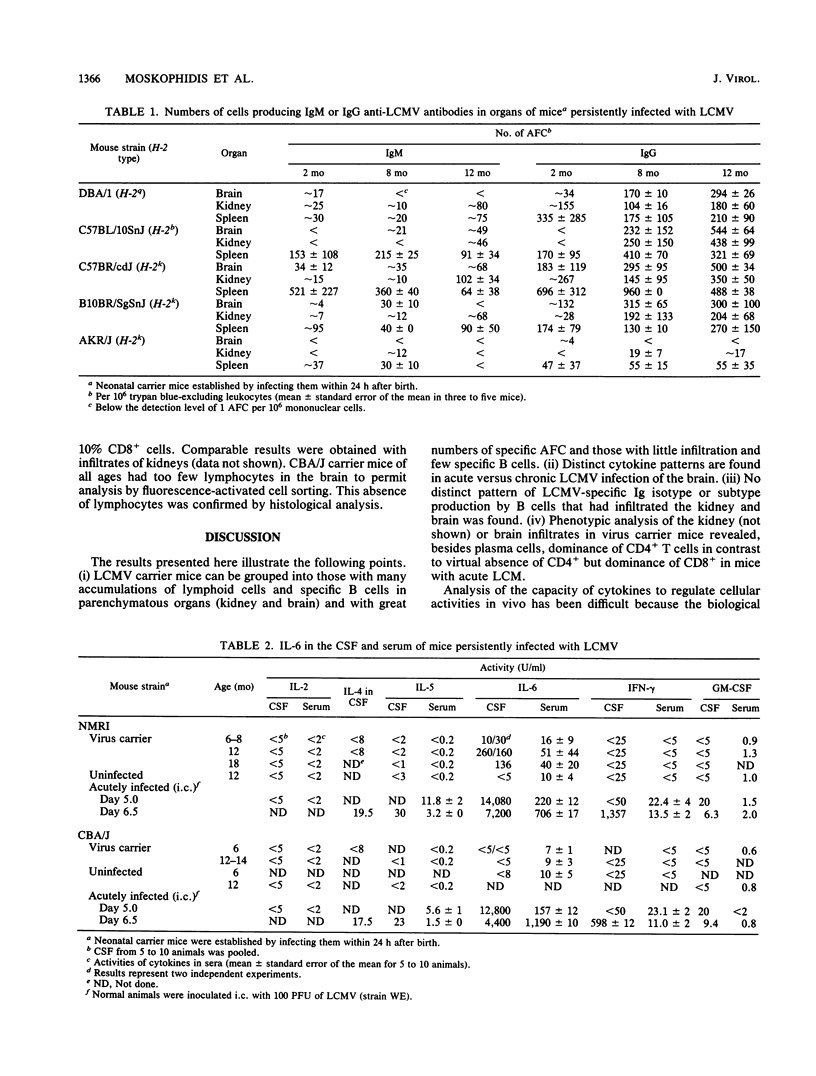
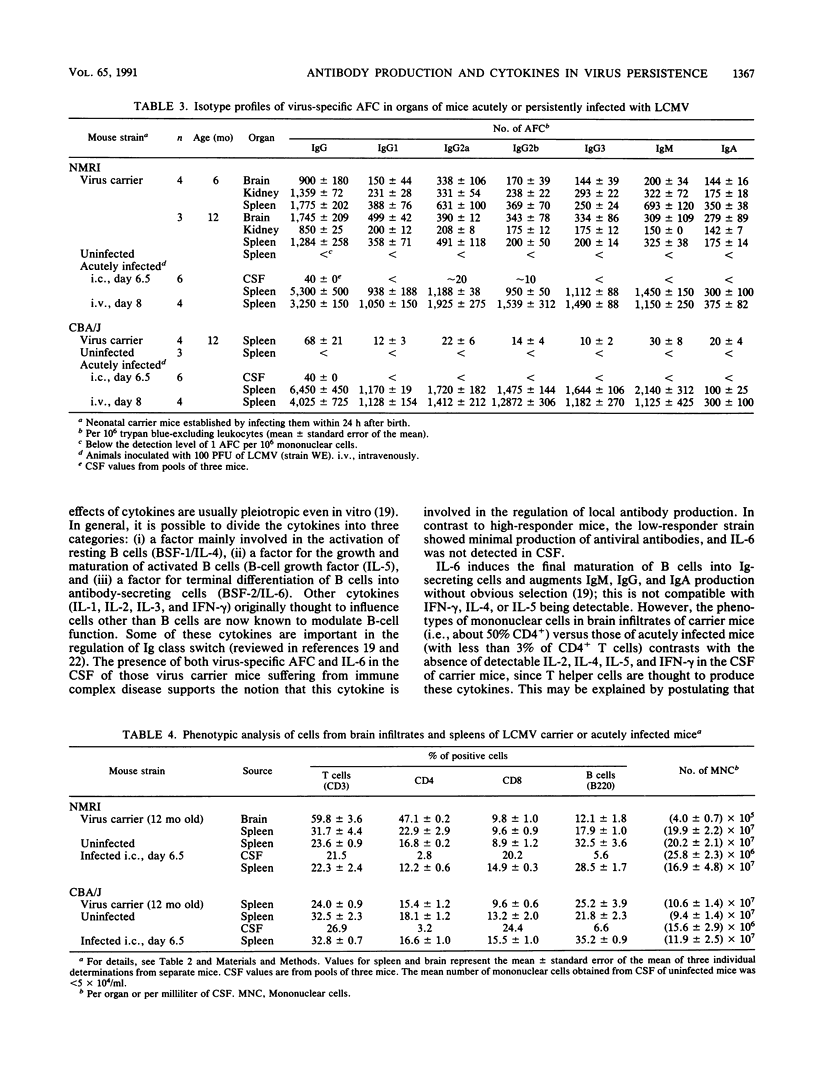
The activities of cytokines were determined in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and serum of mice persistently or intracerebrally acutely infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis (LCM) virus (LCMV). In contrast to CBA/J (LCMV carrier) mice that responded with low levels of LCMV-specific antibody, high-responder NMRI (carrier) mice showed antibody production by B cells outside of lymphoid organs. The B cells that had infiltrated the brains of LCMV carrier mice exhibited no preferential immunoglobulin isotype or subtype virus-specific antibody production. Phenotypic analysis of the brain infiltrates in virus carrier mice revealed dominance of CD4+ T cells in contrast to virtual absence of CD4+ and dominance of CD8+ in mice with acute LCM. In NMRI but not in CBA/J carrier mice, significant concentrations of interleukin-6 (IL-6) were detected in CSF and serum; IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, granulocyte-macrophage CSF (GM-CSF), and gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) were not elevated. In contrast, during acute, lethal LCM, IL-6 and IFN-gamma were found at high concentrations, and IL-4, IL-5, and GM-CSF were detectable in CSF and serum, but virus-specific antibody-producing cells were not (yet) detectable in the brain. Thus, distinct cytokine patterns are found in acute versus chronic LCMV infection of the brain: in LCM carrier mice, local random-class immunoglobulin production correlated with the absence of IL-2, IL-4, IL-5, and IFN-gamma but active secretion of IL-6.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. R. Viral encephalitis and its pathology. Curr Top Pathol. 1988;76:23–60. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71353-8_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmeier M. J., Welsh R. M., Dutko F. J., Oldstone M. B. The virology and immunobiology of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection. Adv Immunol. 1980;30:275–331. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60197-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceredig R., Allan J. E., Tabi Z., Lynch F., Doherty P. C. Phenotypic analysis of the inflammatory exudate in murine lymphocytic choriomeningitis. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1539–1551. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Weissman I. L. A monoclonal antibody that recognizes B cells and B cell precursors in mice. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):269–279. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coutelier J. P., van der Logt J. T., Heessen F. W., Warnier G., Van Snick J. IgG2a restriction of murine antibodies elicited by viral infections. J Exp Med. 1987 Jan 1;165(1):64–69. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.1.64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter T. M., Garland J., Scott D., Scolnick E., Metcalf D. Growth of factor-dependent hemopoietic precursor cell lines. J Exp Med. 1980 Oct 1;152(4):1036–1047. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.4.1036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dialynas D. P., Wilde D. B., Marrack P., Pierres A., Wall K. A., Havran W., Otten G., Loken M. R., Pierres M., Kappler J. Characterization of the murine antigenic determinant, designated L3T4a, recognized by monoclonal antibody GK1.5: expression of L3T4a by functional T cell clones appears to correlate primarily with class II MHC antigen-reactivity. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:29–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Allan J. E., Lynch F., Ceredig R. Dissection of an inflammatory process induced by CD8+ T cells. Immunol Today. 1990 Feb;11(2):55–59. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(90)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frei K., Leist T. P., Meager A., Gallo P., Leppert D., Zinkernagel R. M., Fontana A. Production of B cell stimulatory factor-2 and interferon gamma in the central nervous system during viral meningitis and encephalitis. Evaluation in a murine model infection and in patients. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):449–453. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frei K., Malipiero U. V., Leist T. P., Zinkernagel R. M., Schwab M. E., Fontana A. On the cellular source and function of interleukin 6 produced in the central nervous system in viral diseases. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Apr;19(4):689–694. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Smith K. A. Long term culture of tumour-specific cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):154–156. doi: 10.1038/268154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu-Li J., Ohara J., Watson C., Tsang W., Paul W. E. Derivation of a T cell line that is highly responsive to IL-4 and IL-2 (CT.4R) and of an IL-2 hyporesponsive mutant of that line (CT.4S). J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):800–807. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T. The biology of interleukin-6. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):1–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Herzenberg L. A. Xenogeneic monoclonal antibodies to mouse lymphoid differentiation antigens. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:63–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann-Grube F., Ambrassat J. A new method to detect lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus-specific antibody in human sera. J Gen Virol. 1977 Oct;37(1):85–92. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-37-1-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leist T. P., Frei K., Kam-Hansen S., Zinkernagel R. M., Fontana A. Tumor necrosis factor alpha in cerebrospinal fluid during bacterial, but not viral, meningitis. Evaluation in murine model infections and in patients. J Exp Med. 1988 May 1;167(5):1743–1748. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.5.1743. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskophidis D., Löhler J., Lehmann-Grube F. Antiviral antibody-producing cells in parenchymatous organs during persistent virus infection. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):705–719. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Garra A., Umland S., De France T., Christiansen J. 'B-cell factors' are pleiotropic. Immunol Today. 1988 Feb;9(2):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91259-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B., Dixon F. J. Lymphocytic choriomeningitis: production of antibody by "tolerant" infected mice. Science. 1967 Dec 1;158(3805):1193–1195. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3805.1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oldstone M. B. Viral persistence. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):517–520. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90573-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul W. E. Pleiotropy and redundancy: T cell-derived lymphokines in the immune response. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):521–524. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90121-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivers T. M., Scott T. F. MENINGITIS IN MAN CAUSED BY A FILTERABLE VIRUS : II. IDENTIFICATION OF THE ETIOLOGICAL AGENT. J Exp Med. 1936 Feb 29;63(3):415–432. doi: 10.1084/jem.63.3.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rolink A. G., Melchers F., Palacios R. Monoclonal antibodies reactive with the mouse interleukin 5 receptor. J Exp Med. 1989 May 1;169(5):1693–1701. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.5.1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroop W. G., Baringer J. R. Persistent, slow and latent viral infections. Prog Med Virol. 1982;28:1–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomsen A. R., Volkert M., Marker O. Different isotype profiles of virus-specific antibodies in acute and persistent lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus infection in mice. Immunology. 1985 Jun;55(2):213–223. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomonari K. A rat antibody against a structure functionally related to the mouse T-cell receptor/T3 complex. Immunogenetics. 1988;28(6):455–458. doi: 10.1007/BF00355379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


